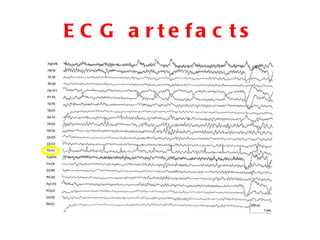
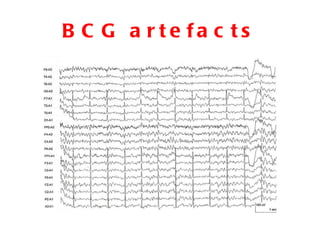
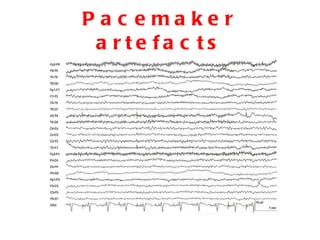
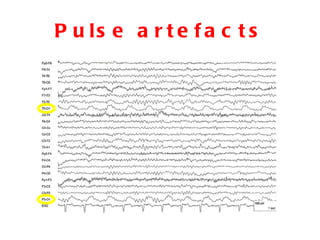
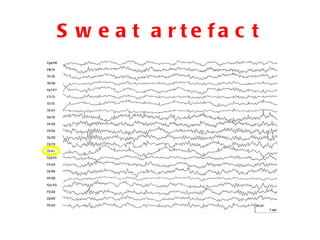
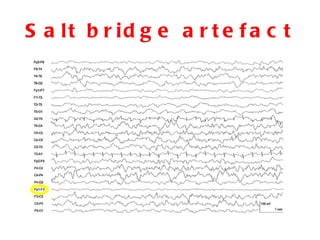
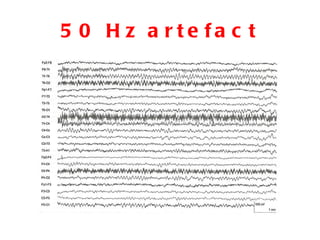
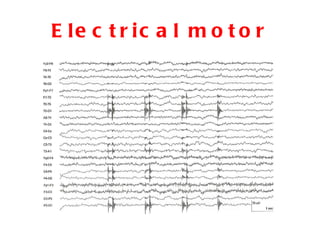
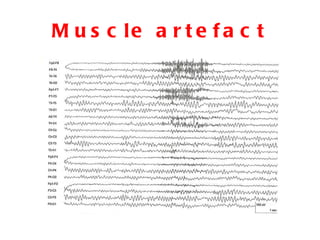
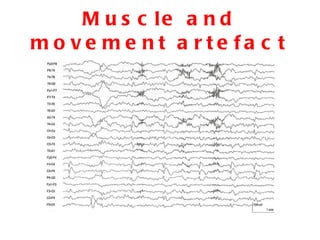
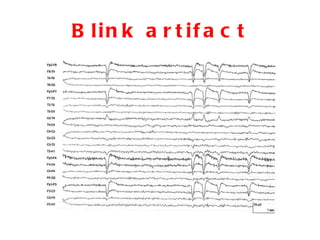
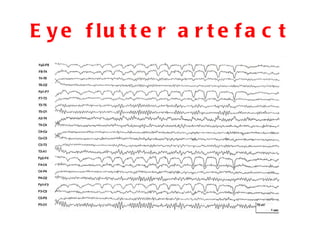
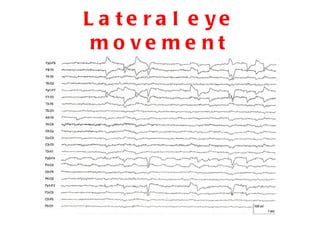
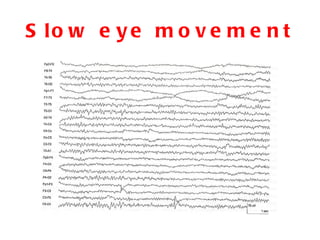
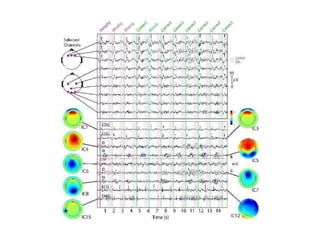
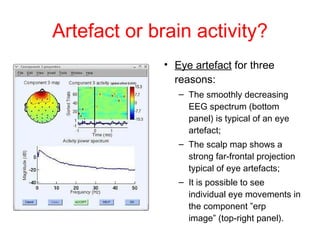
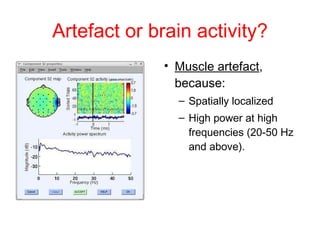
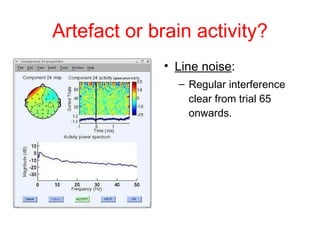
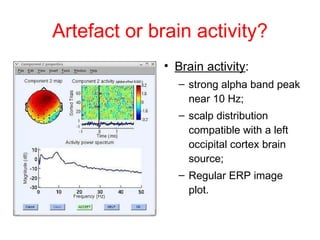
EEG artefacts arise from unwanted electrical activity from sources other than the brain, such as eye movements, muscle activity, and environmental noise. Identifying artefacts can be challenging as some resemble brain activity. Methods for removing artefacts include filtering, regression-based approaches, and independent component analysis, which transforms scalp channel data into spatially independent sources that may represent brain or non-brain activity. Careful inspection of component properties like scalp maps, time courses, and spectra is needed to classify them as representing brain activity or artefacts.