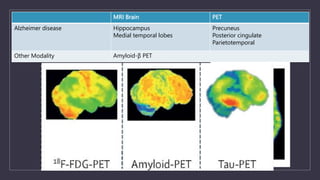
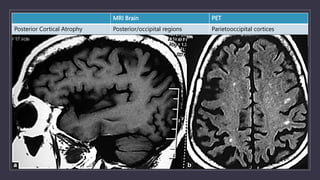
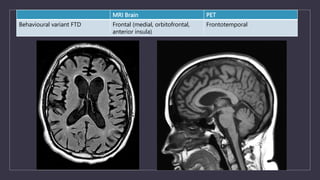
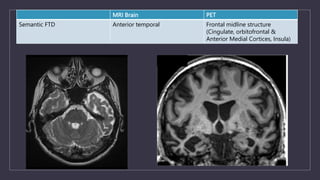
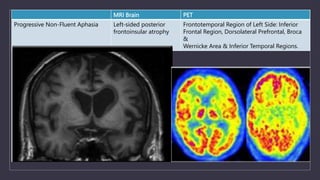
Young onset dementia (YOD) refers to dementia with an onset before age 65. About 5% of all dementias are YOD. Common causes include Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, frontotemporal lobar degeneration, and dementia with Lewy bodies. A thorough evaluation includes medical history, physical and neurological exams, imaging like MRI and PET, and may involve genetic testing. Management focuses on treating underlying causes if possible, addressing behavioral and psychiatric symptoms, and providing social support. Prognosis varies by the specific cause but on average YOD results in 10-15 years shorter life expectancy than later onset dementia.









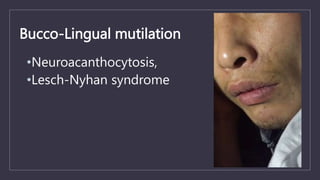

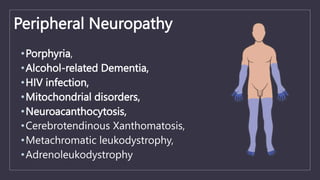

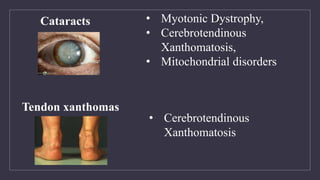

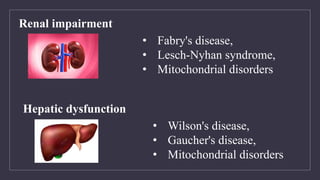











![Tissue Biopsy
•Skin biopsy- CADASIL, NPC.
•Muscle biopsy - Mitochondrial d/o
•Tonsillar biopsy – suspected vCJD
•Brain biopsy - [Exceptional cases]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yod-230320060001-bb00345d/85/Young-Onset-Dementia-pptx-35-320.jpg)