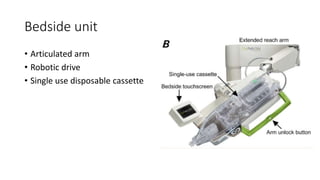
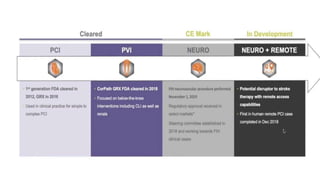
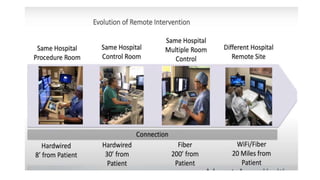
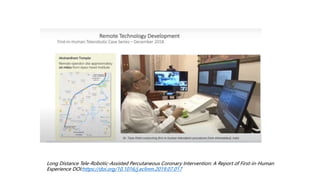
Remote robotic thrombectomy is a promising technique to expand access to endovascular thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke. The Corindus robotic system allows neurointerventionists to perform thrombectomy procedures remotely using robotic arms. This could allow thrombectomy-capable centers to treat patients from further distances. Early studies show robotic thrombectomy is technically feasible and reduces radiation exposure compared to manual procedures. However, further research is still needed as robotic systems require additional training and have limitations such as lack of haptic feedback. Overall, remote robotic thrombectomy may help more patients receive timely endovascular treatment for stroke.