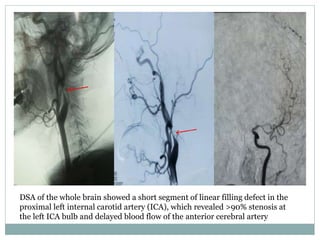
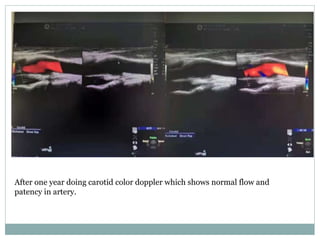
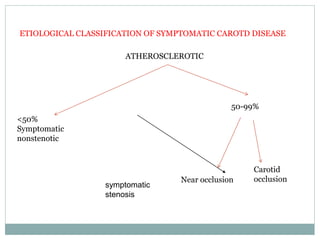
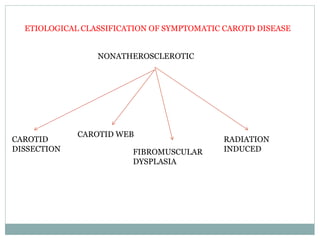
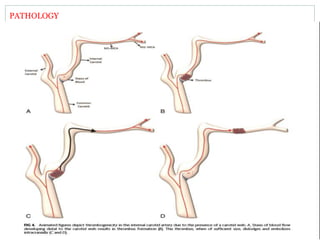
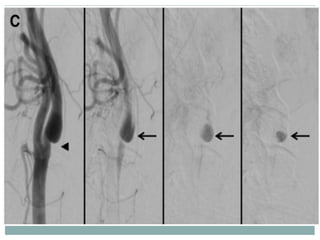
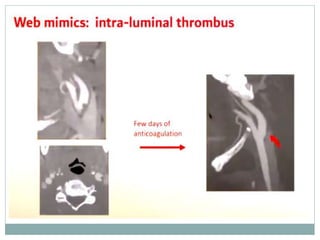
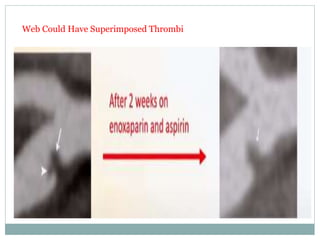
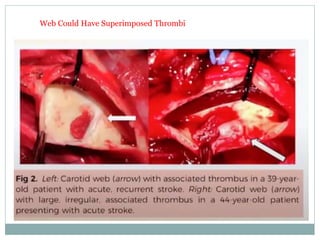
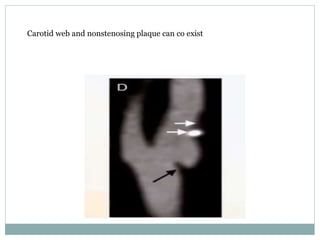
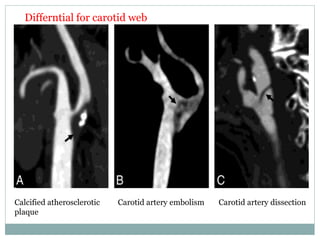
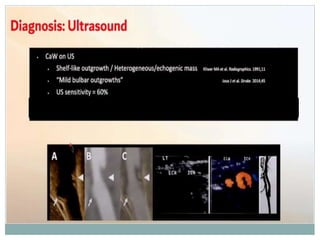
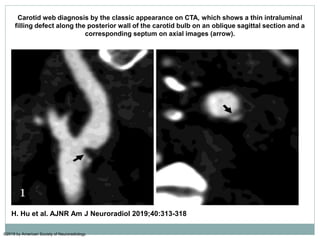
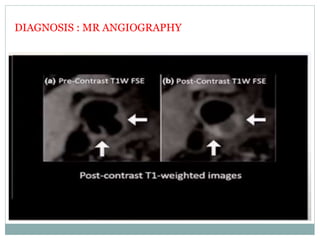
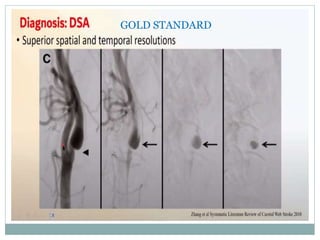
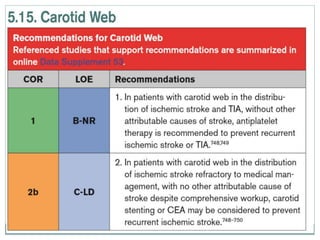
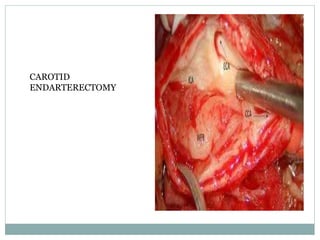
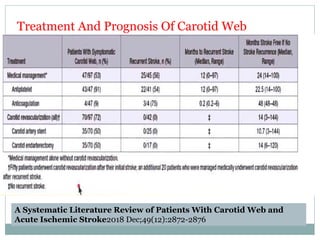
A 42-year-old male patient was admitted with repeated dizziness and right-sided weakness for over 3 months. Imaging showed a linear filling defect in the proximal left internal carotid artery, revealing over 90% stenosis and delayed blood flow. The patient underwent carotid endarterectomy and was discharged on medical therapy. Three months later, the patient experienced recurrent symptoms. Carotid web was considered a potential cause given the patient's age and lack of atherosclerosis history. Intervention may be a safe and effective option for symptomatic carotid web in addition to medical management, with recurrent risk up to 26.8% with medical management alone.