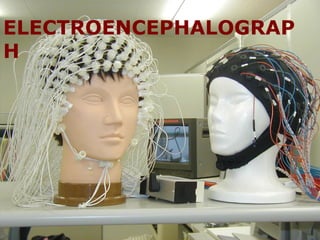
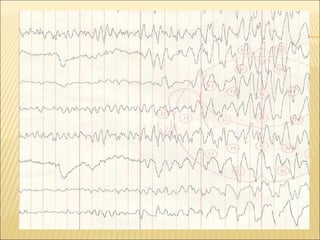
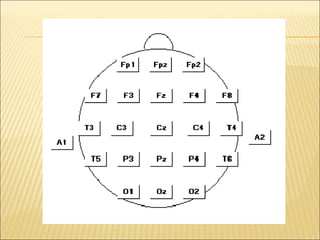
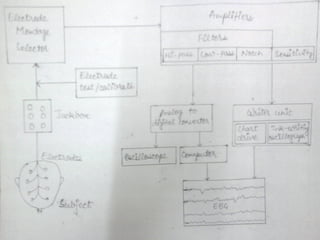
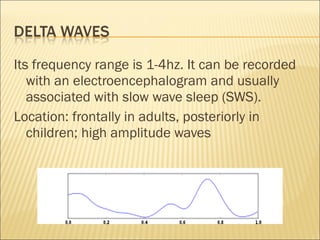
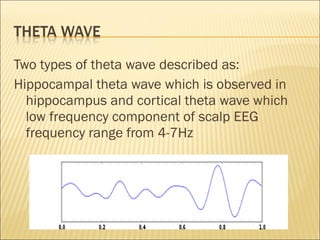
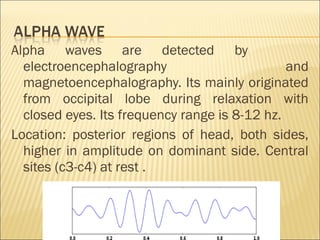
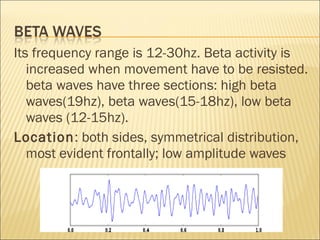
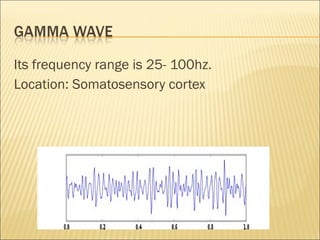
EEG is used to record the electrical activity of the brain. It uses electrodes placed on the scalp that are smaller than those used in ECGs. EEG can be used to diagnose neurological disorders like epilepsy. There are different types of brain waves like delta, theta, alpha, beta, and gamma waves that are defined by their frequency ranges and locations in the brain. Evoked potentials involve stimulating specific sensory pathways and measuring the electrical response in certain brain areas to help diagnose conditions.