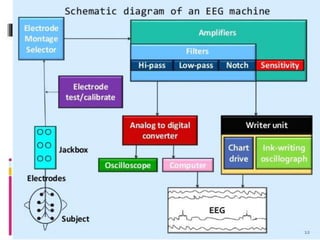
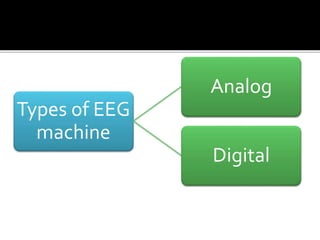
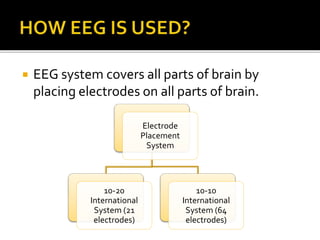
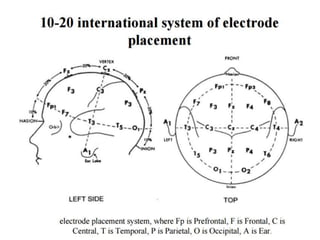
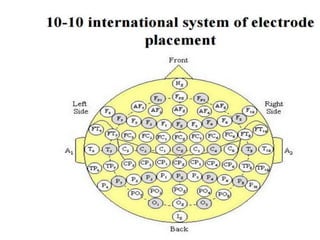
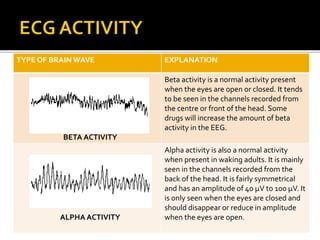
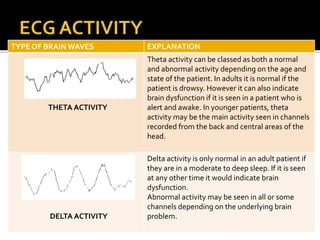
The document discusses electroencephalography (EEG), which is a medical imaging technique that reads electrical activity in the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp. An EEG machine consists of electrodes, amplifiers, filters, and a recording unit. EEGs are used to diagnose epilepsy, monitor brain activity during anesthesia, and investigate sleep disorders. The document describes the components of an EEG machine and preparation of patients for EEG recording. It also explains the different types of brain waves - beta, alpha, theta, and delta - that are analyzed during EEG interpretation.