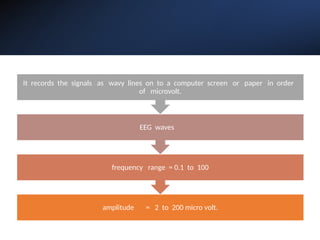
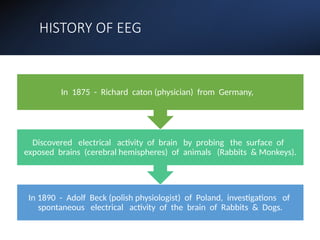
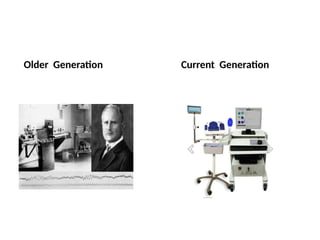
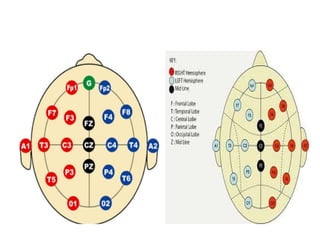
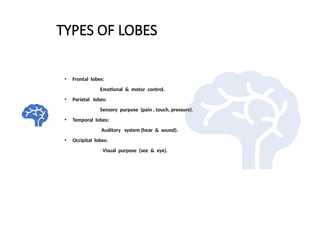
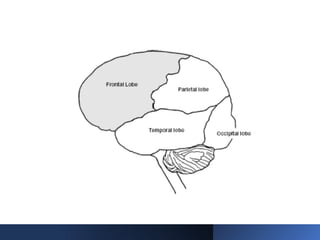
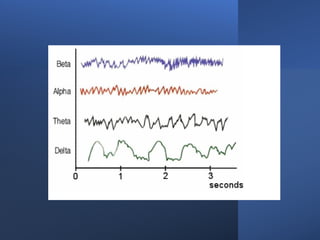
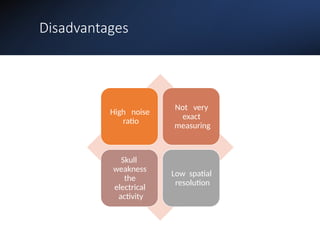
Electroencephalography (EEG) records the brain's electrical activity using electrodes placed on the scalp, with a history dating back to the 19th century. EEG is utilized to diagnose conditions such as epilepsy, brain tumors, and assess brain function in comatose patients, while types of brain waves (alpha, beta, theta, delta) are analyzed for different states of mind and conditions. Advantages include being non-invasive and lower costs; disadvantages are related to noise and resolution limitations.