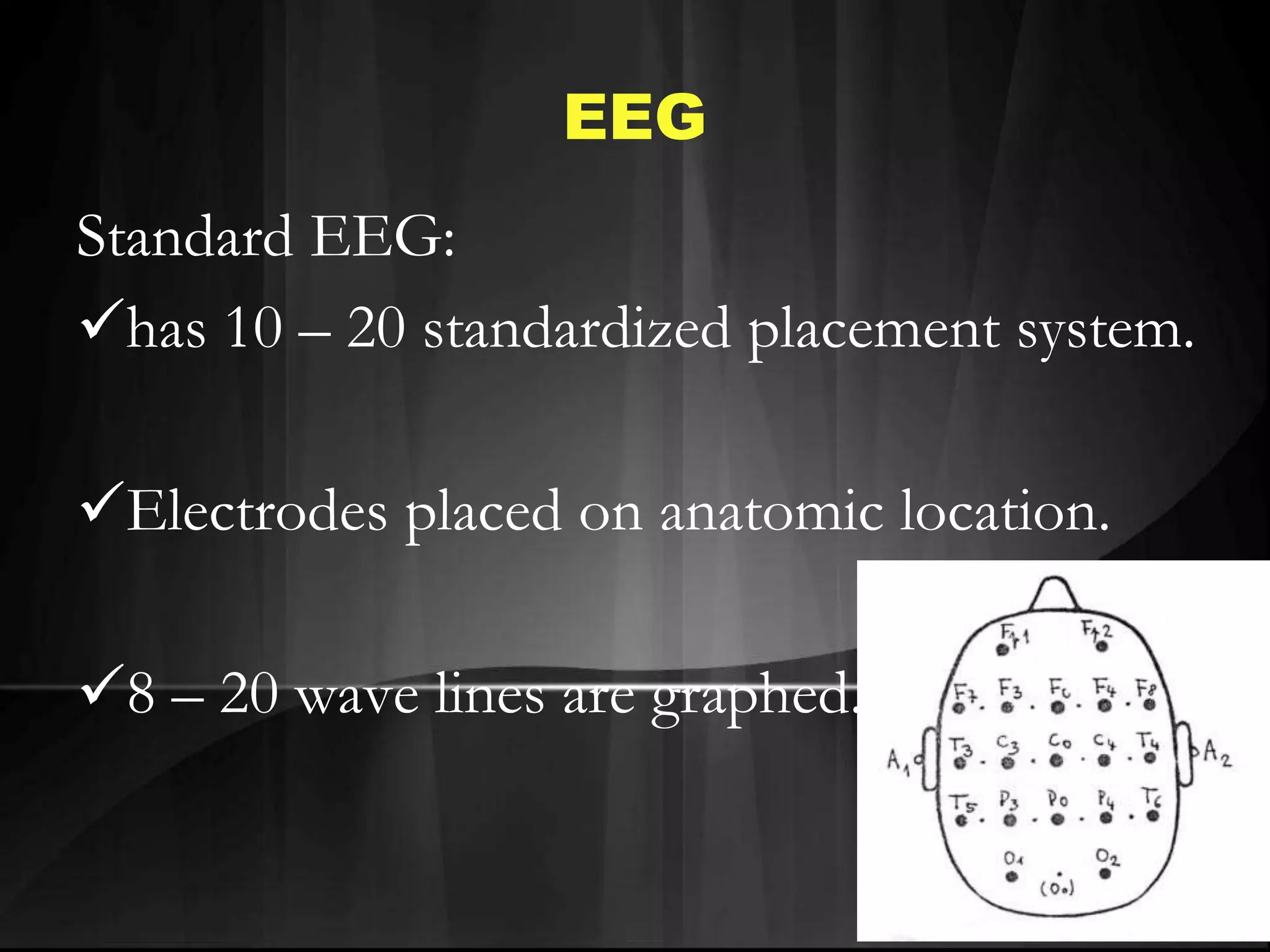
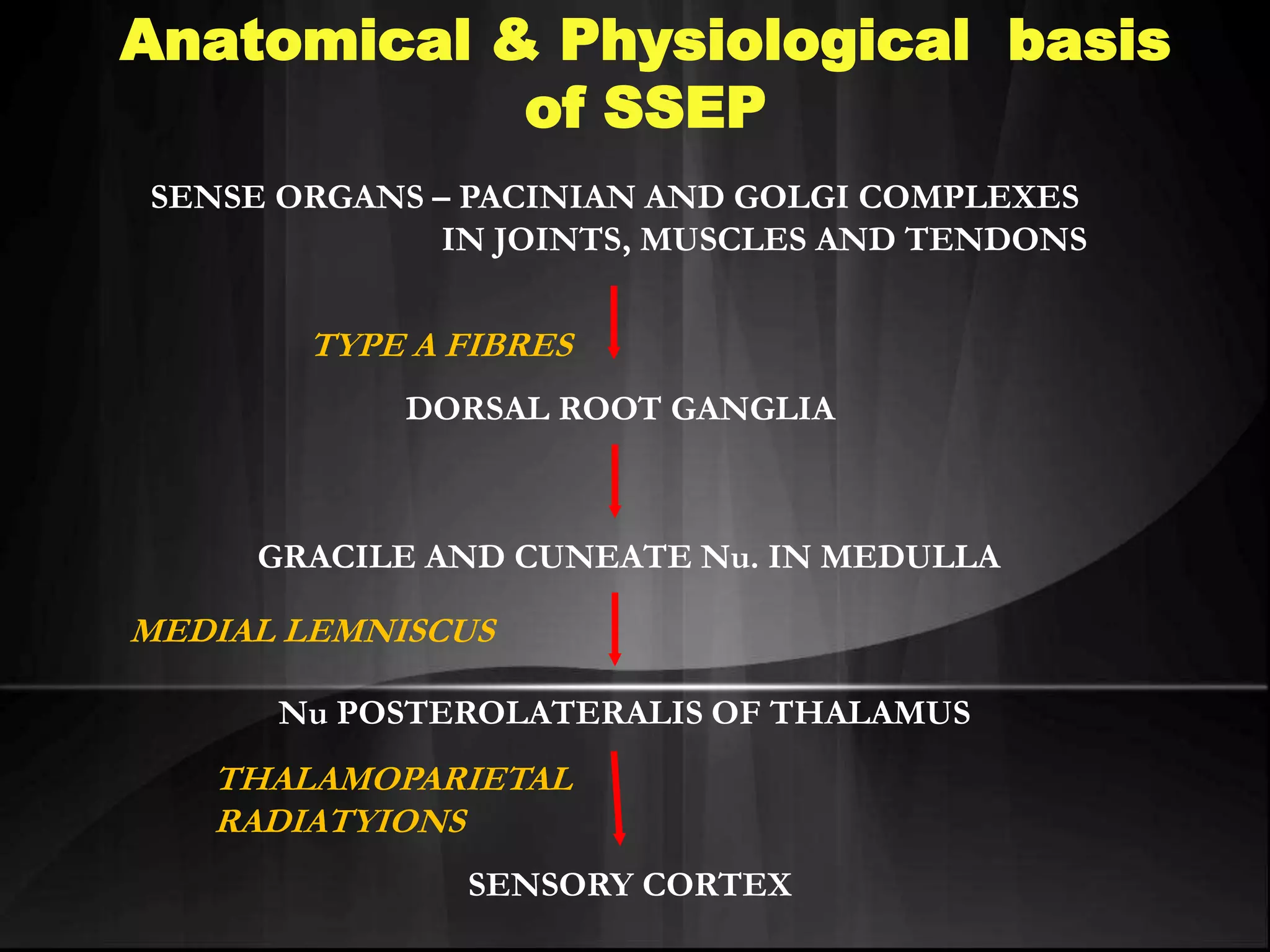
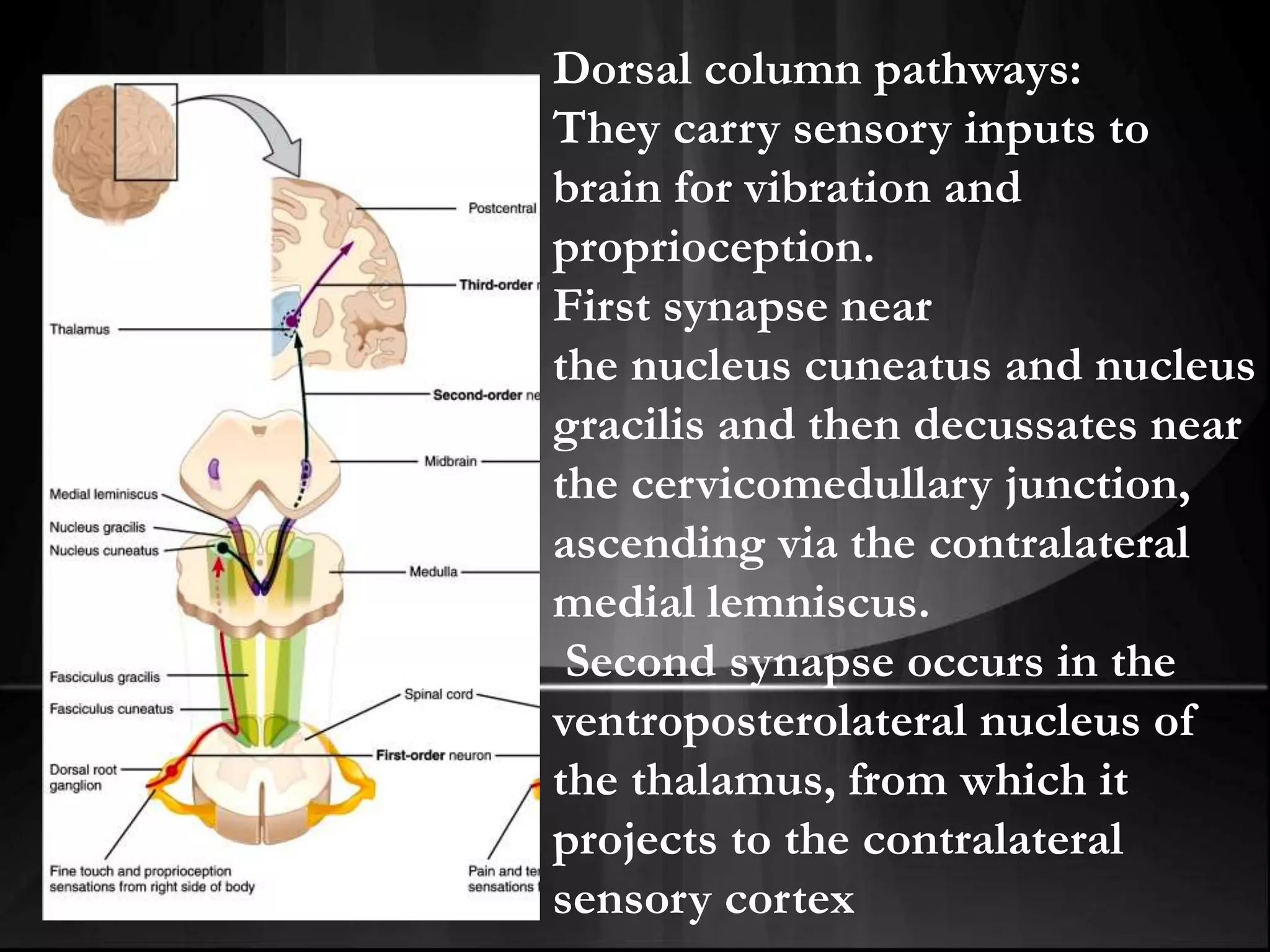
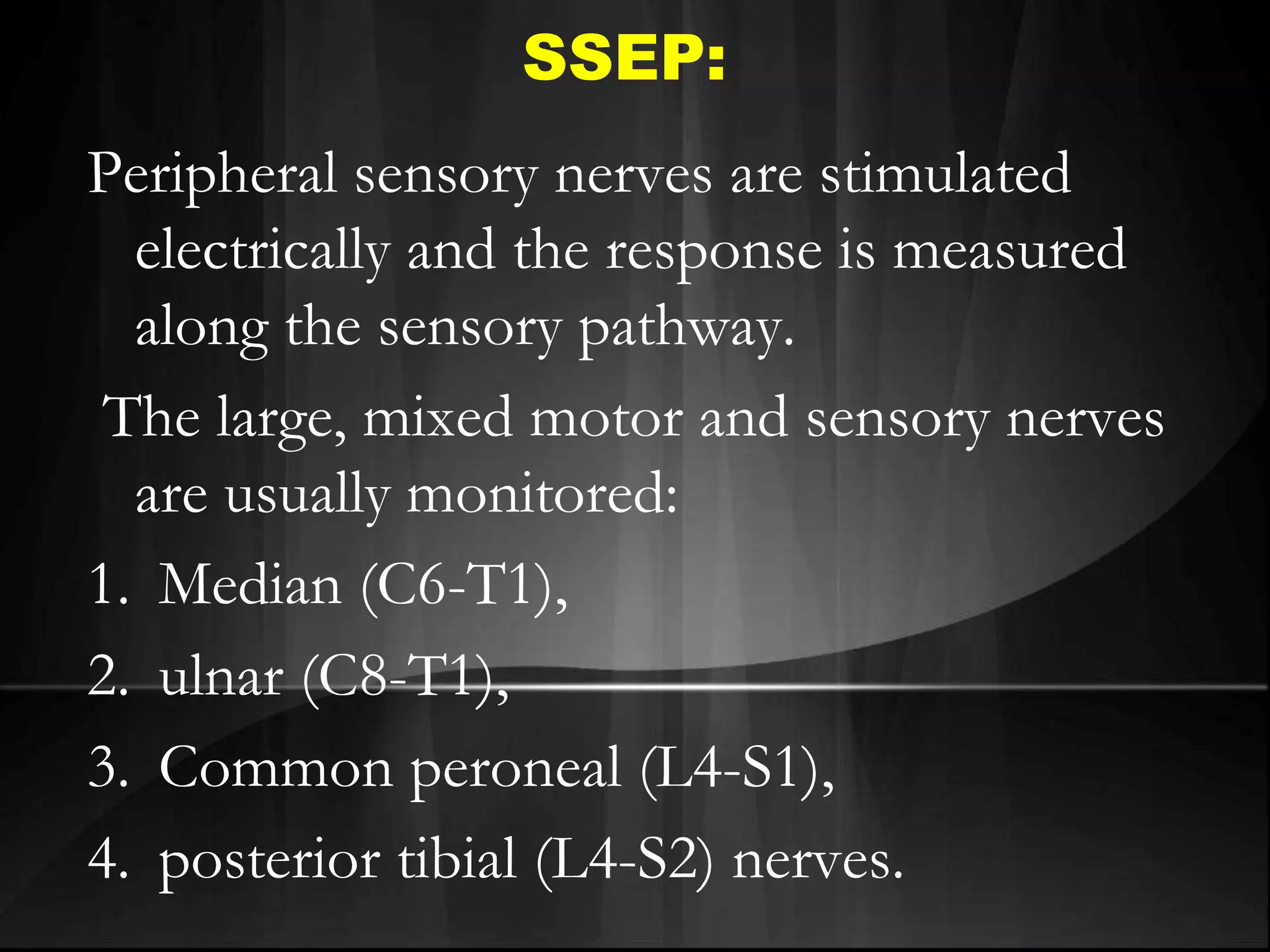
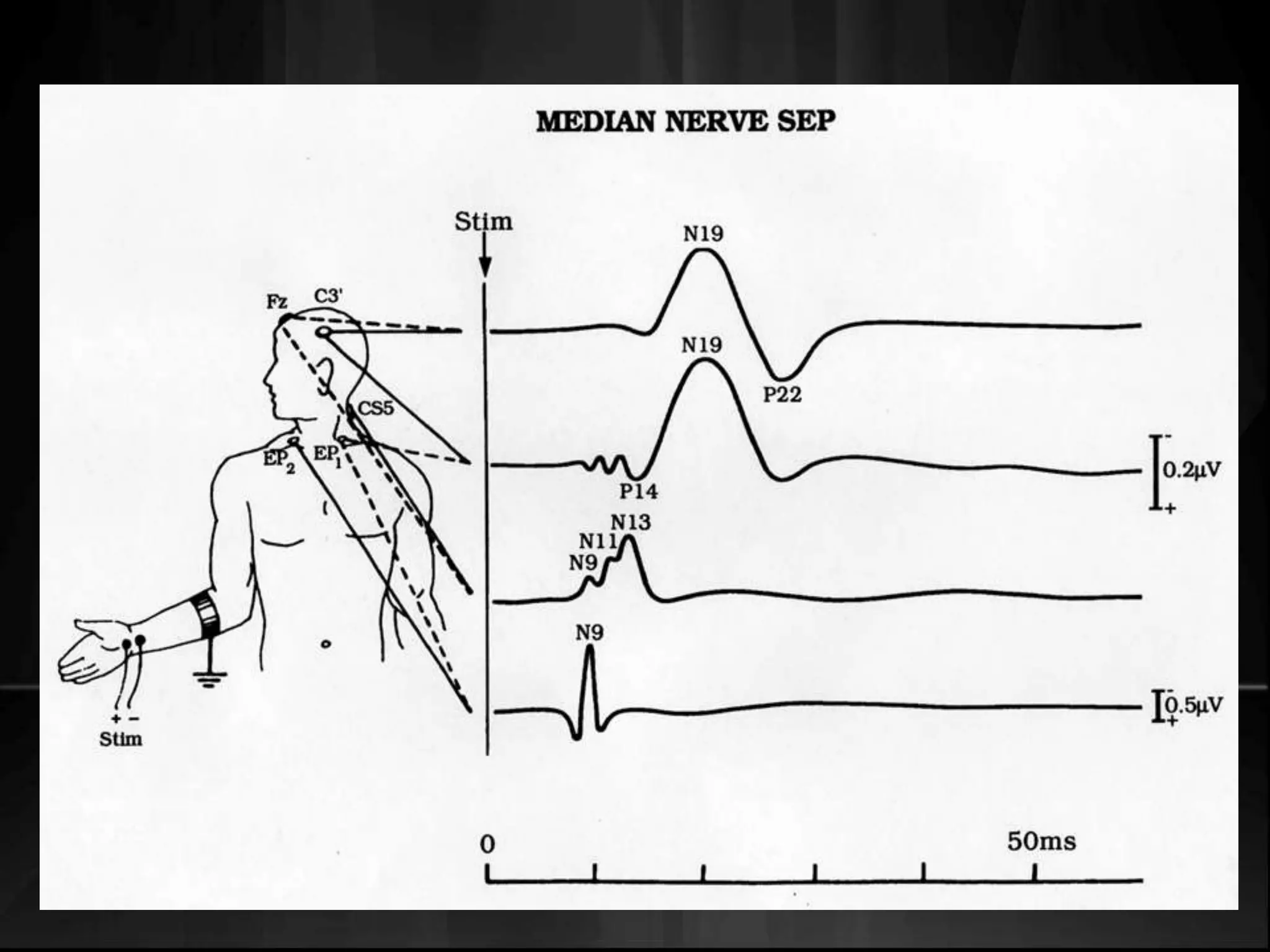
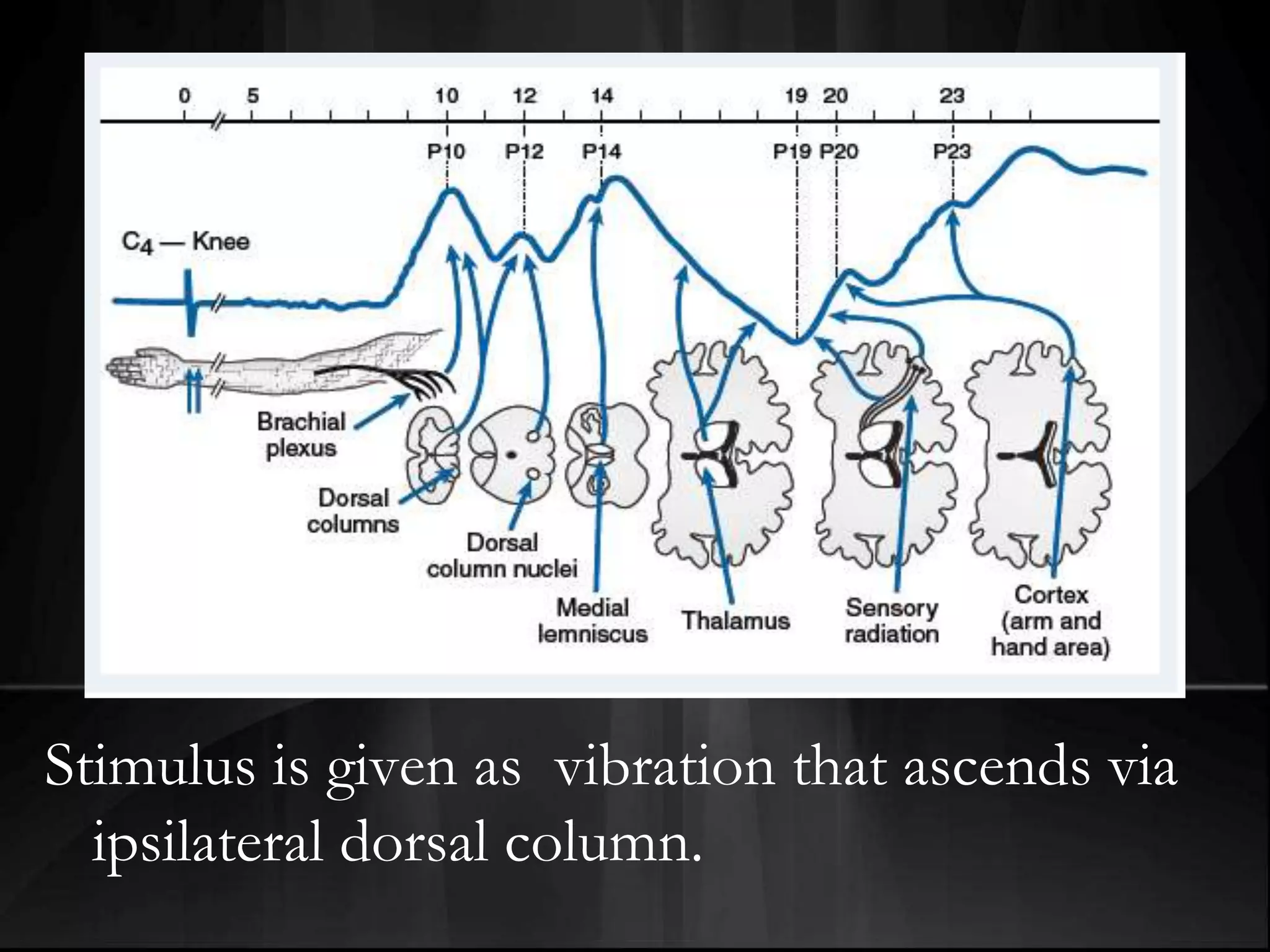
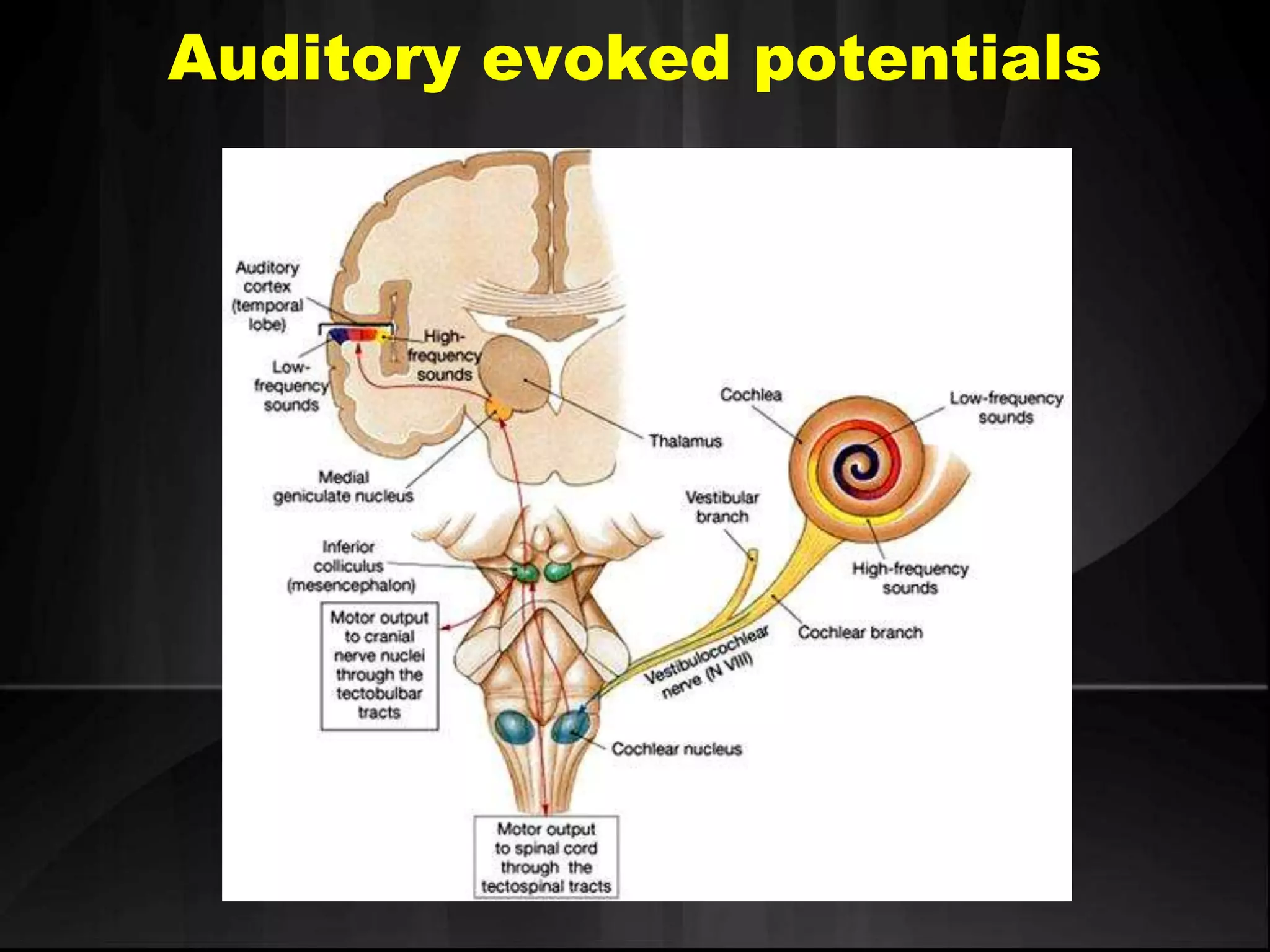
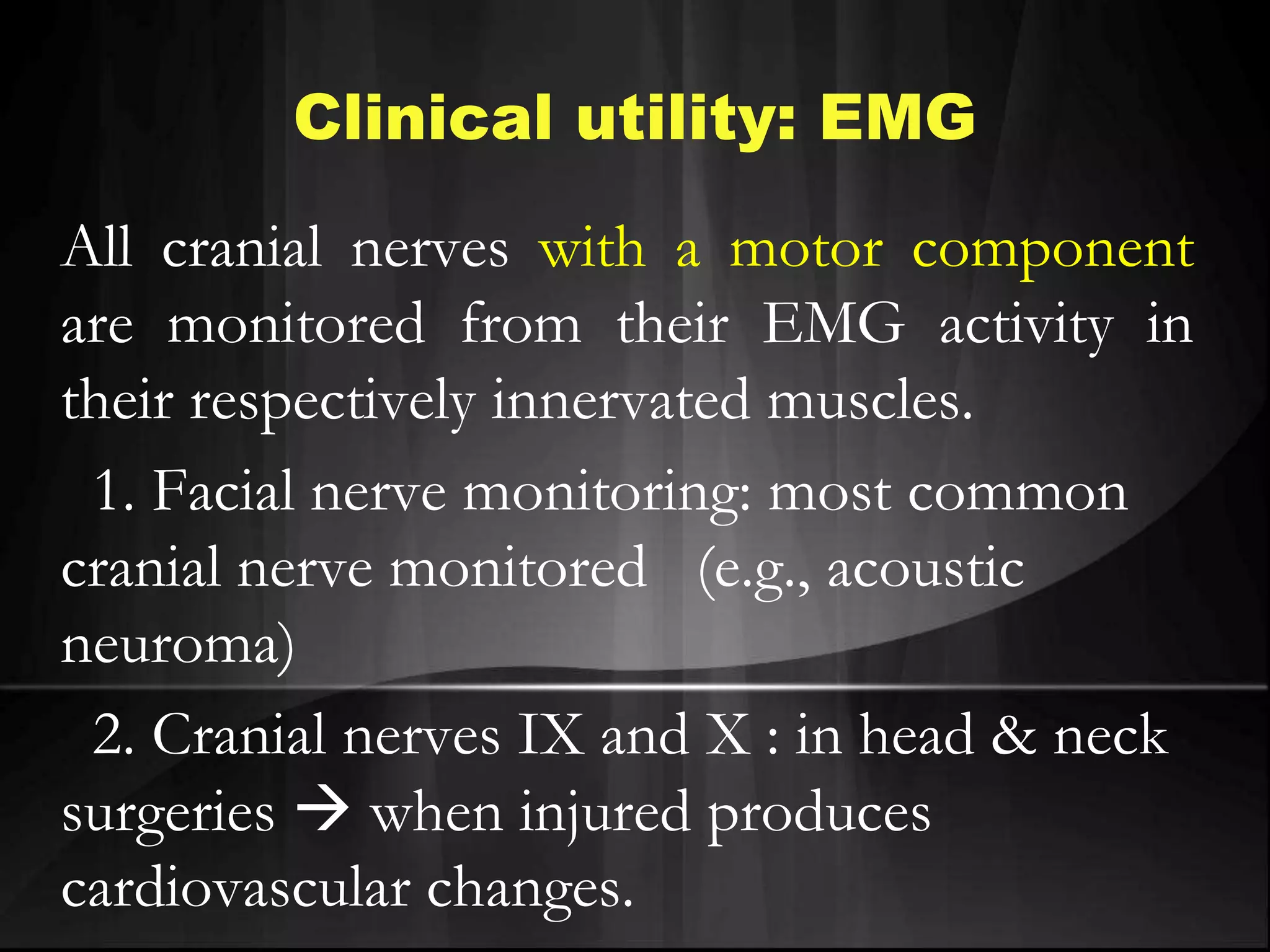
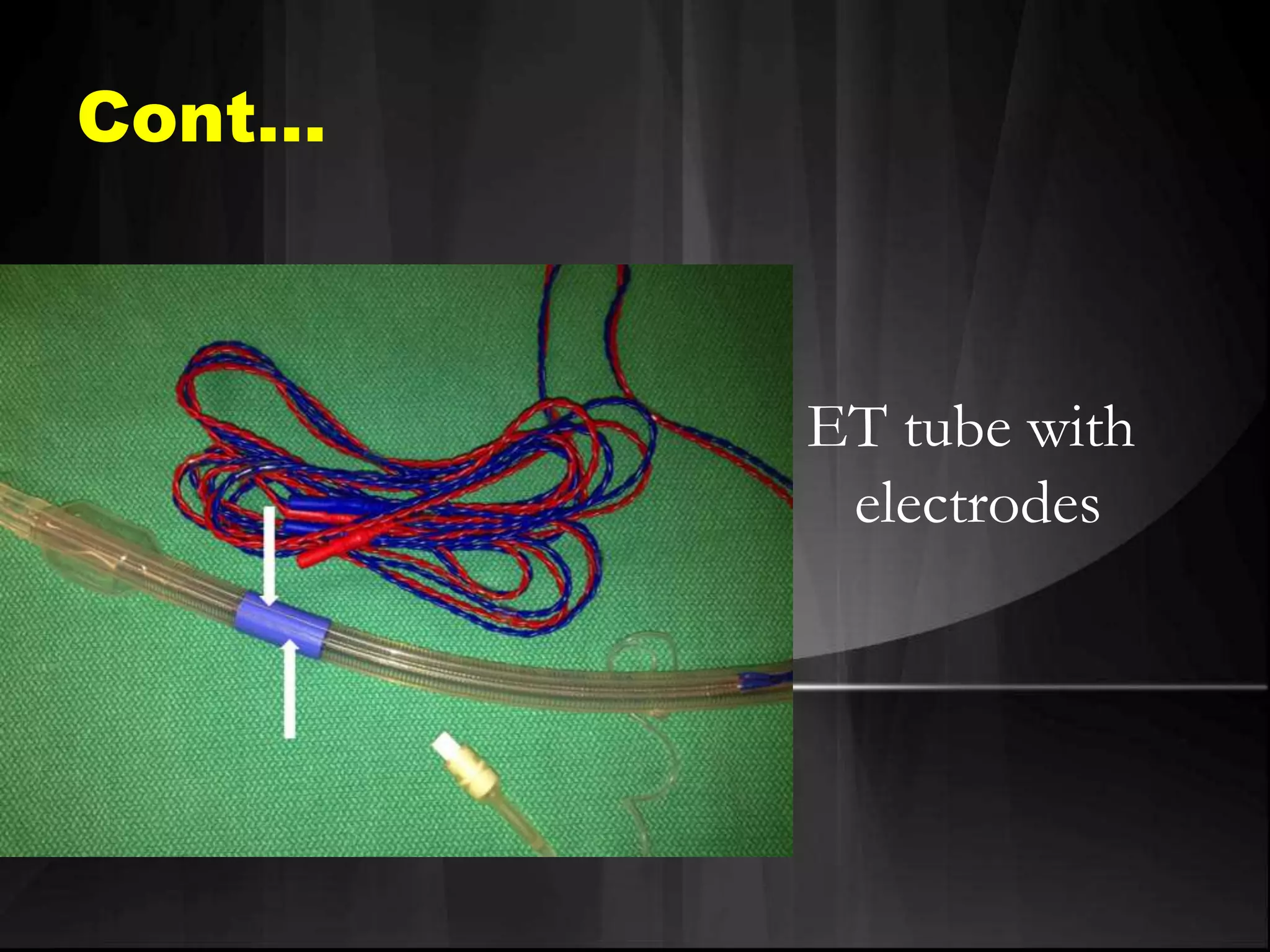
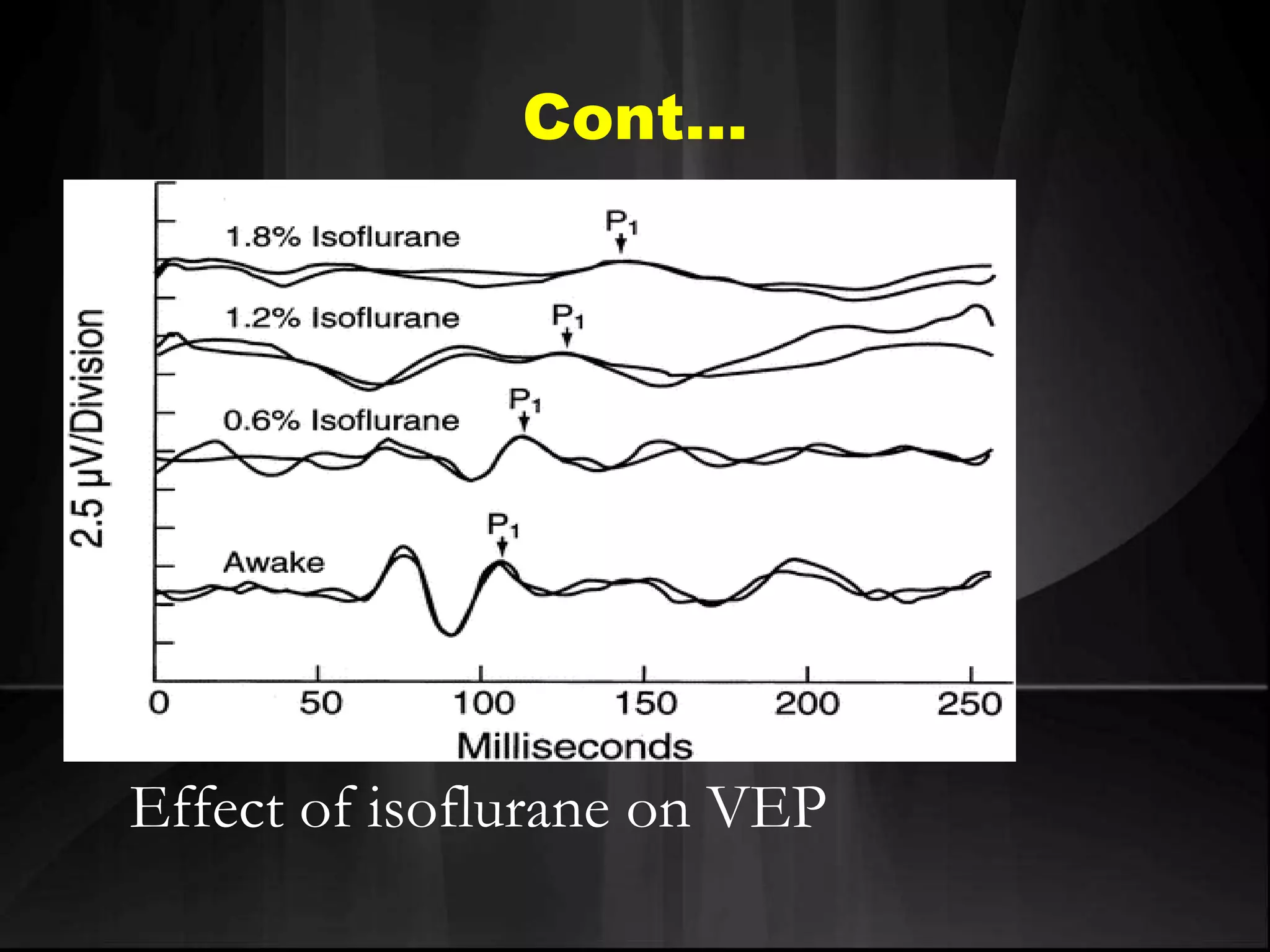
EEG measures the electrical activity of the brain through electrodes placed on the scalp. It can detect different wave patterns associated with different brain states. Evoked potentials involve stimulating a sensory pathway and measuring the electrical response along the pathway. This allows localization of lesions. Somatosensory evoked potentials involve stimulating a peripheral nerve like the median nerve and measuring the response along the pathway to detect spinal cord or brain injuries. Auditory evoked potentials involve measuring the brainstem response to a click stimulus to detect acoustic neuromas or other posterior fossa lesions. Both evoked potentials and EMG monitoring are used during surgery to detect injuries.