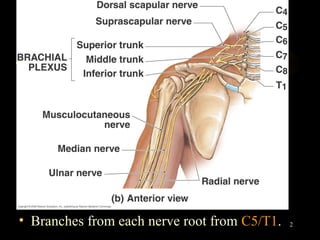
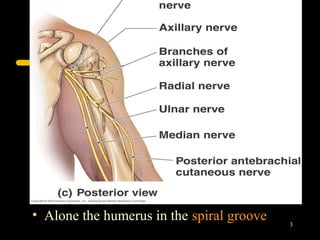
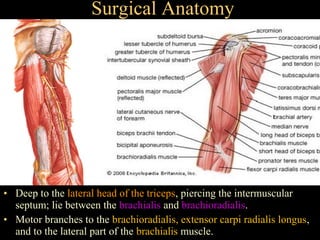
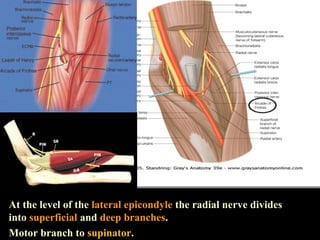
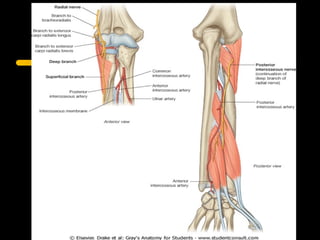
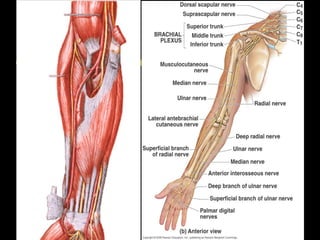
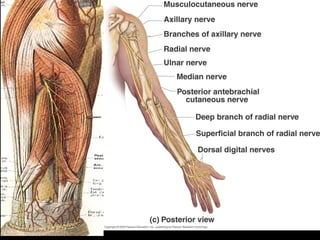
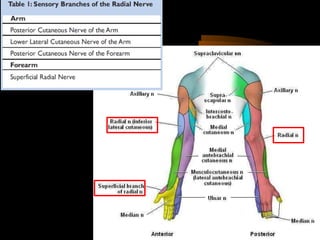
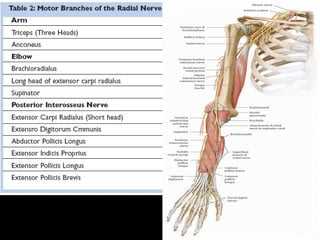
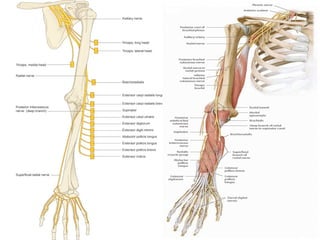
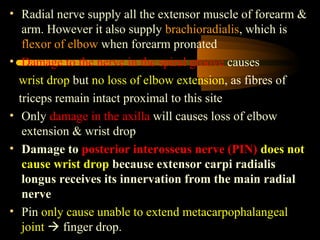
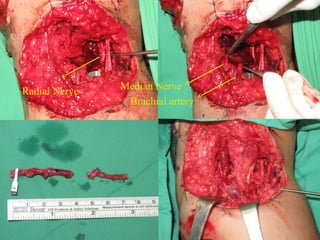
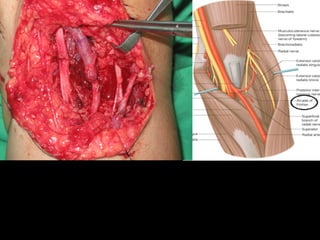
The radial nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus and passes posterior to the axillary artery between the triceps muscle heads. It lies in the spiral groove on the humerus and pierces the lateral intermuscular septum to run between the brachialis and brachioradialis muscles. At the lateral epicondyle, the radial nerve divides into the posterior interosseous nerve and superficial radial nerve. The radial nerve supplies all the extensor muscles of the forearm and arm, and the brachioradialis muscle. Damage to the radial nerve in the spiral groove causes wrist drop but spares elbow extension.