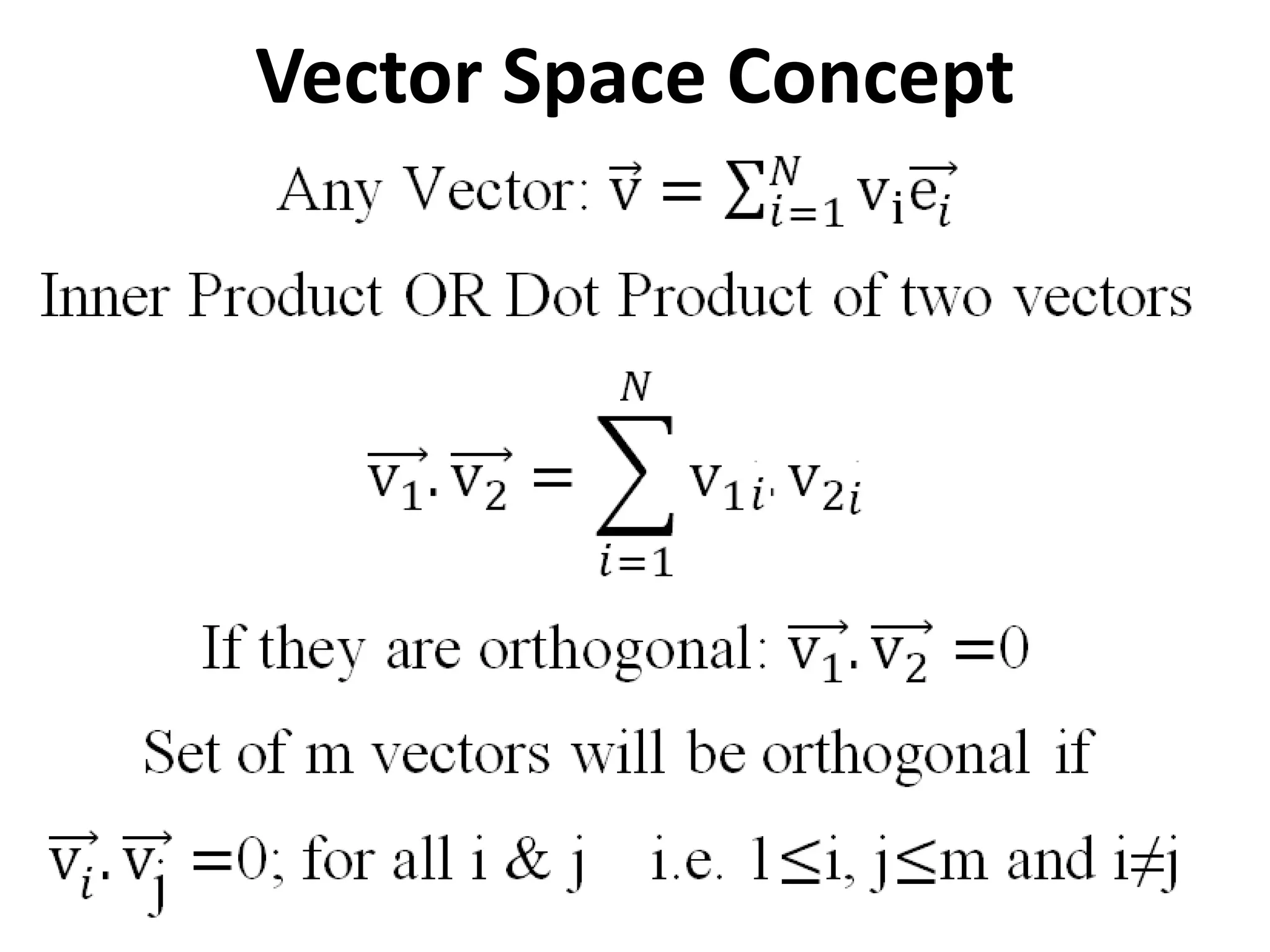
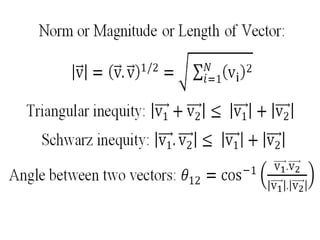
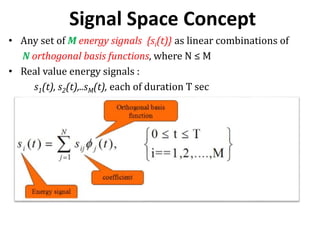
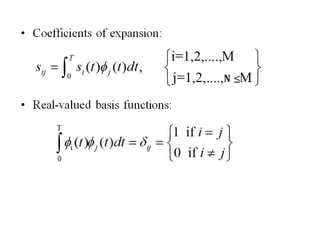
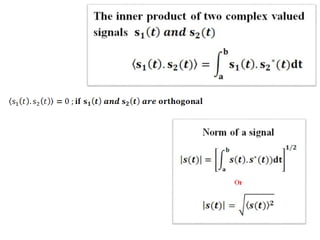
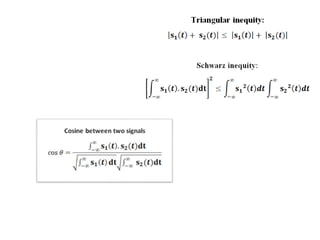
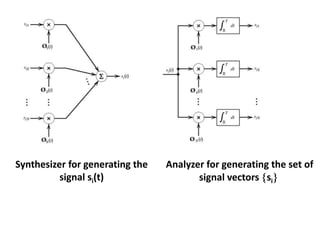
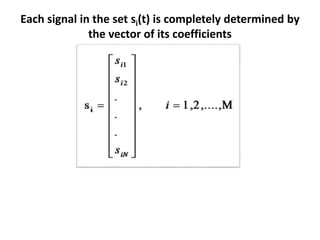
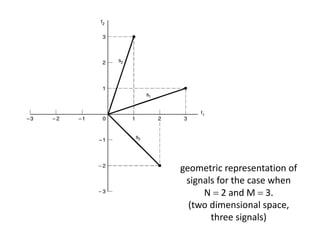
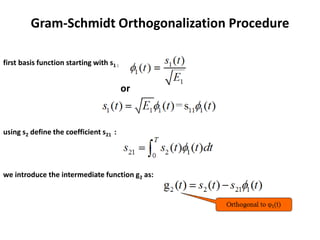
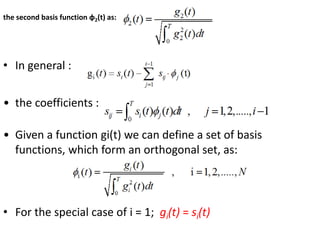
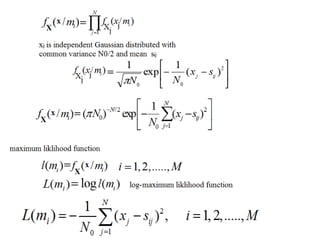
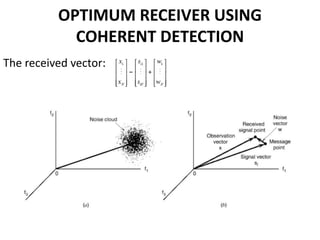
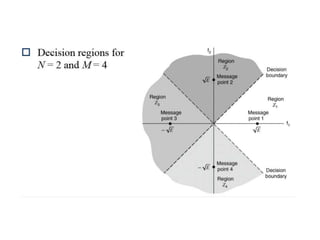
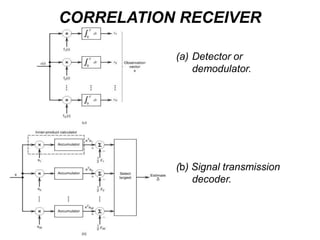
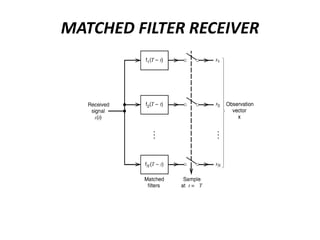
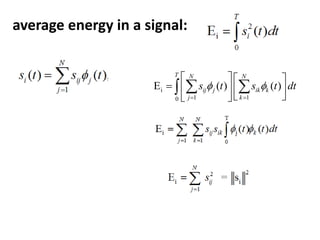Vector space concepts can be used to represent energy signals. Any set of signals can be represented as linear combinations of orthogonal basis functions in an N-dimensional vector space. Each signal is determined by its vector of coefficients. This geometric representation in vector spaces allows defining properties like vector lengths, angles between vectors, and inner products. It provides a mathematical basis for analyzing signals and noise in communication systems.