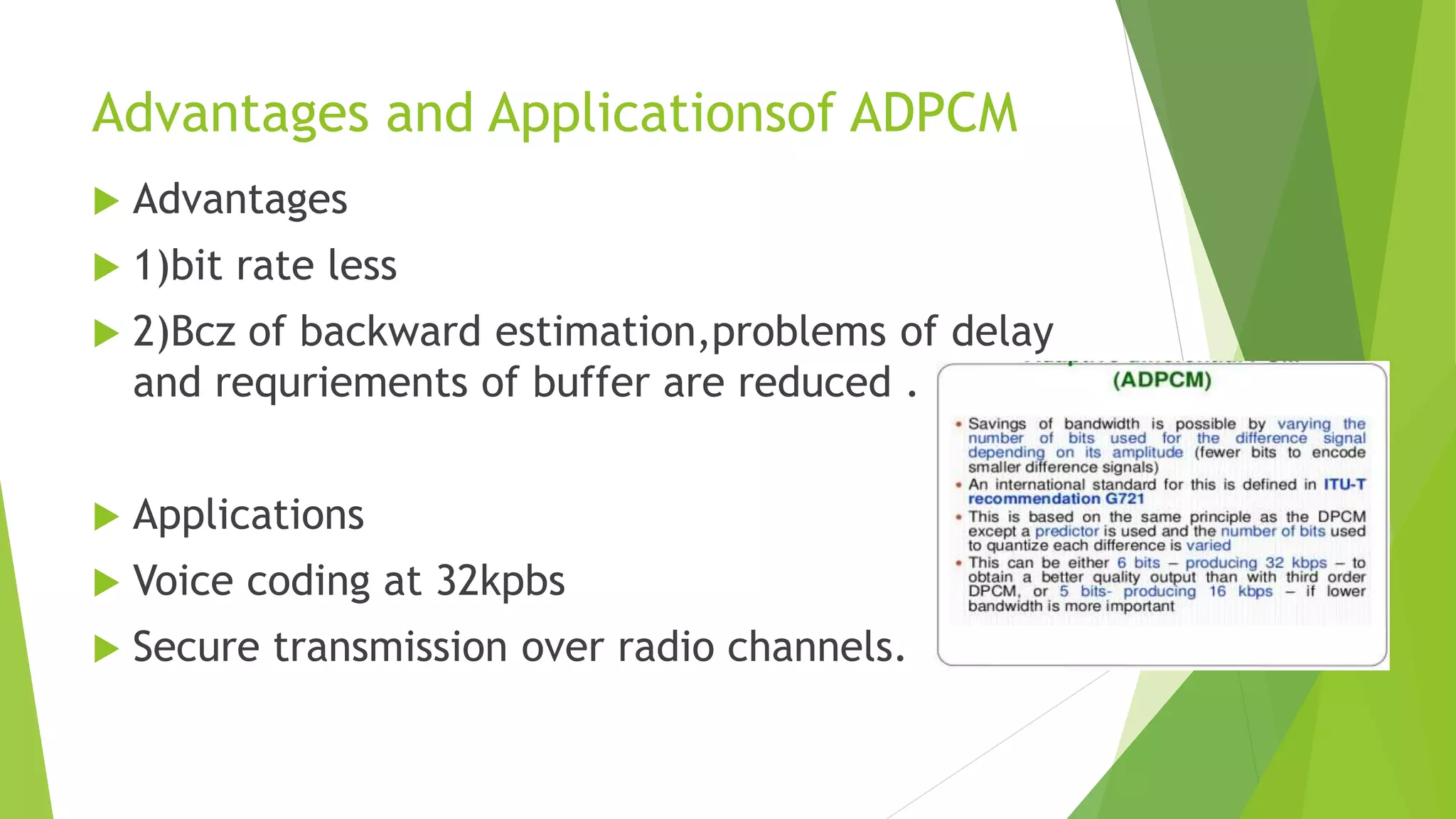
The document discusses Differential Pulse Code Modulation (DPCM), which addresses the redundancy in Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) by encoding the difference between actual and predicted sample values to reduce bit rate. It explains the advantages of DPCM over PCM, including its ability to handle highly correlated samples more efficiently. Additionally, it introduces Adaptive Differential Pulse-Code Modulation (ADPCM), a variant that further optimizes bandwidth by varying the quantization step size.









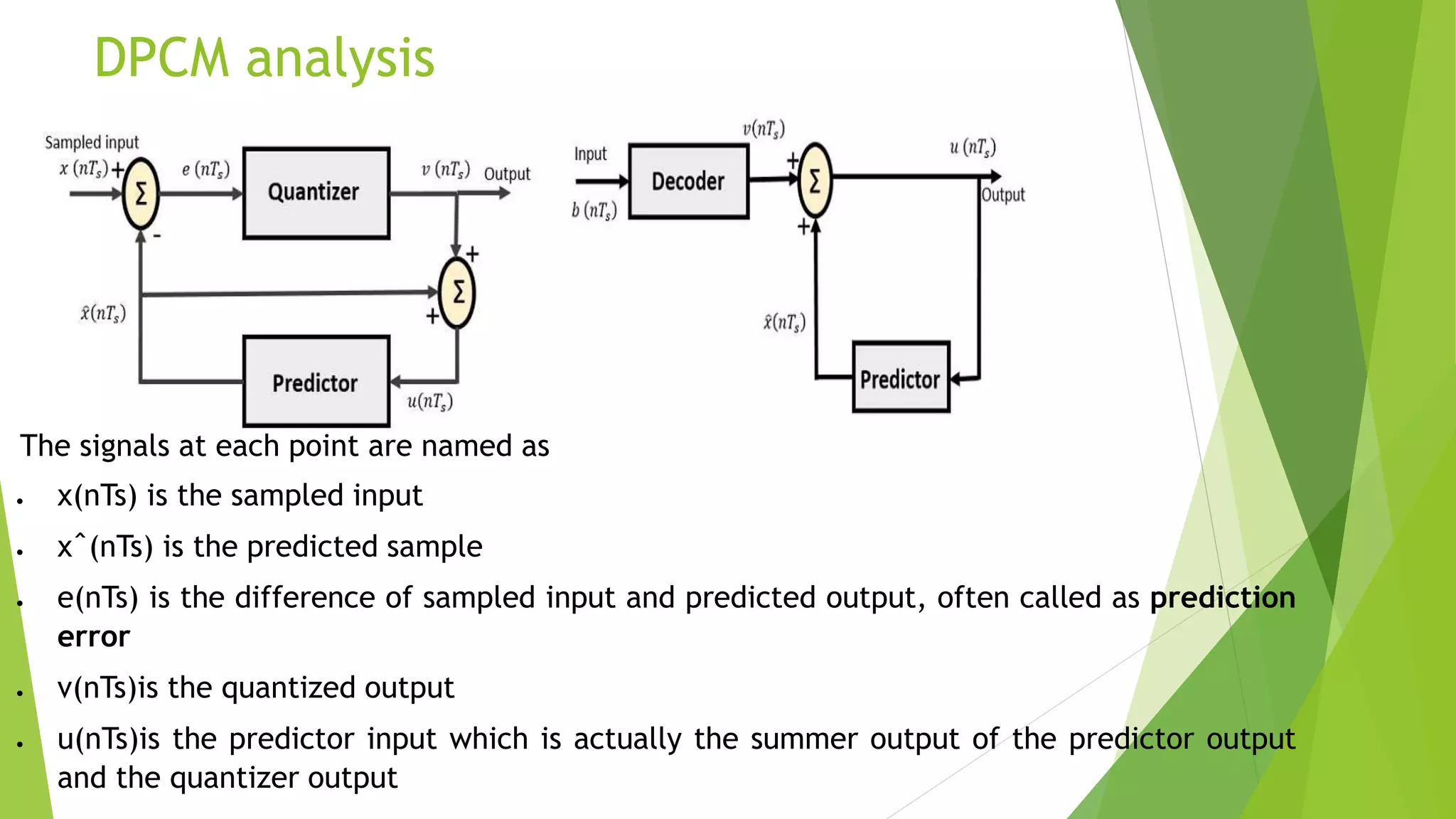
![Quantizer Output is represented as −
v(nTs)=Q[e(nTs)]
=e(nTs)+q(nTs)
v(nTs)= e(nTs)+q(nTs) eqn 1
Where q (nTs) is the quantization error
Predictor input
u(nTs)=xˆ(nTs)+v(nTs) eqn 2
u(nTs)=xˆ(nTs)+e(nTs)+q(nTs) (from eqn 1)
predictor output quantizer output
Result :Predictor input is the sum of
quantizer output and predictor output,
The same predictor circuit is used in the
decoder to reconstruct the original input.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dpcm-210624033808/75/Dpcm-12-2048.jpg)