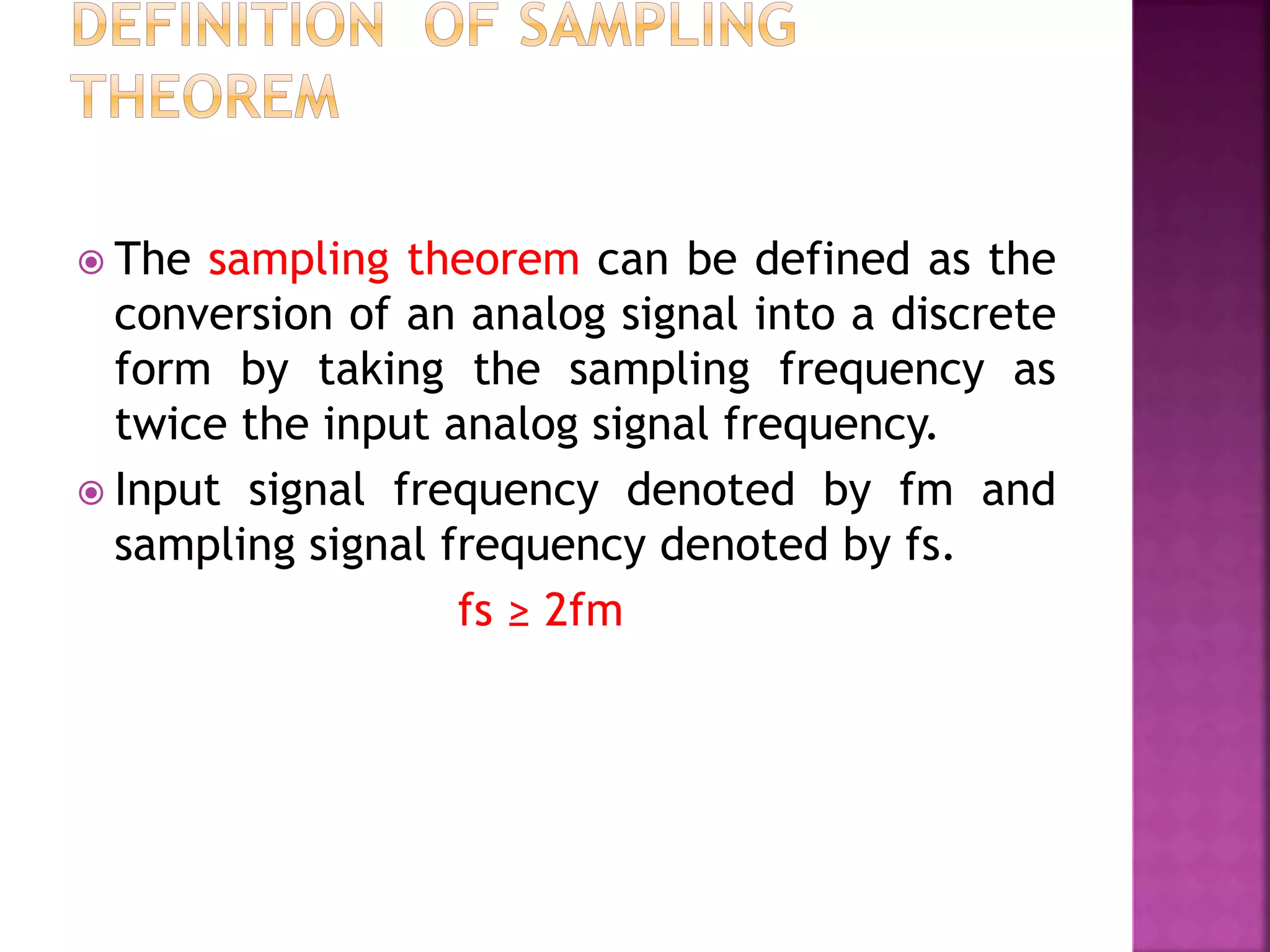
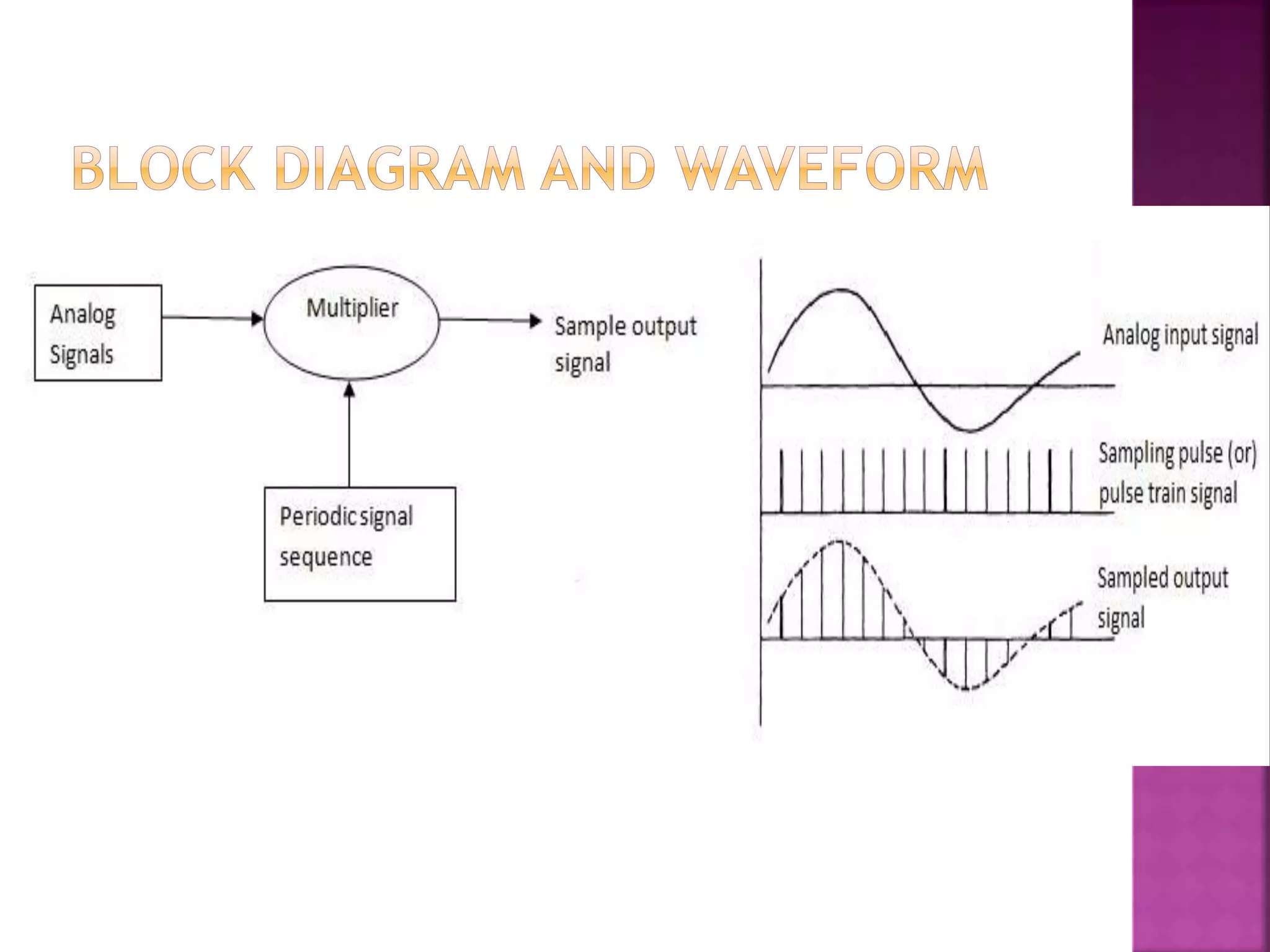
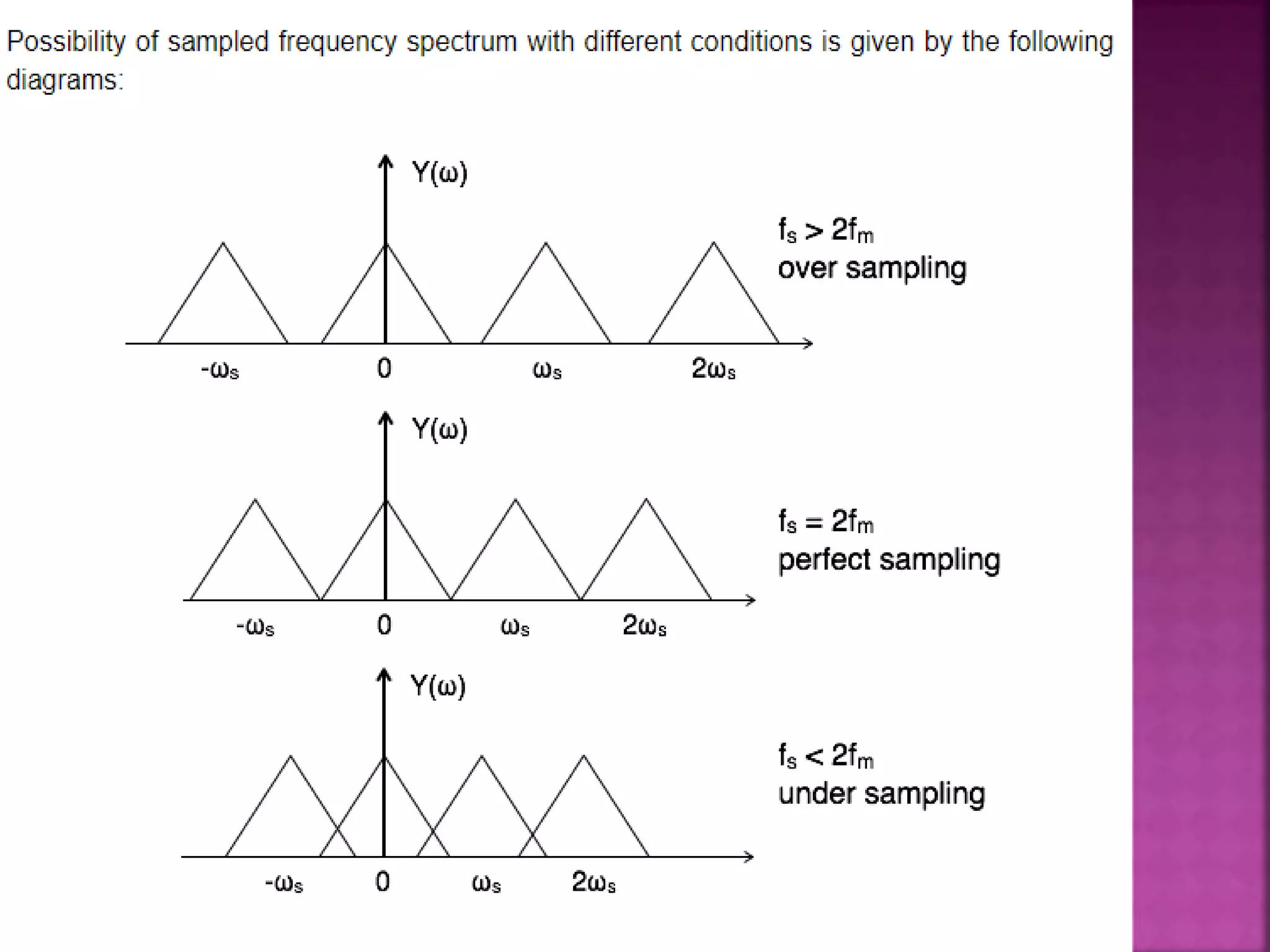
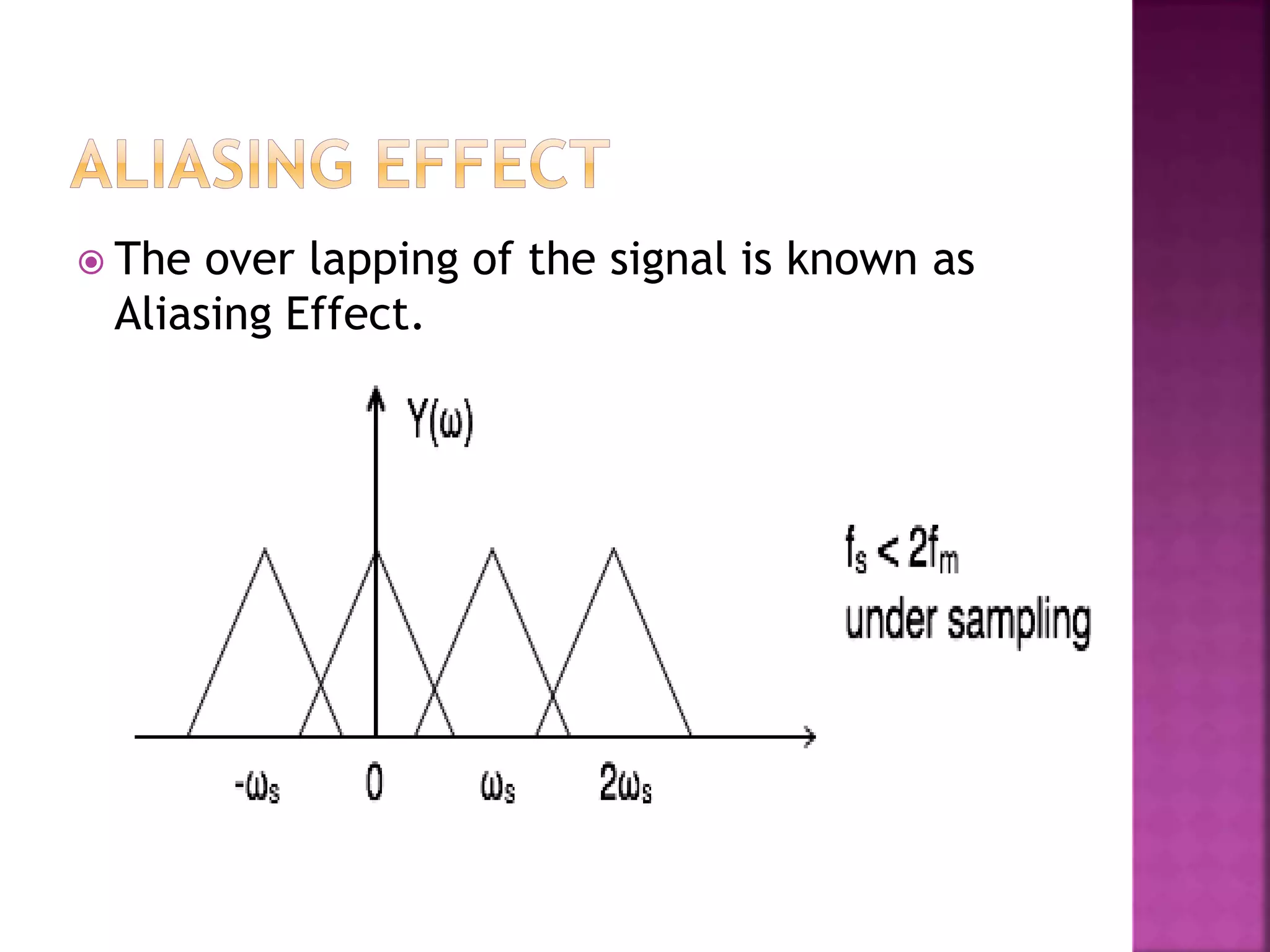
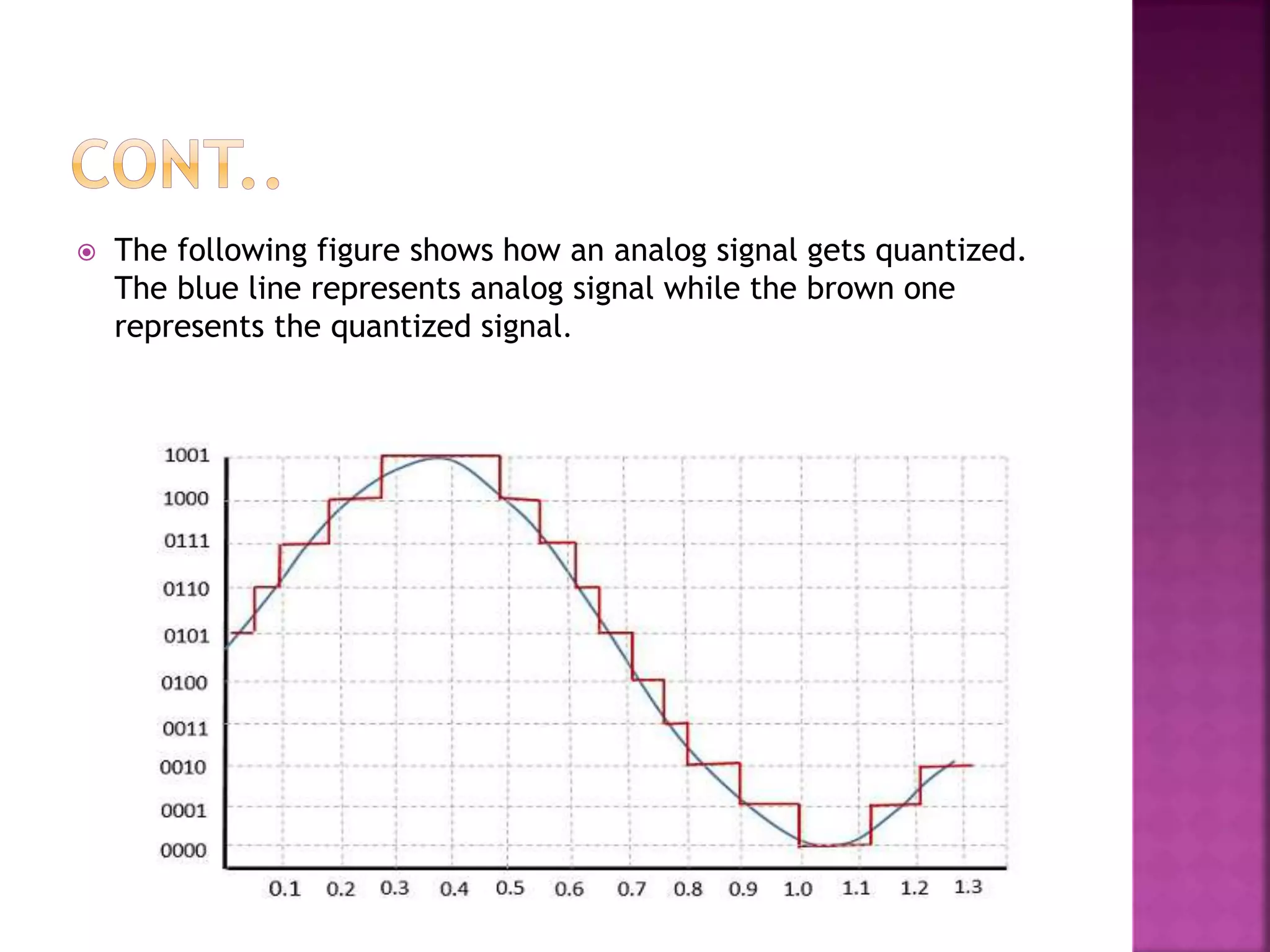
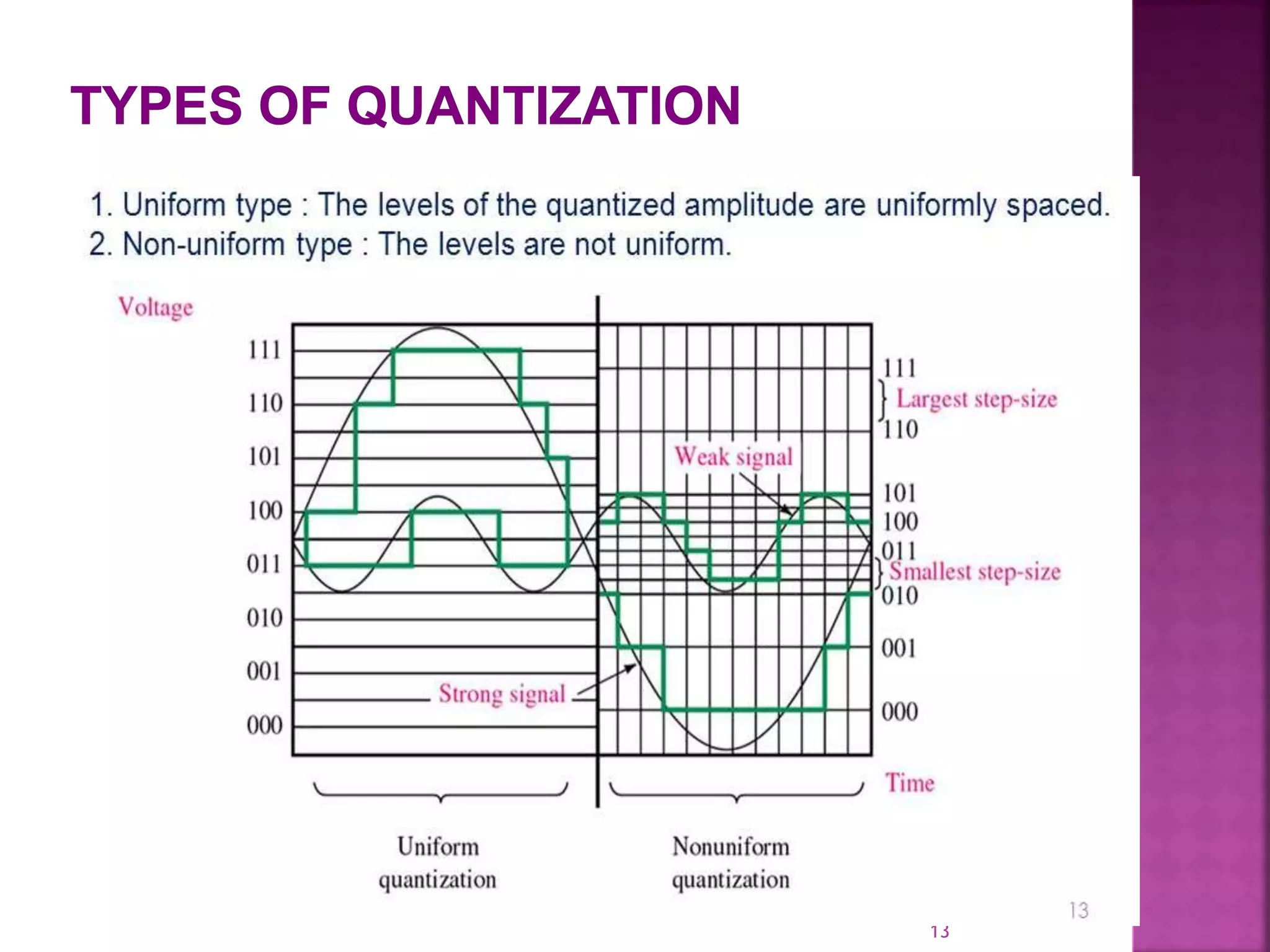
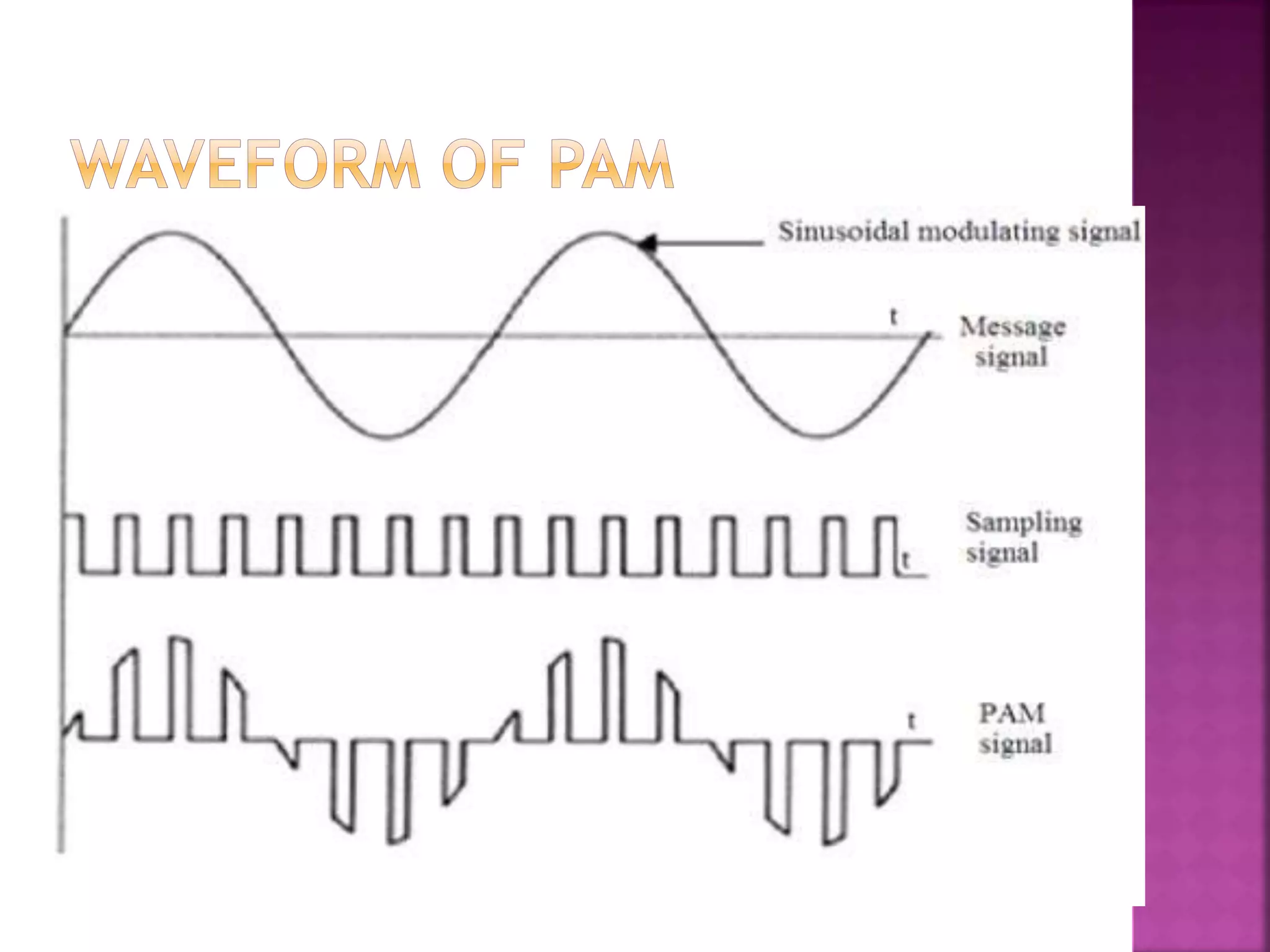
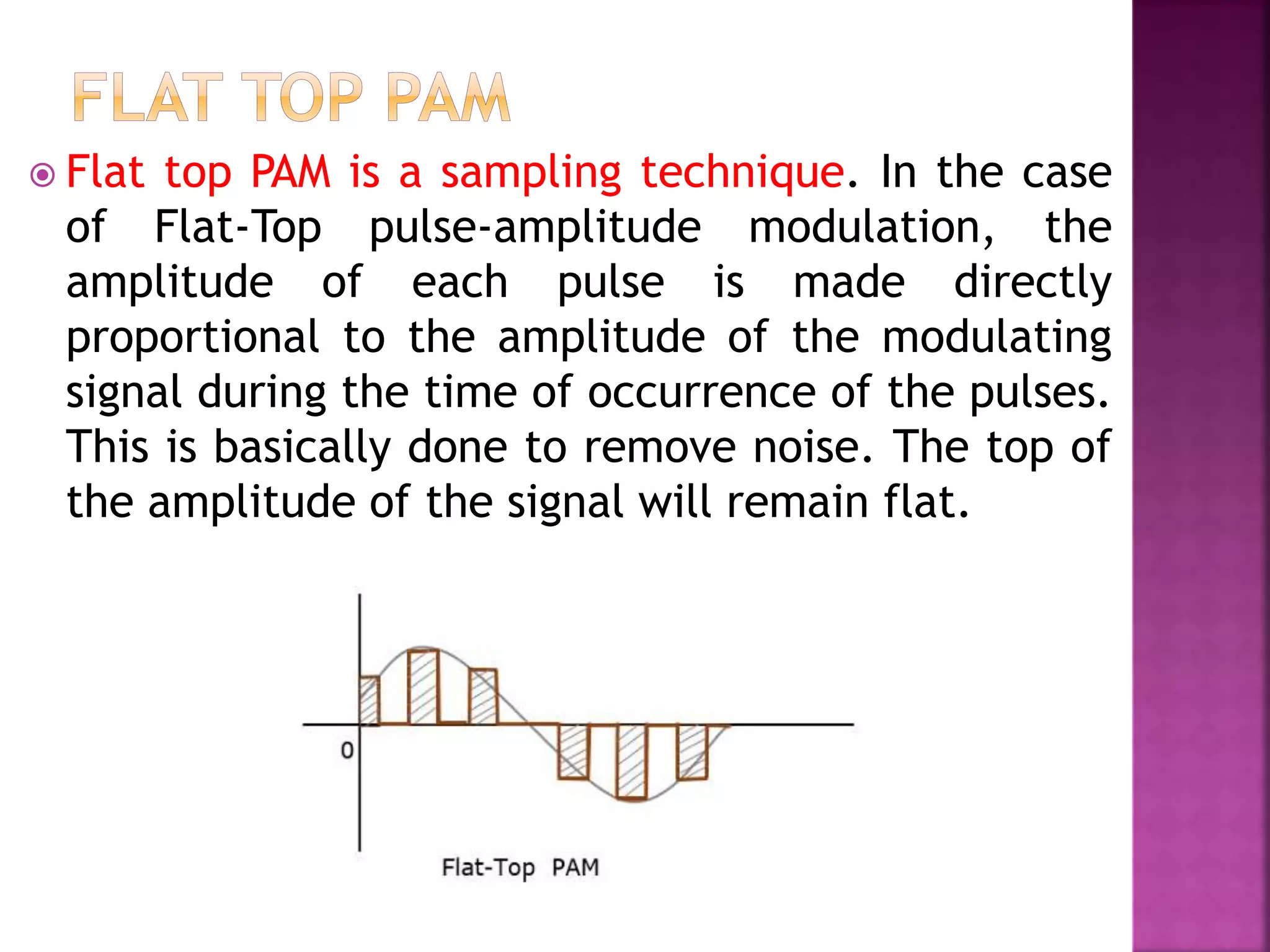
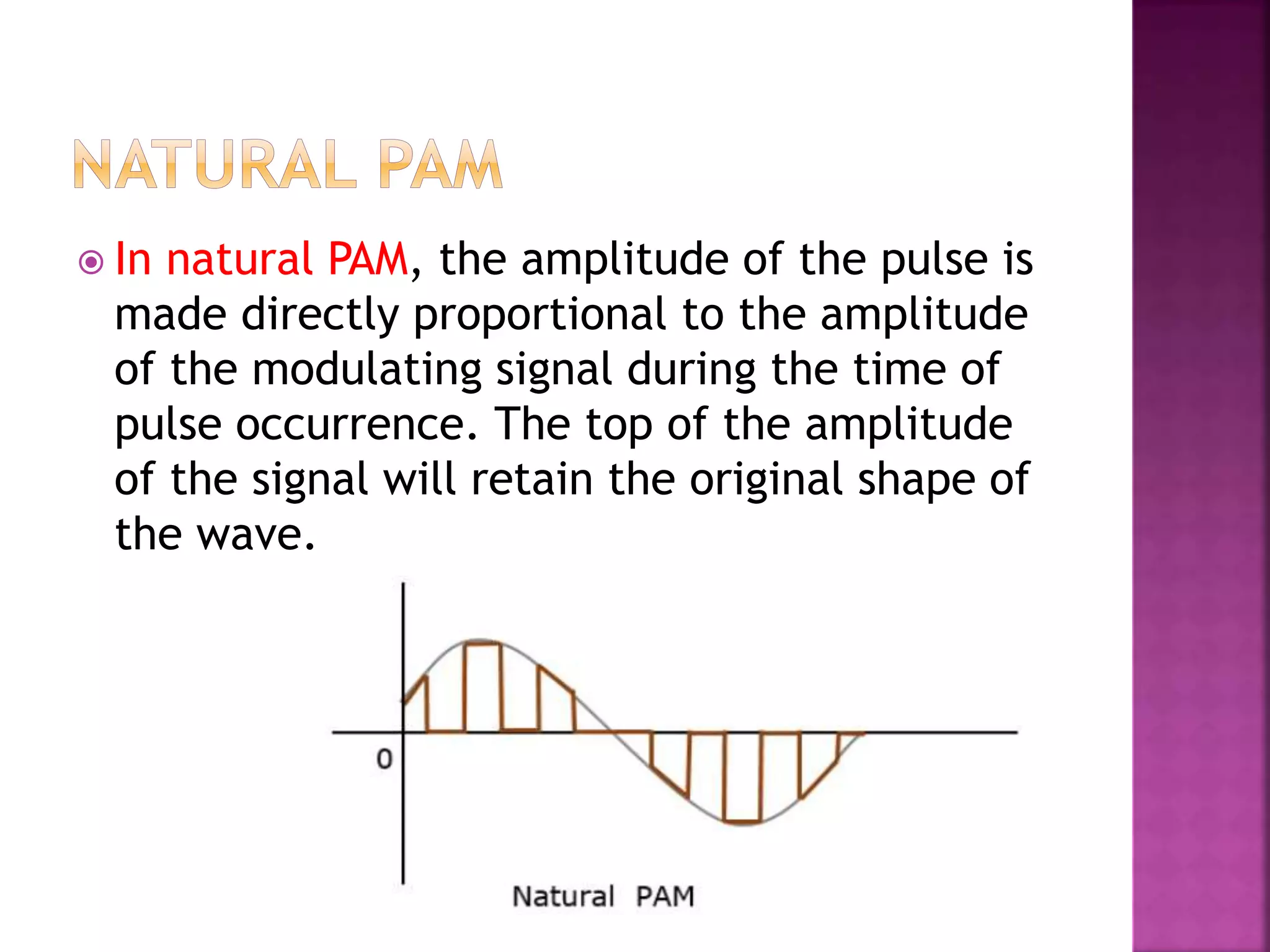
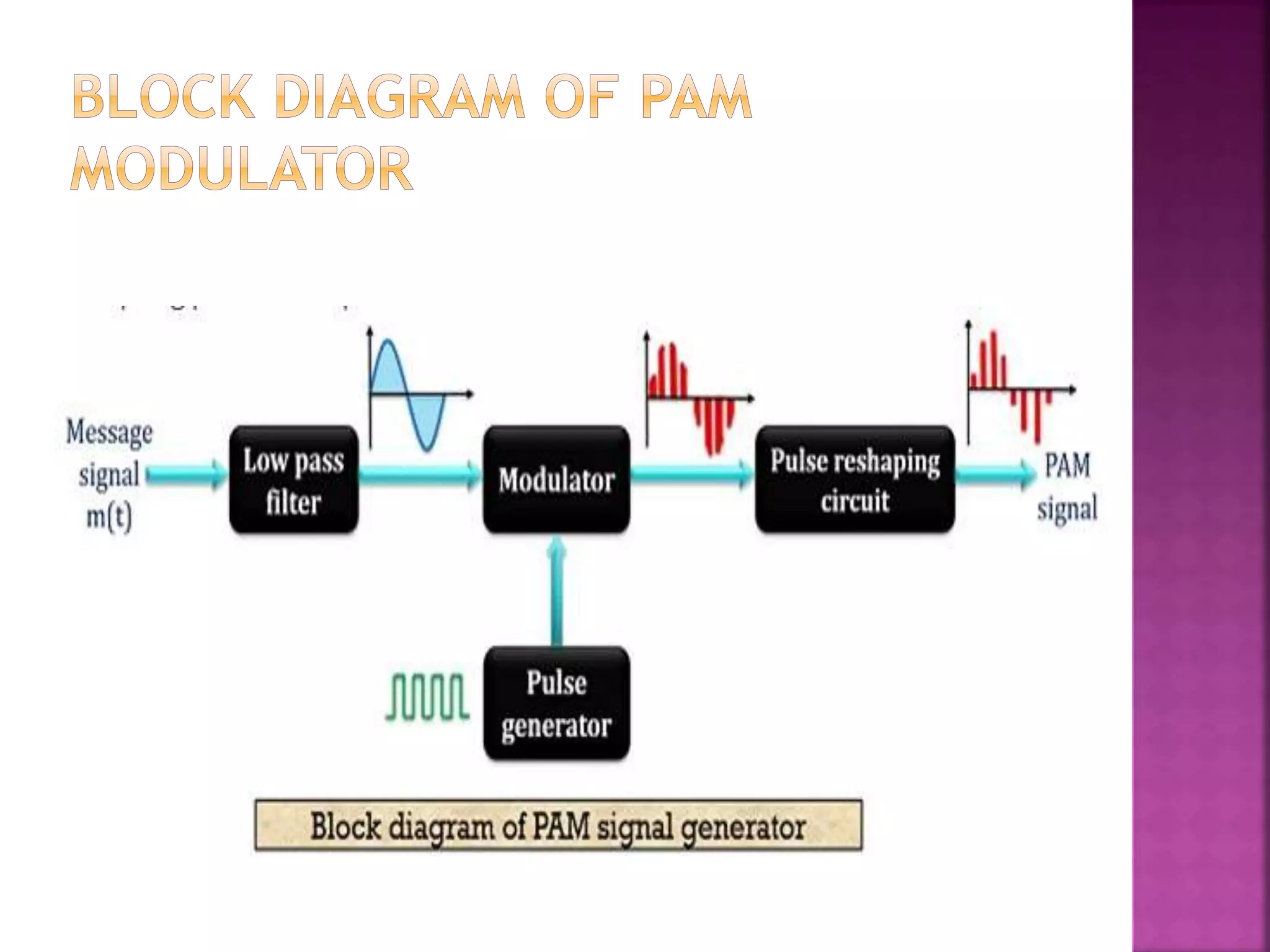
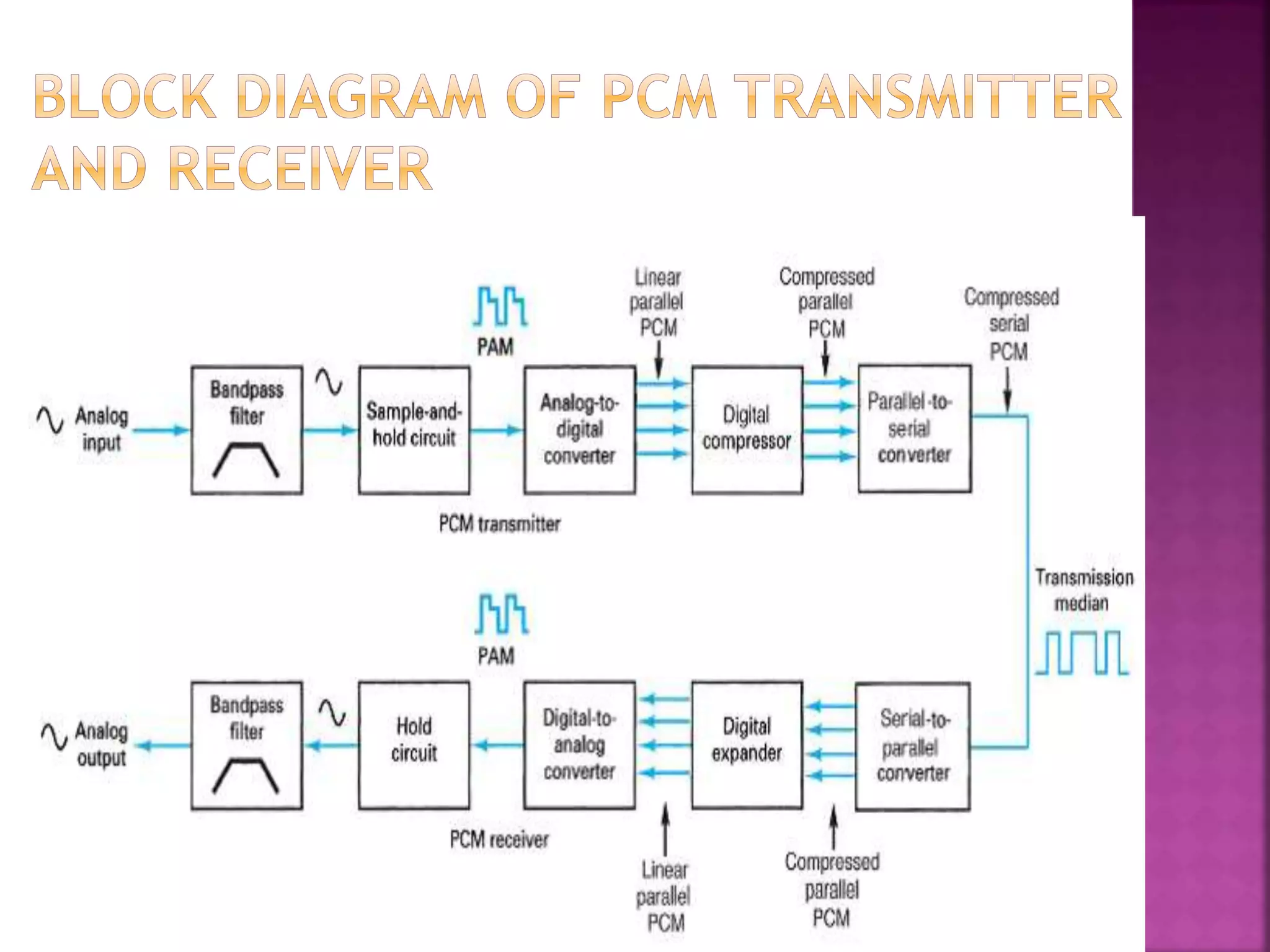
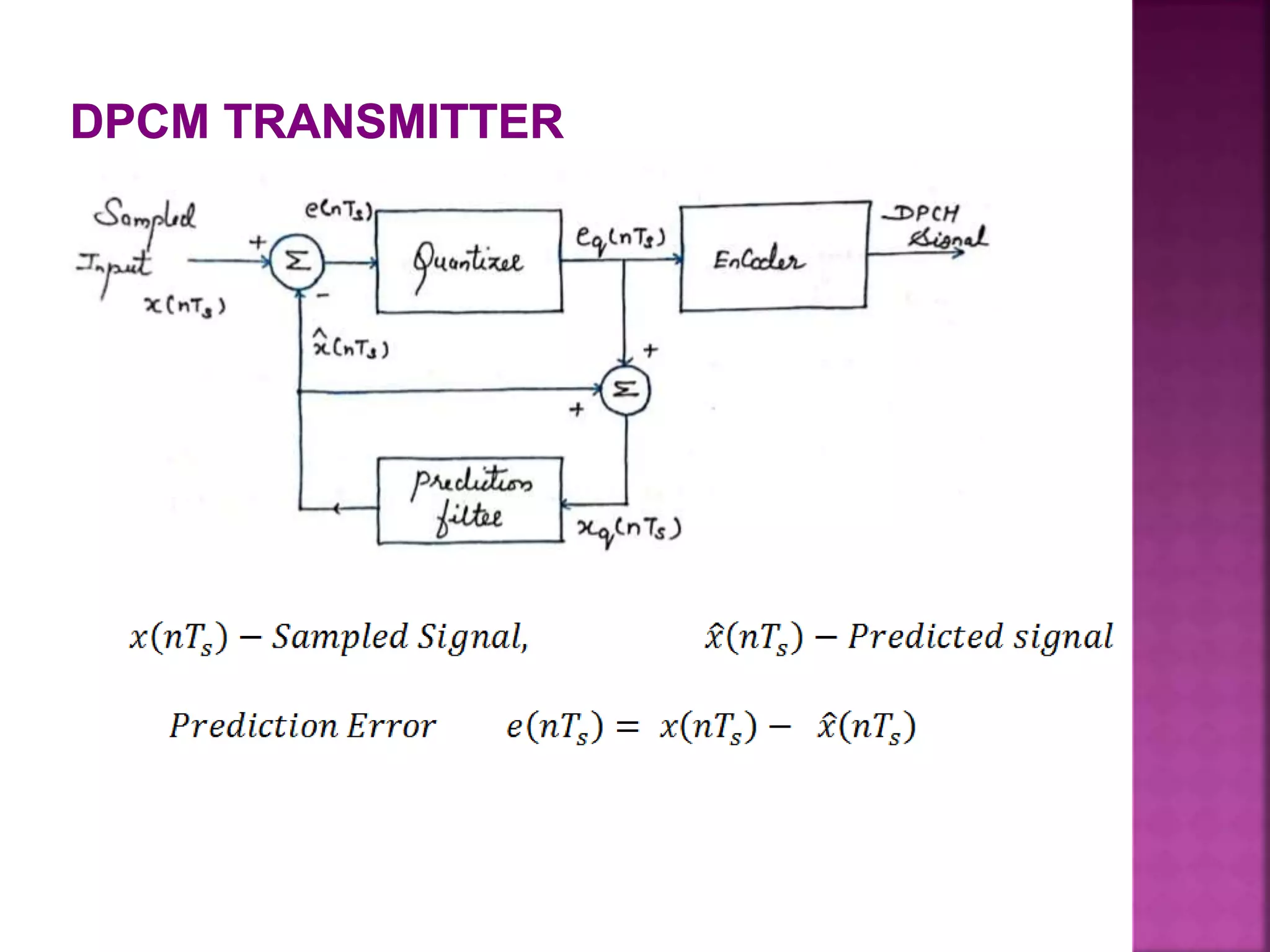
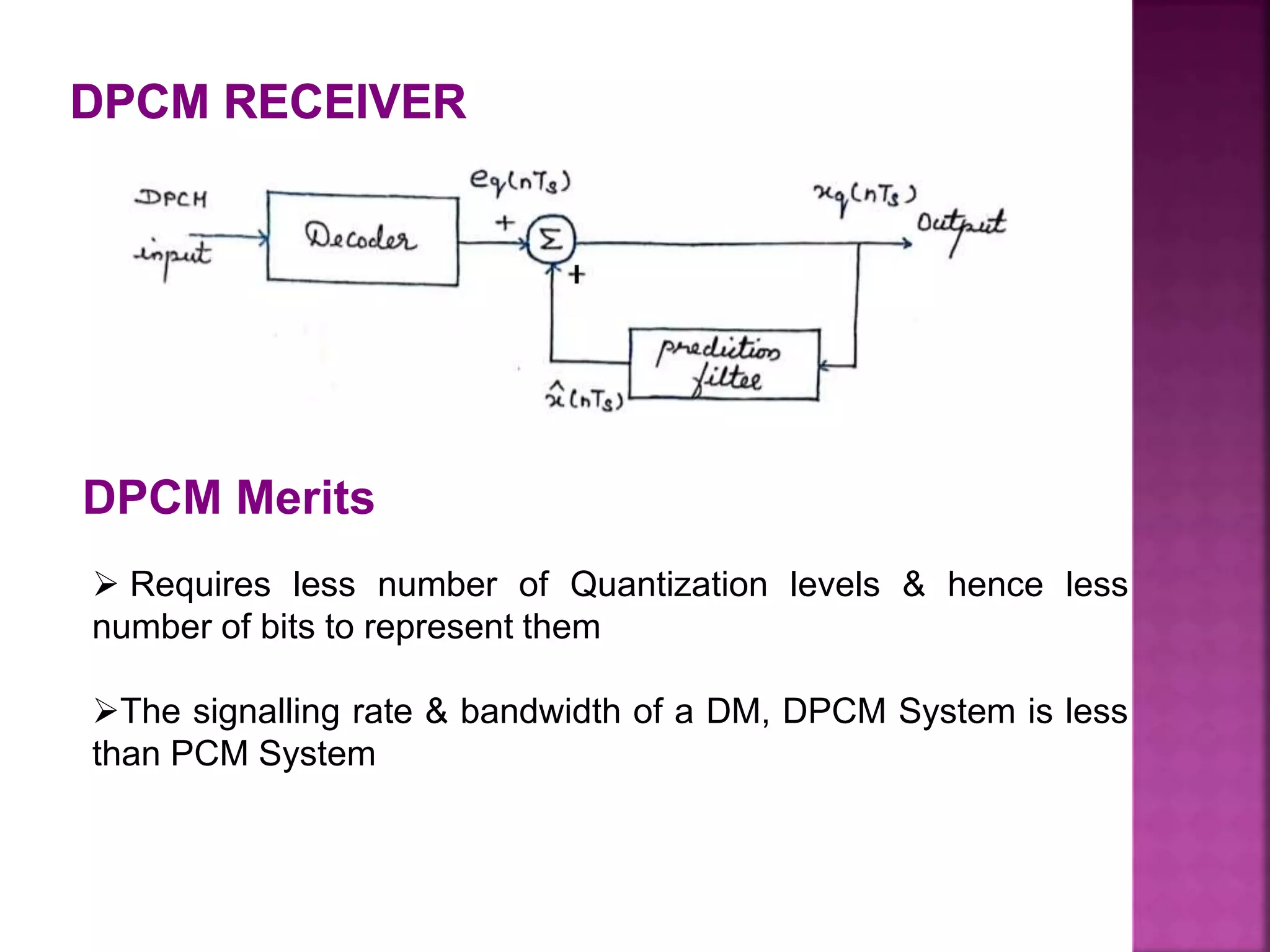
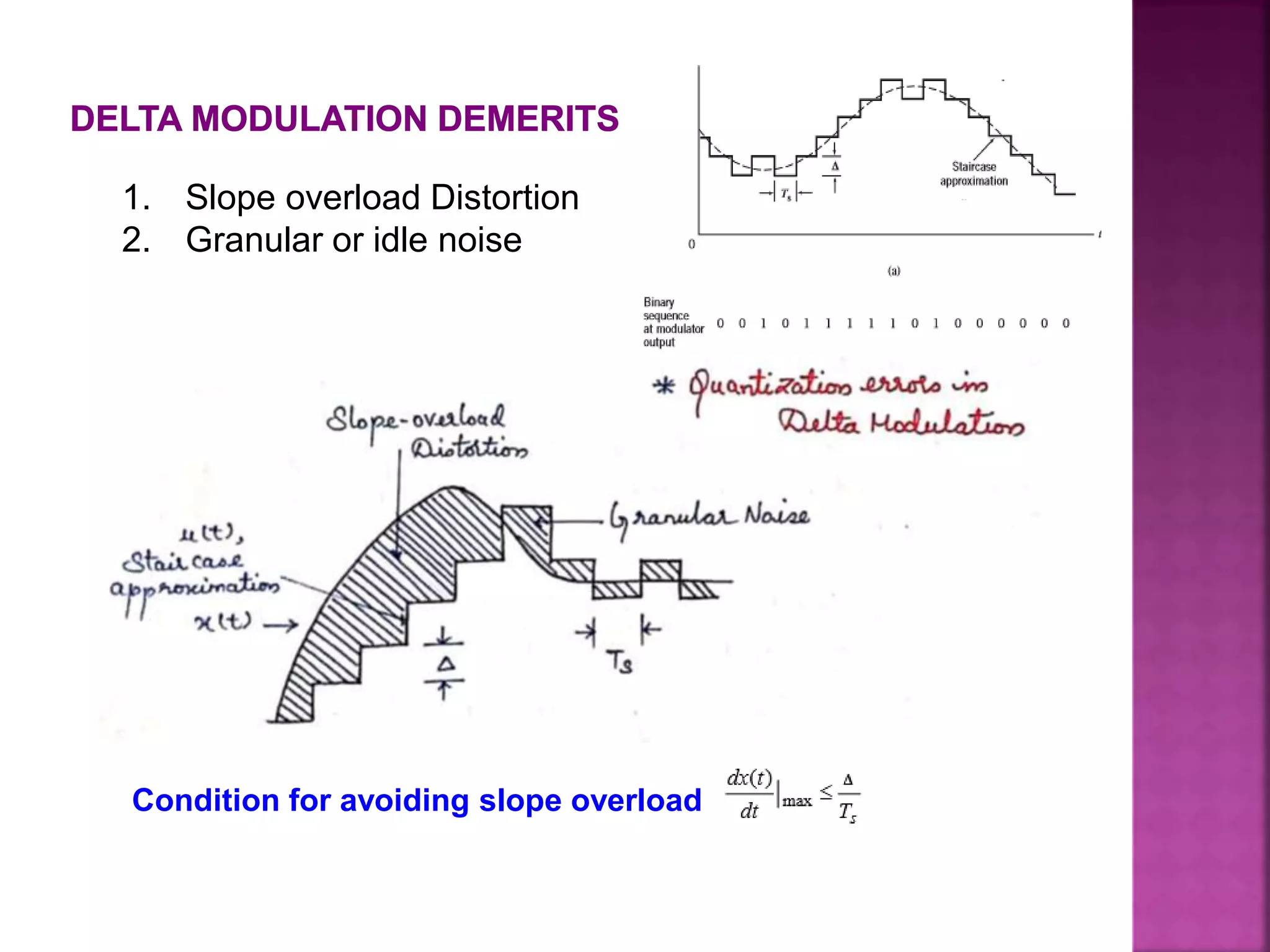
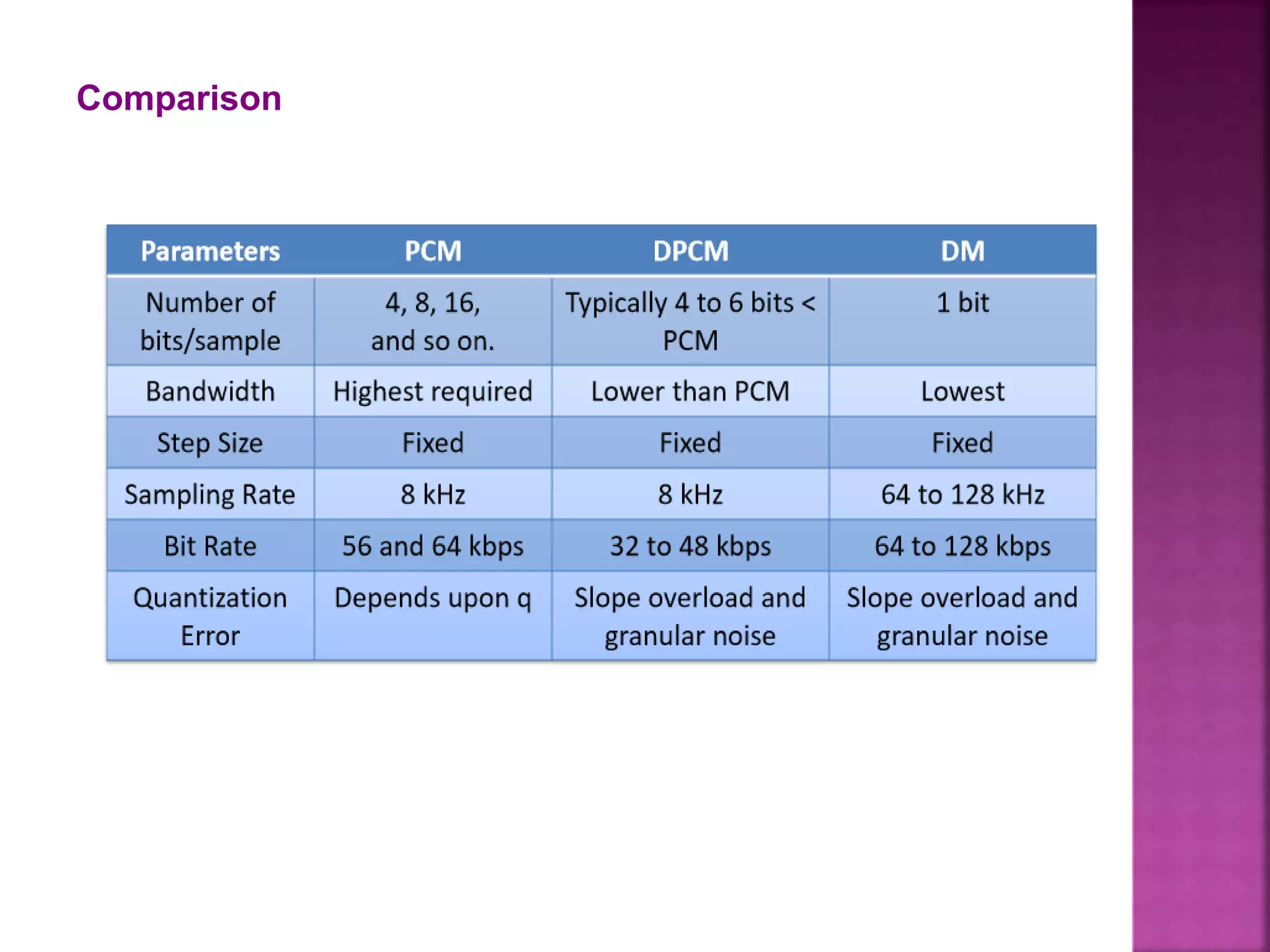
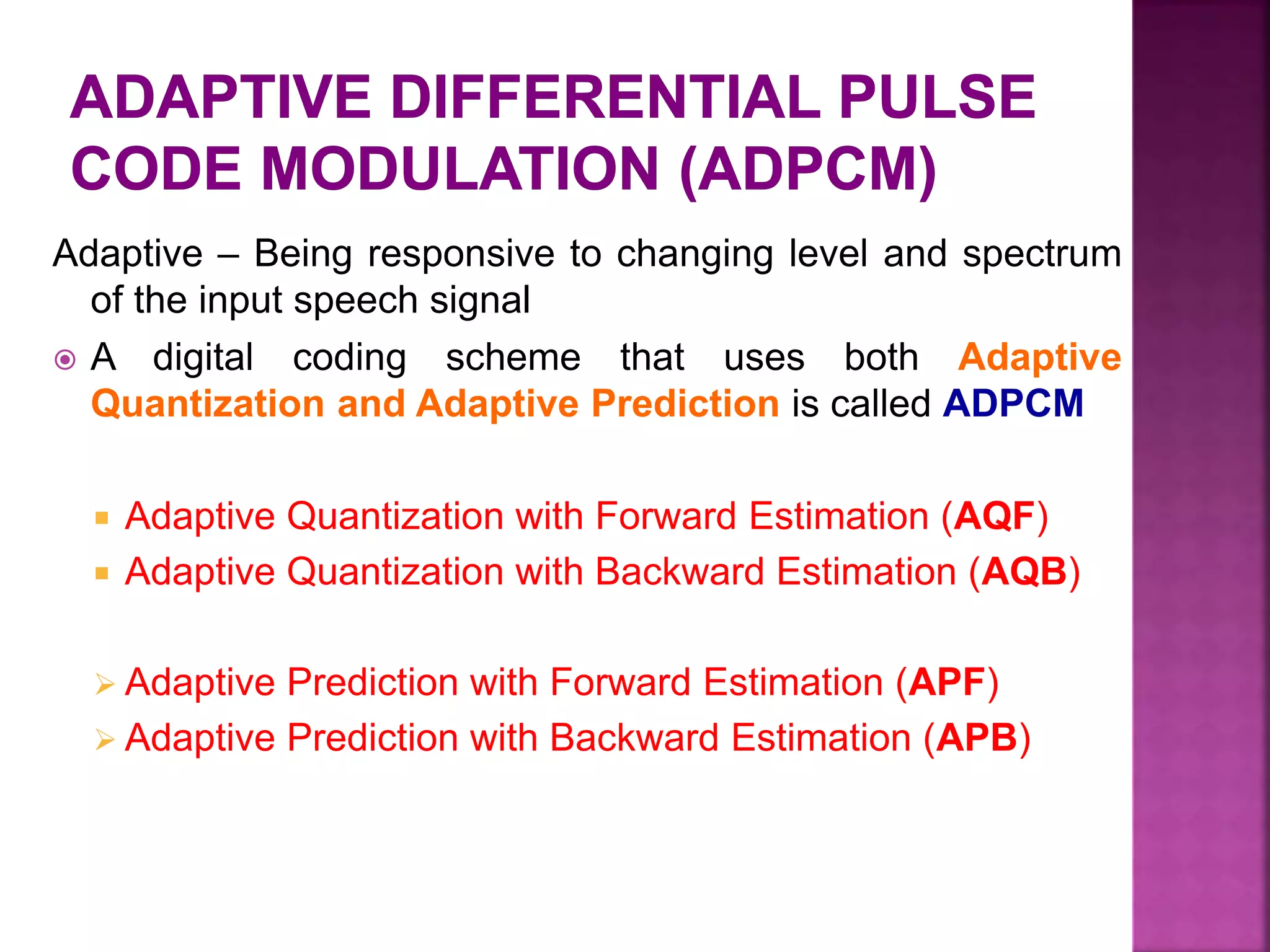
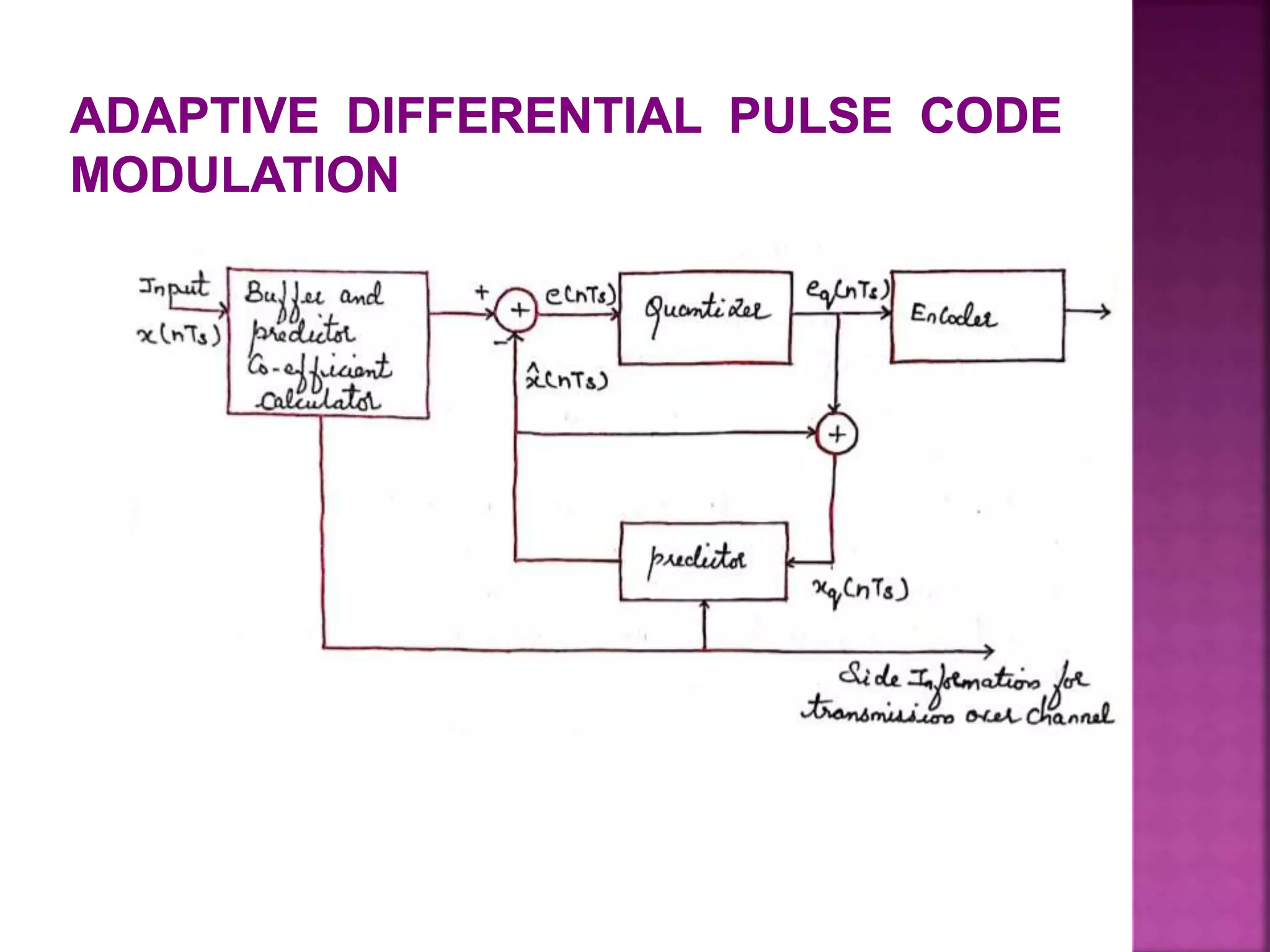
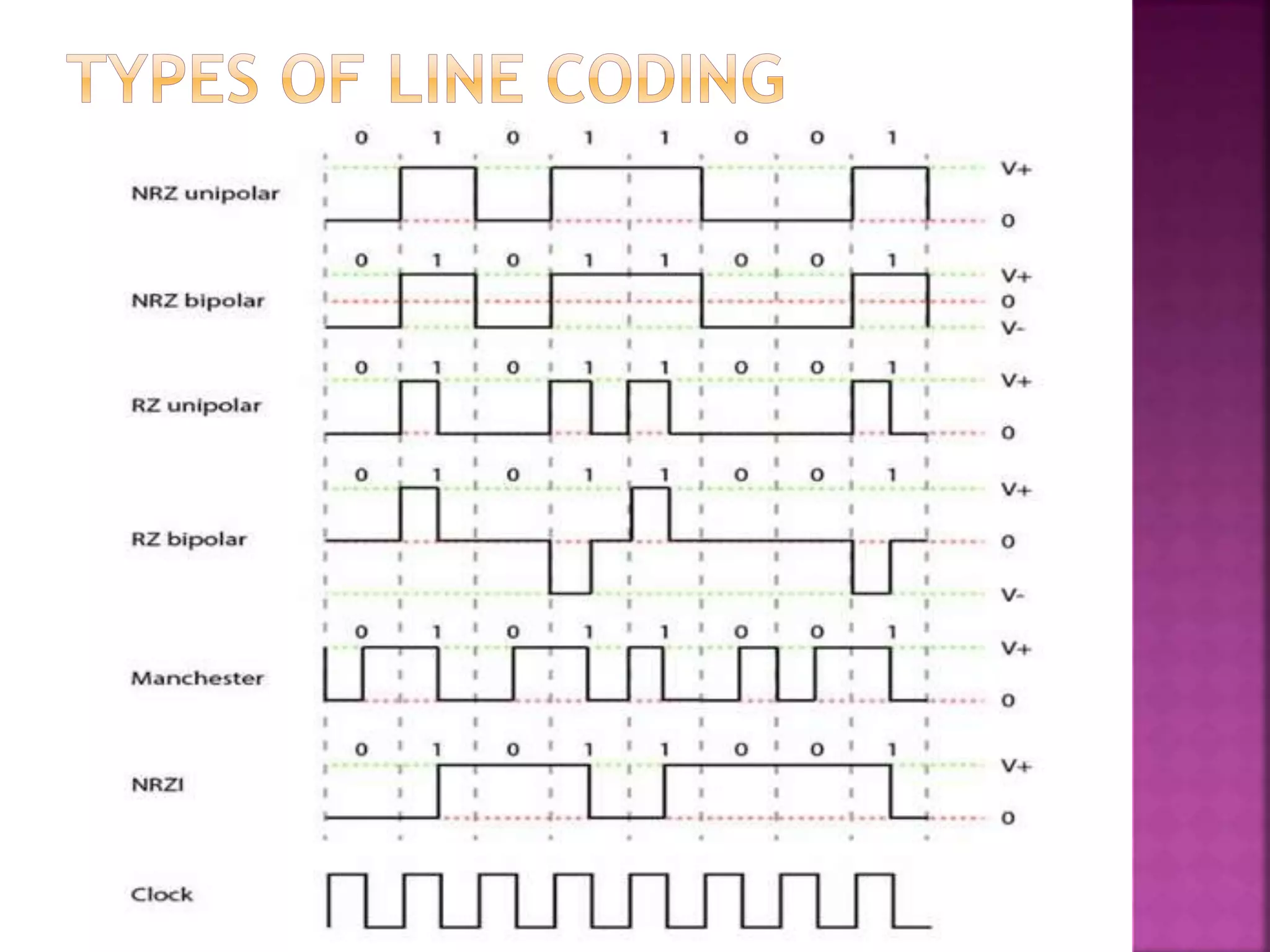
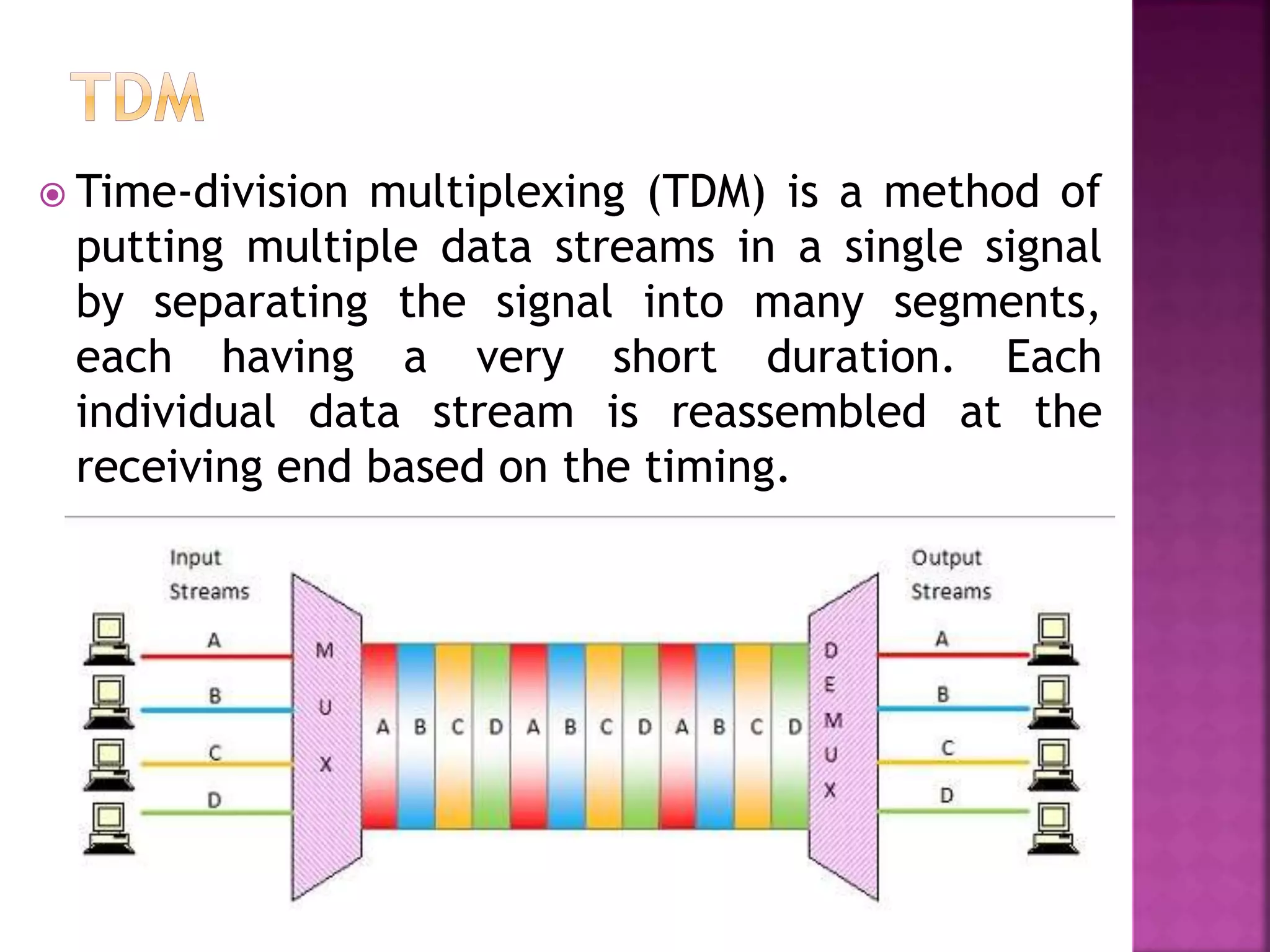
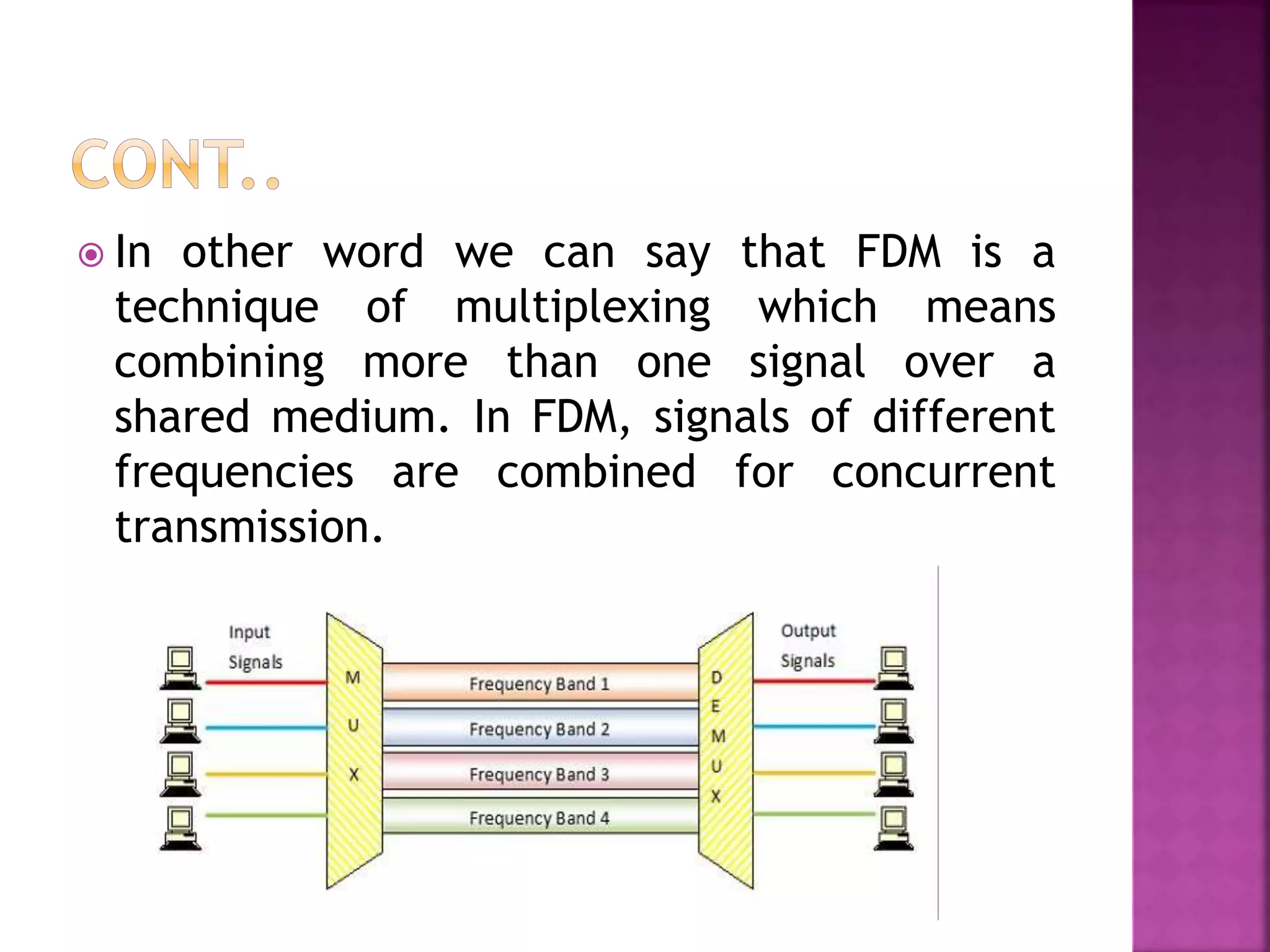
This document discusses various digital modulation and multiplexing techniques. It begins by explaining the differences between analog and pulse modulation. It then discusses key concepts like sampling, quantization, and the sampling theorem. It provides details on pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) including flat top and natural PAM. The document also covers pulse code modulation (PCM), differential PCM (DPCM), delta modulation, and adaptive delta pulse code modulation. It defines line coding and discusses time division multiplexing (TDM) and frequency division multiplexing (FDM).