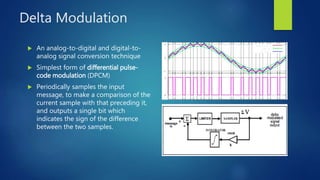
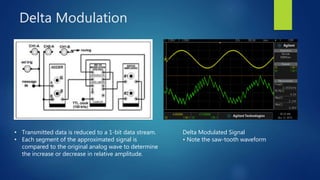
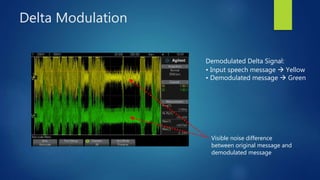
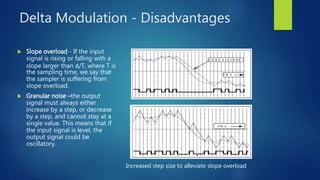
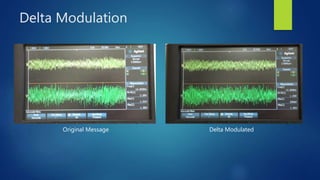
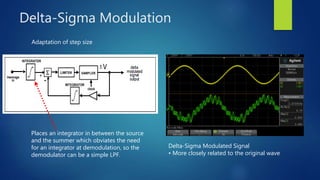
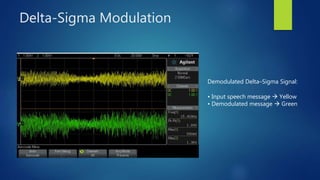
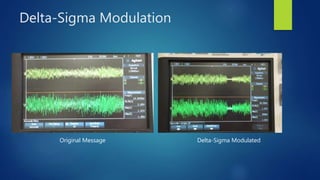
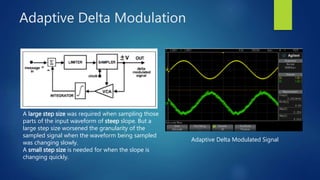
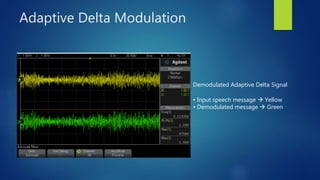
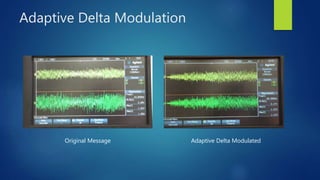
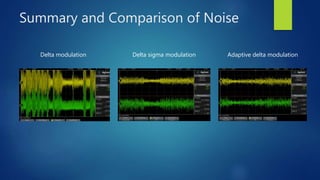
Delta modulation, delta-sigma modulation, and adaptive delta modulation are analog-to-digital conversion techniques. Delta modulation samples an input signal and outputs a single bit indicating the sign of the difference between samples. It has higher SNR than other techniques but can suffer from slope overload and granular noise. Delta-sigma modulation places an integrator between the source and quantizer, reducing quantization error and more closely matching the original wave. Adaptive delta modulation uses a variable step size to better handle rapidly changing slopes and slow changes, improving quality.