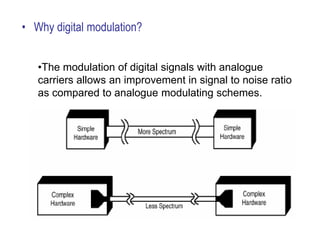
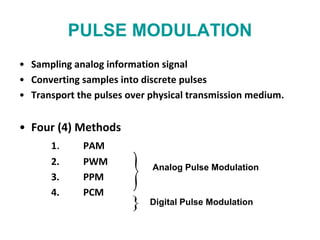
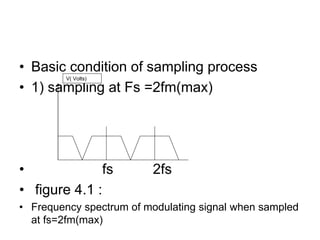
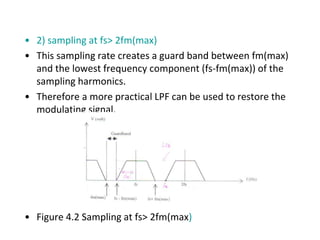
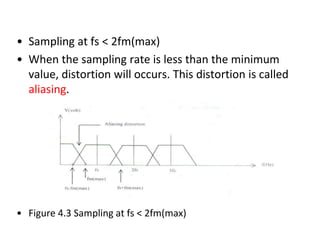
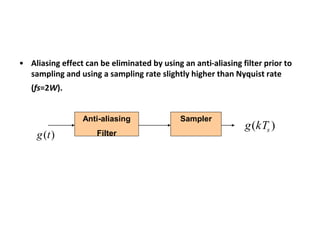
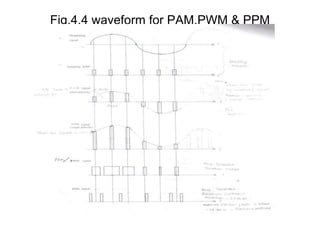
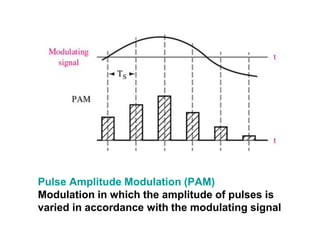
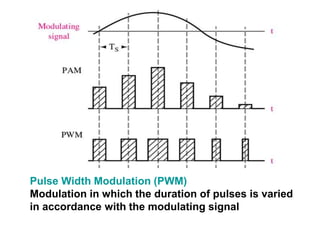
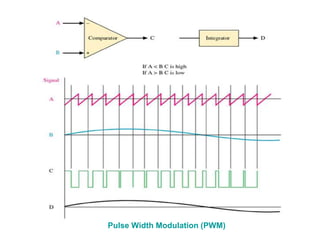
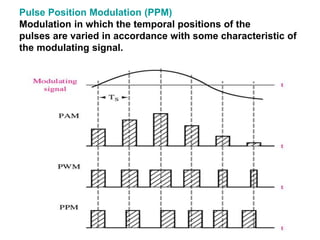
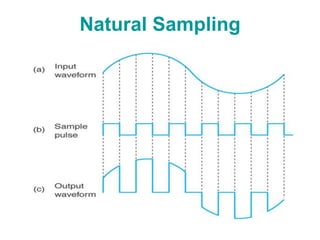
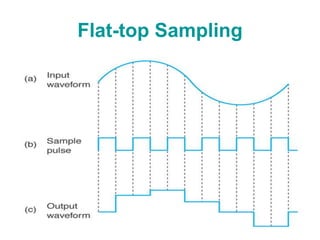
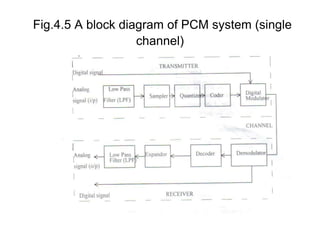
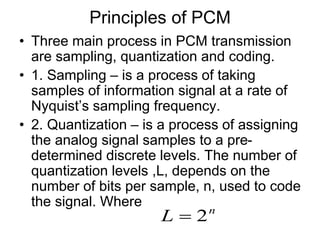
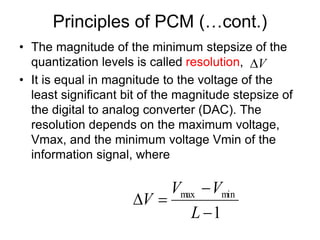
The document explains digital modulation, highlighting its advantages over analog systems, such as better noise immunity and processing ease. It covers pulse modulation techniques, including analog (APM) and digital (DPM), detailing key methods like Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM), Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), and Pulse Position Modulation (PPM). Additionally, it discusses Pulse Code Modulation (PCM), emphasizing its processes of sampling, quantization, and encoding of analog signals into digital form.