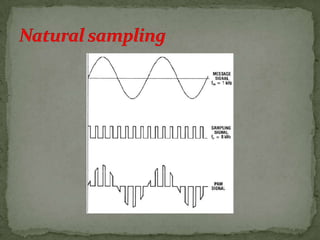
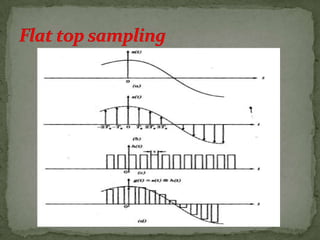
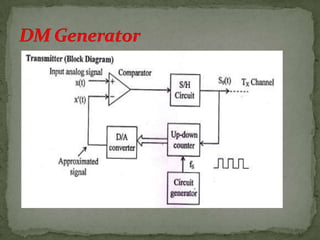
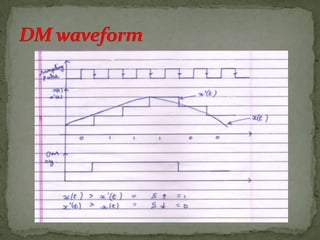
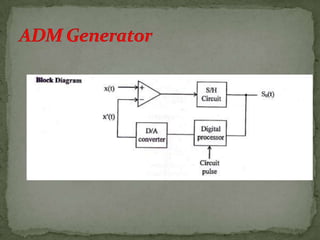
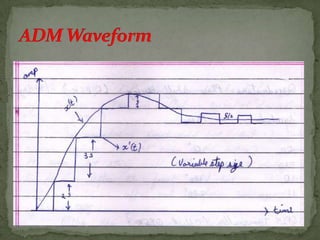
This document summarizes various pulse modulation techniques including:
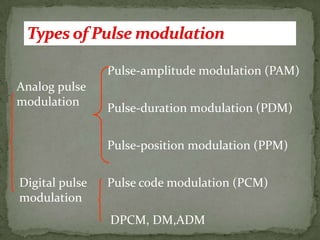
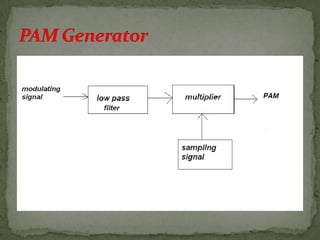
- Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) where the carrier amplitude changes with the message signal amplitude.
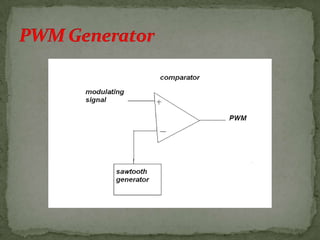
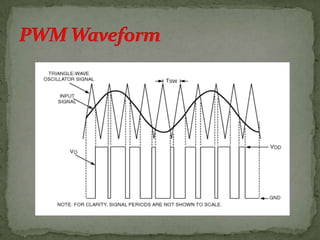
- Pulse-duration modulation (PDM) where the carrier width changes with the message signal amplitude.
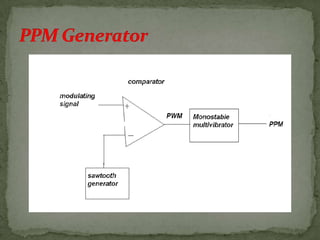
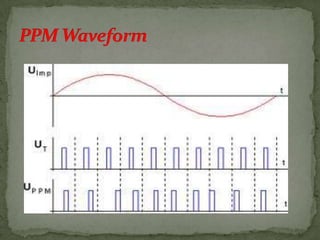
- Pulse-position modulation (PPM) where the carrier position changes with the message signal amplitude.
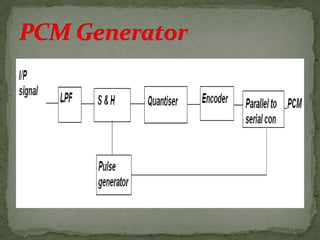
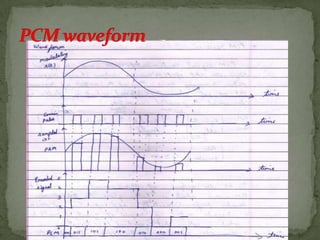
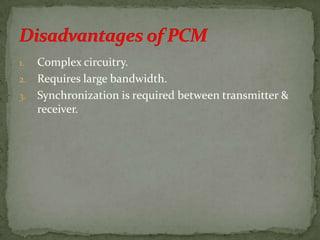
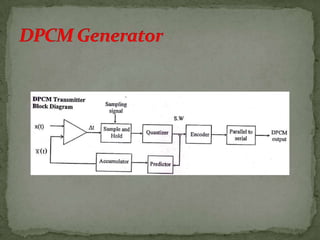
- Digital pulse modulation techniques like pulse code modulation (PCM) and differential PCM (DPCM) are also discussed. Advantages and disadvantages of each technique are provided.