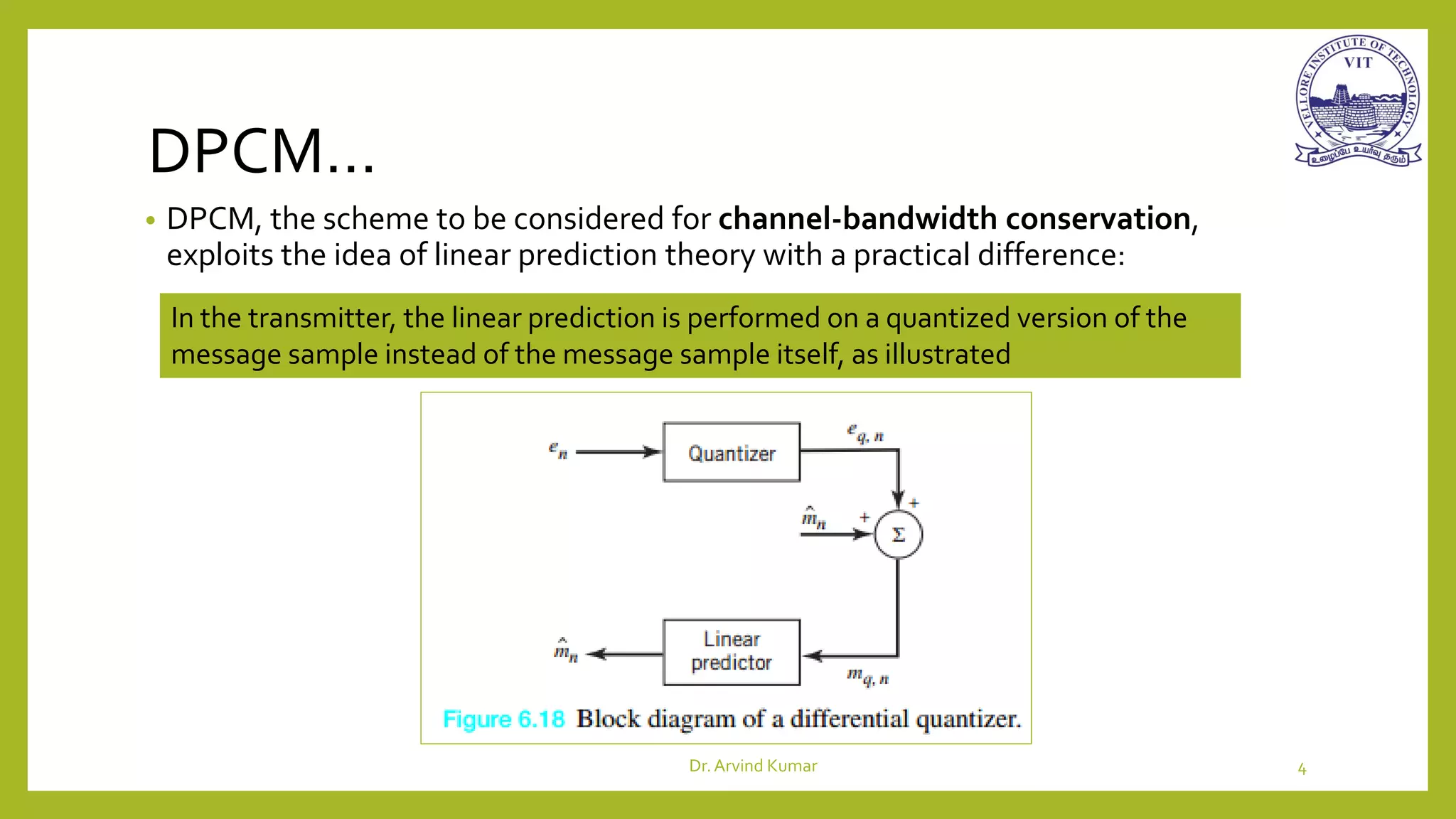
Differential pulse-code modulation (DPCM) is a lossy data compression technique that removes redundancy in messages like voice or video to reduce the bit rate of transmitted data without serious degradation. It exploits linear prediction theory by performing prediction on quantized message samples in the transmitter instead of the original samples. This differential quantization approach caters to both waveform encoding in the transmitter, which requires quantization, and decoding in the receiver, which must process a quantized signal using the same predictors in both.