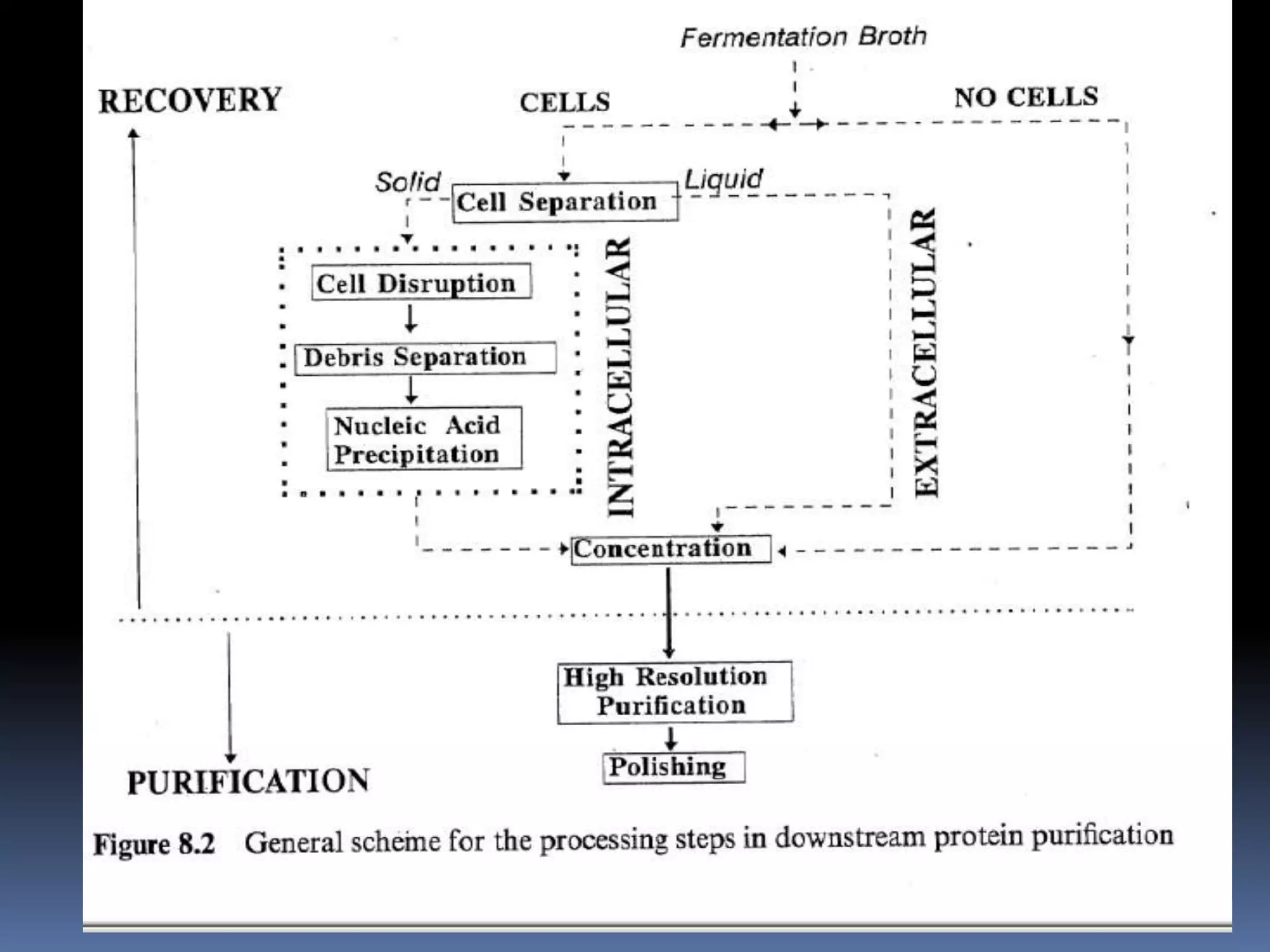
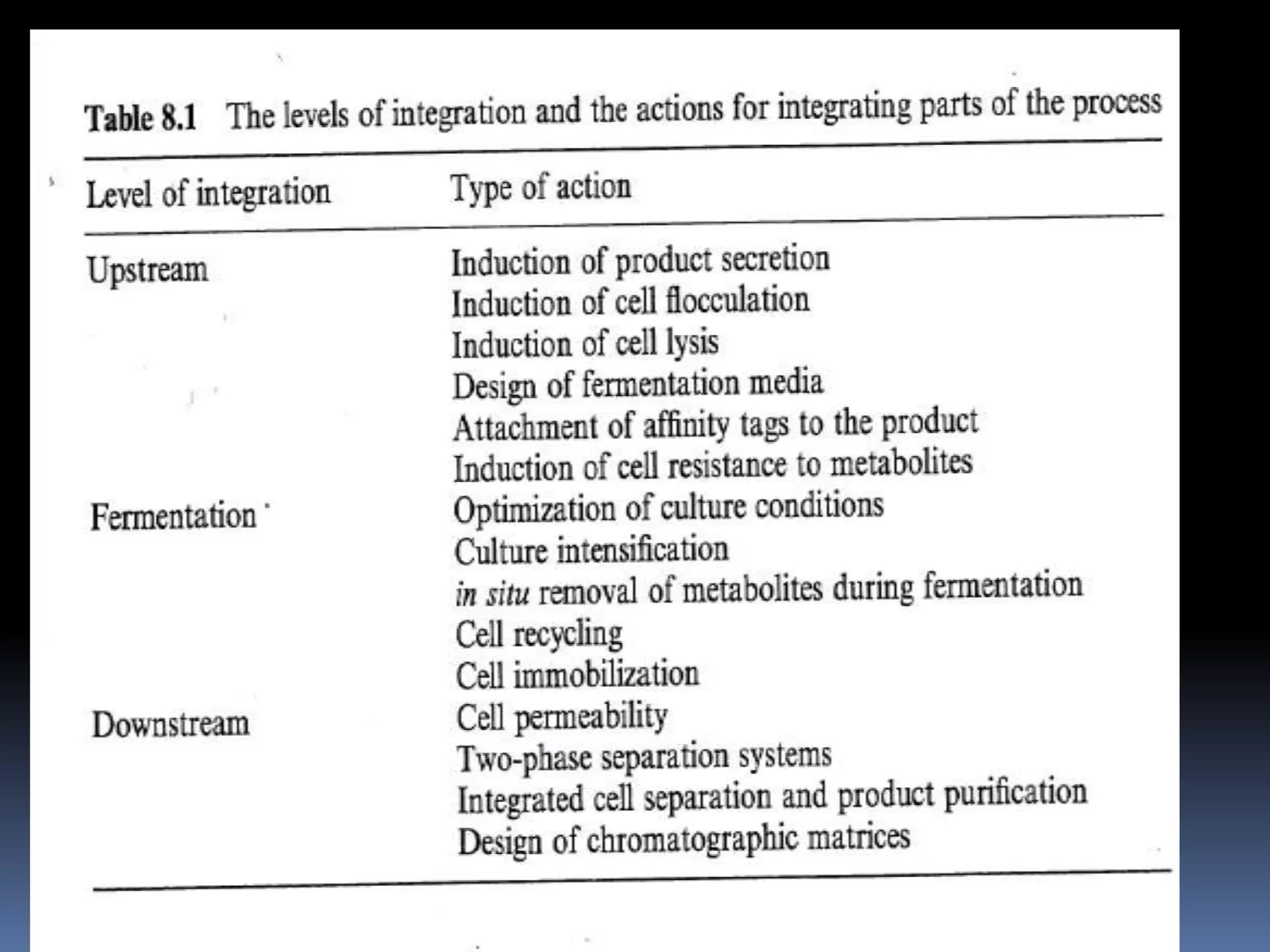
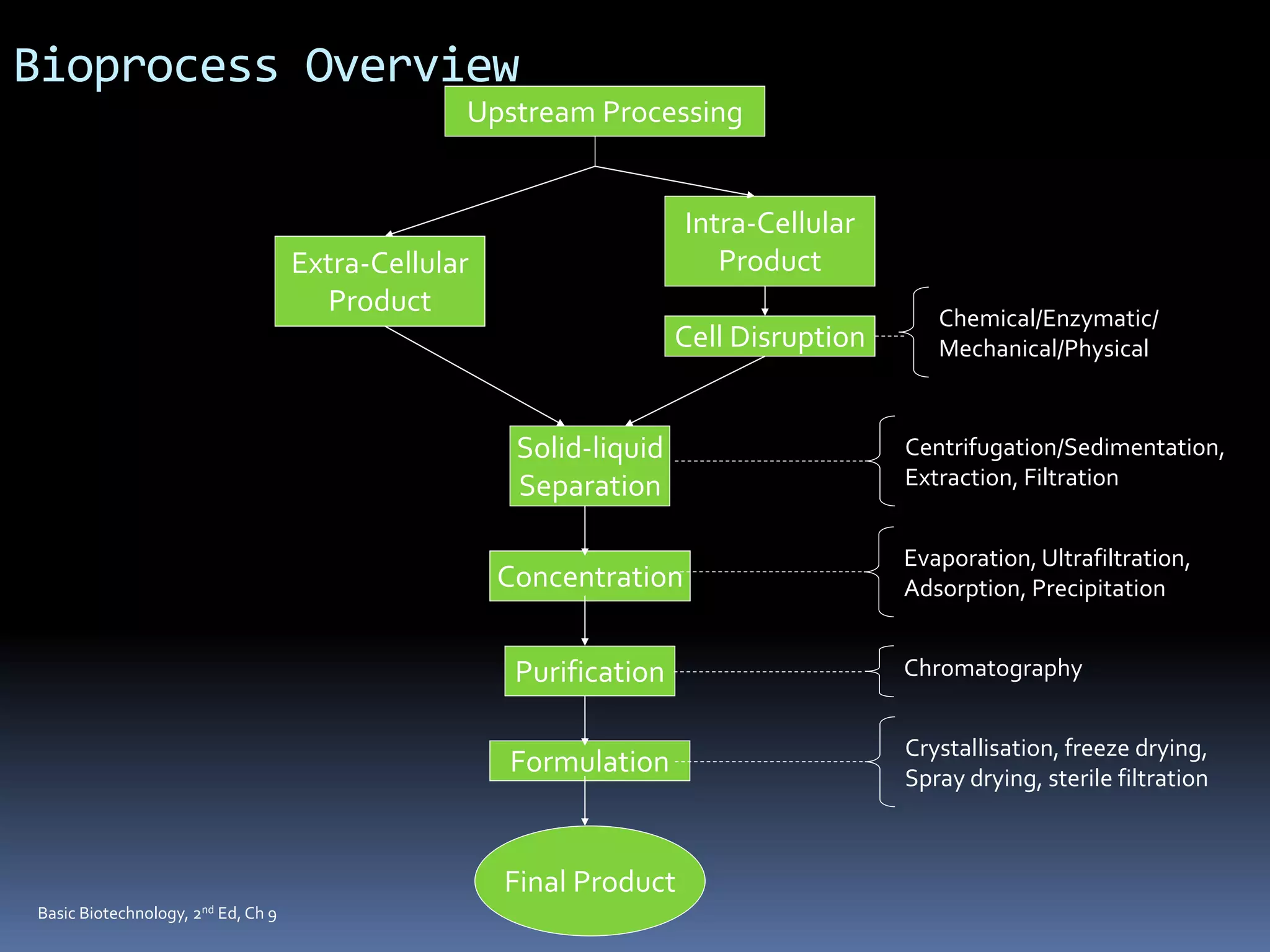
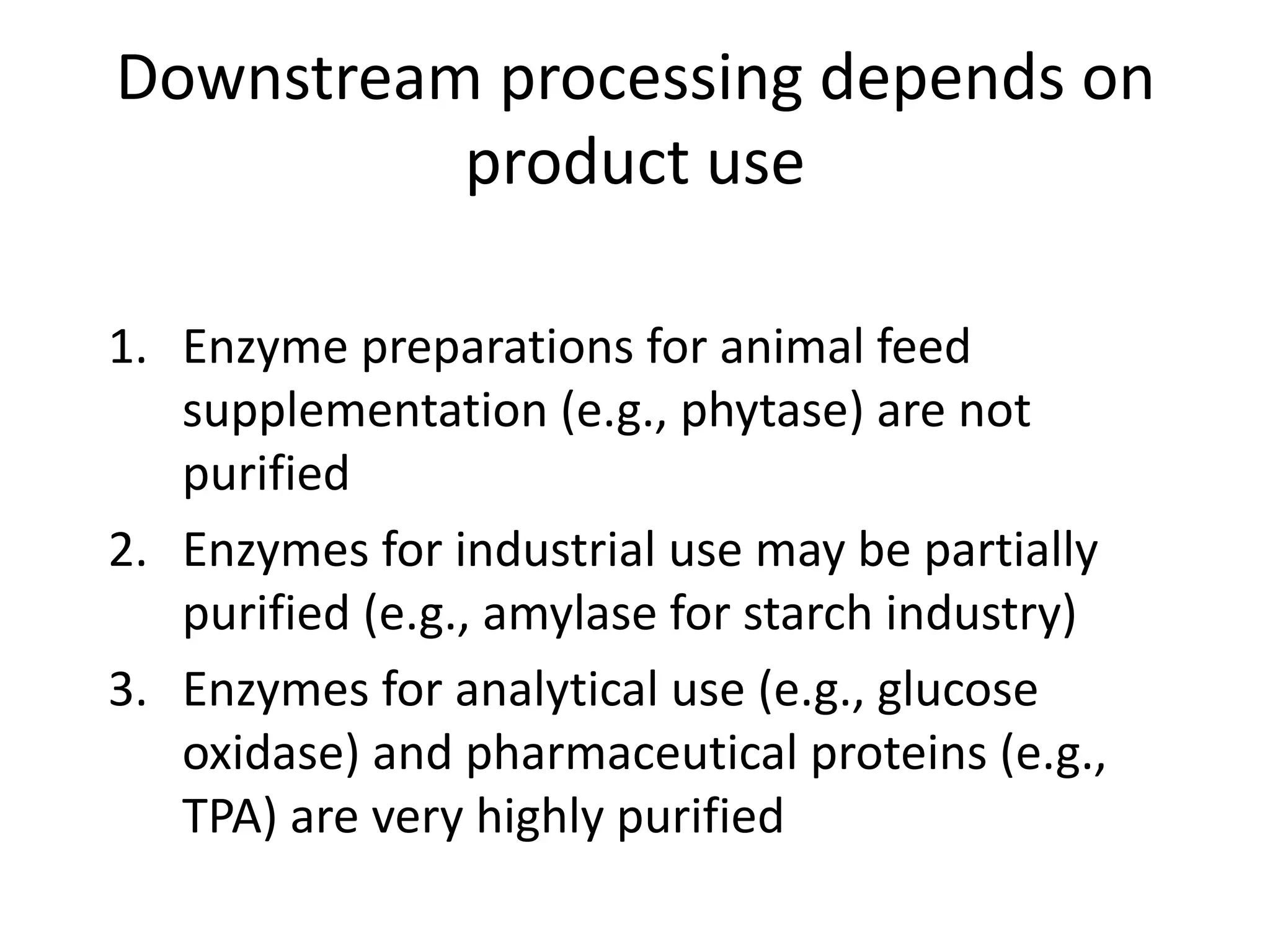
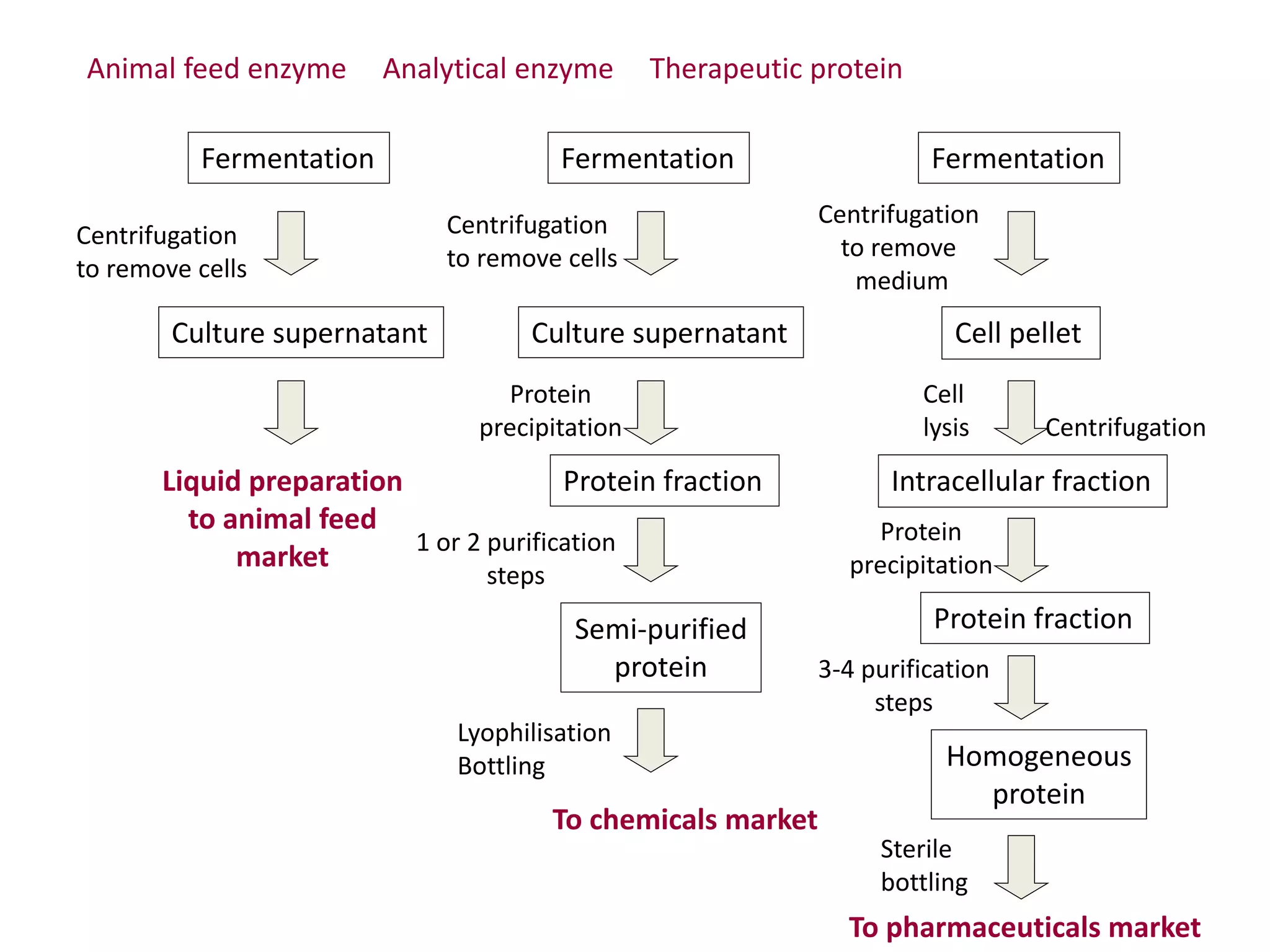
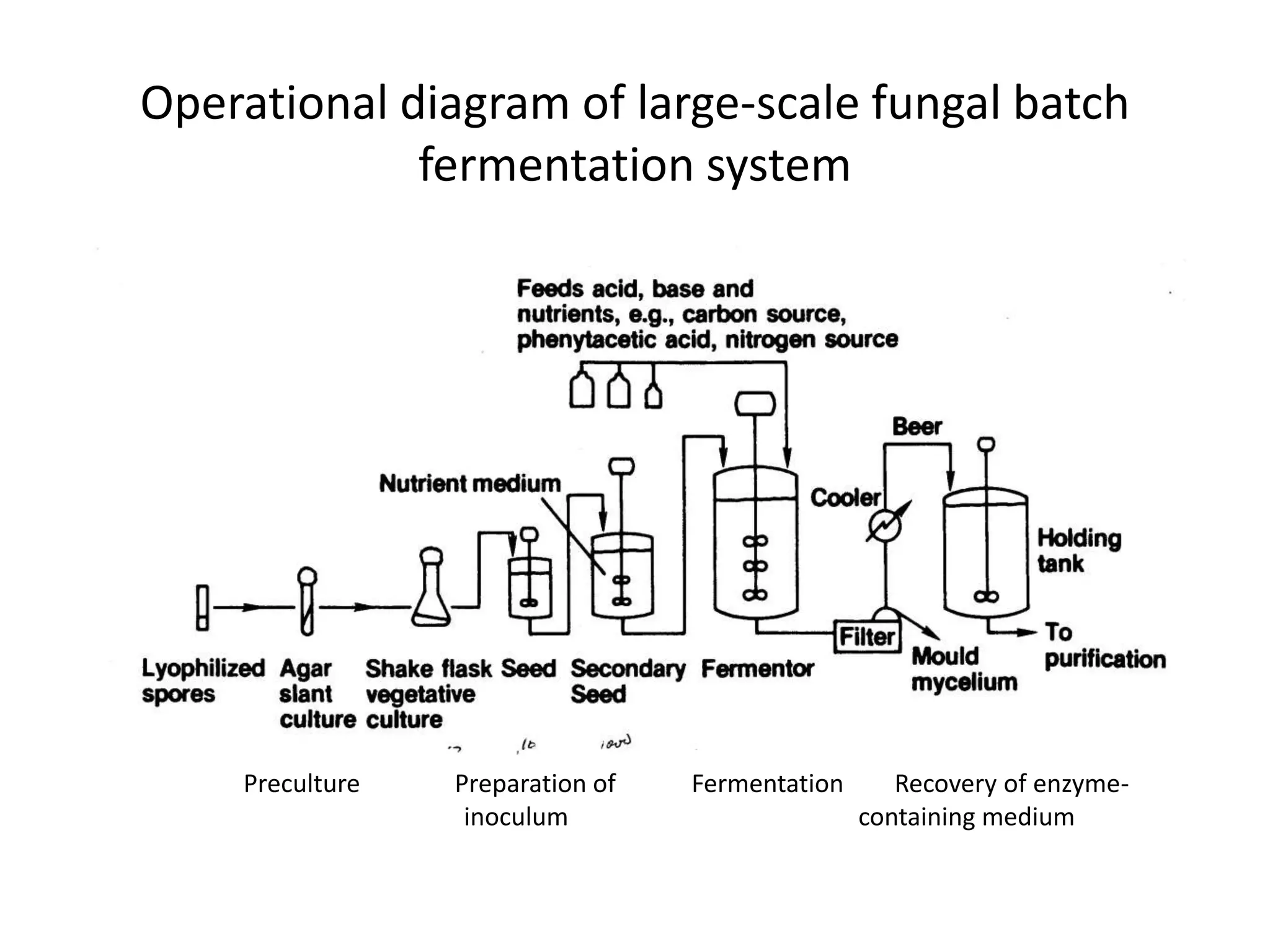
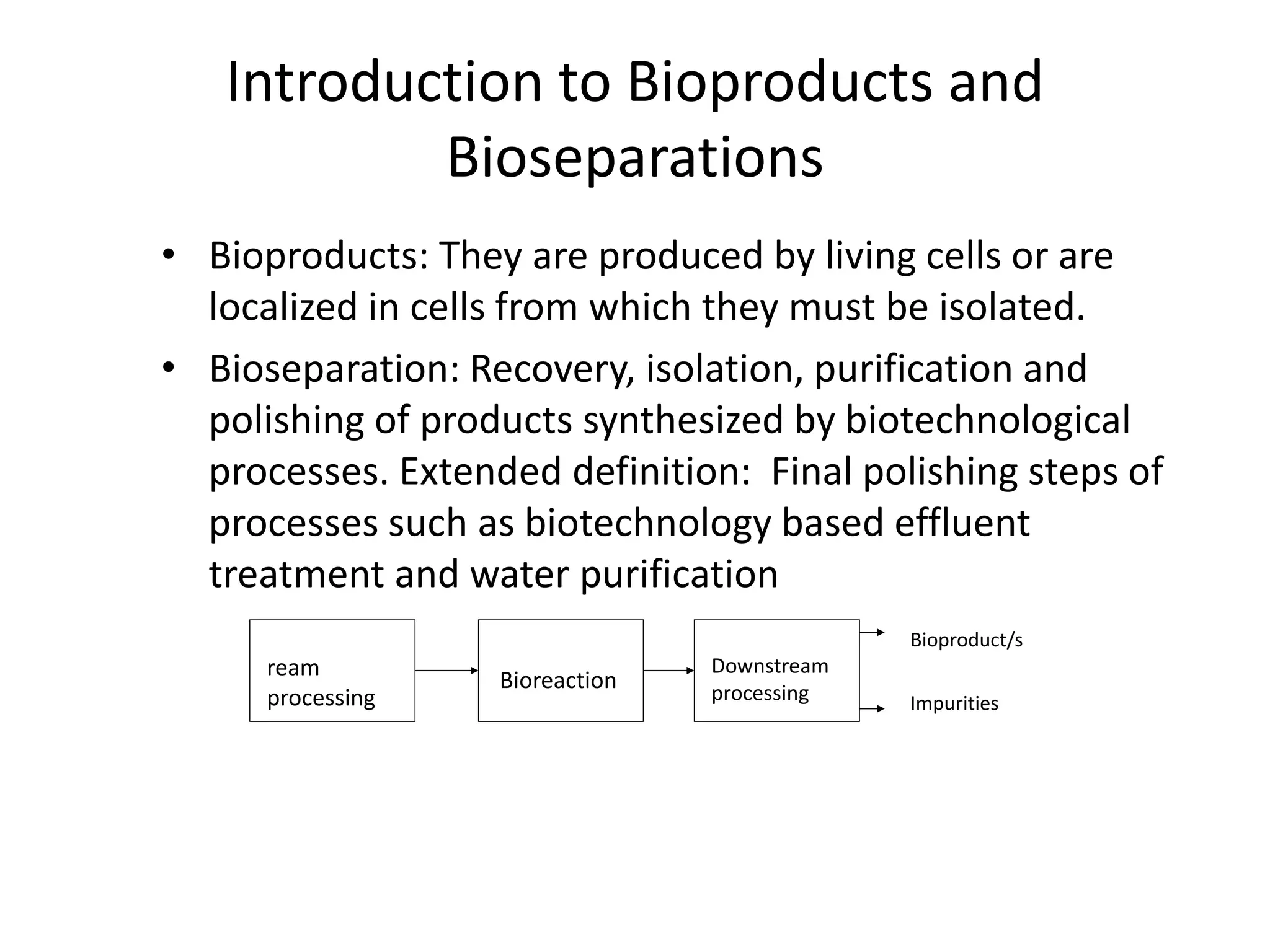
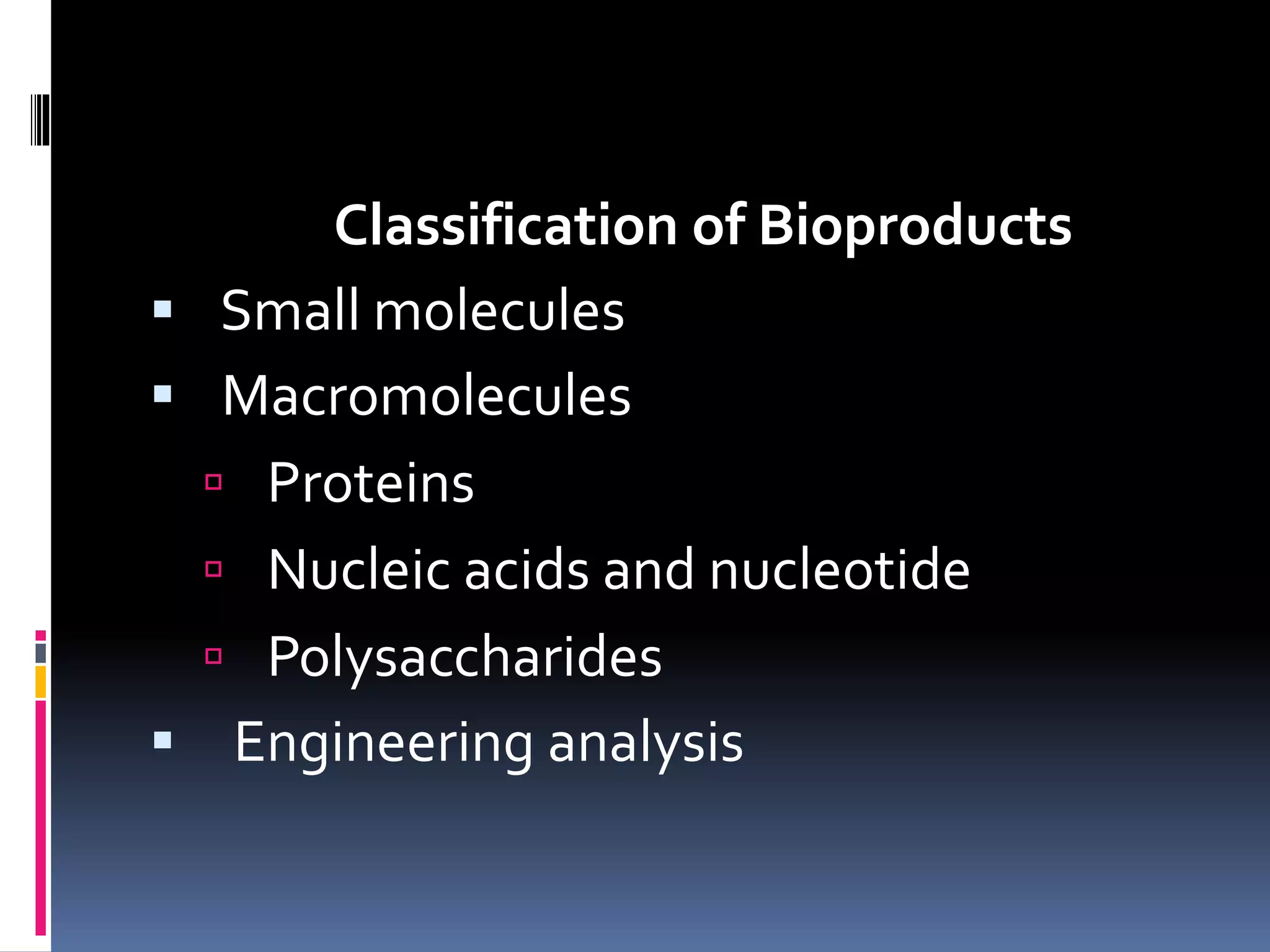
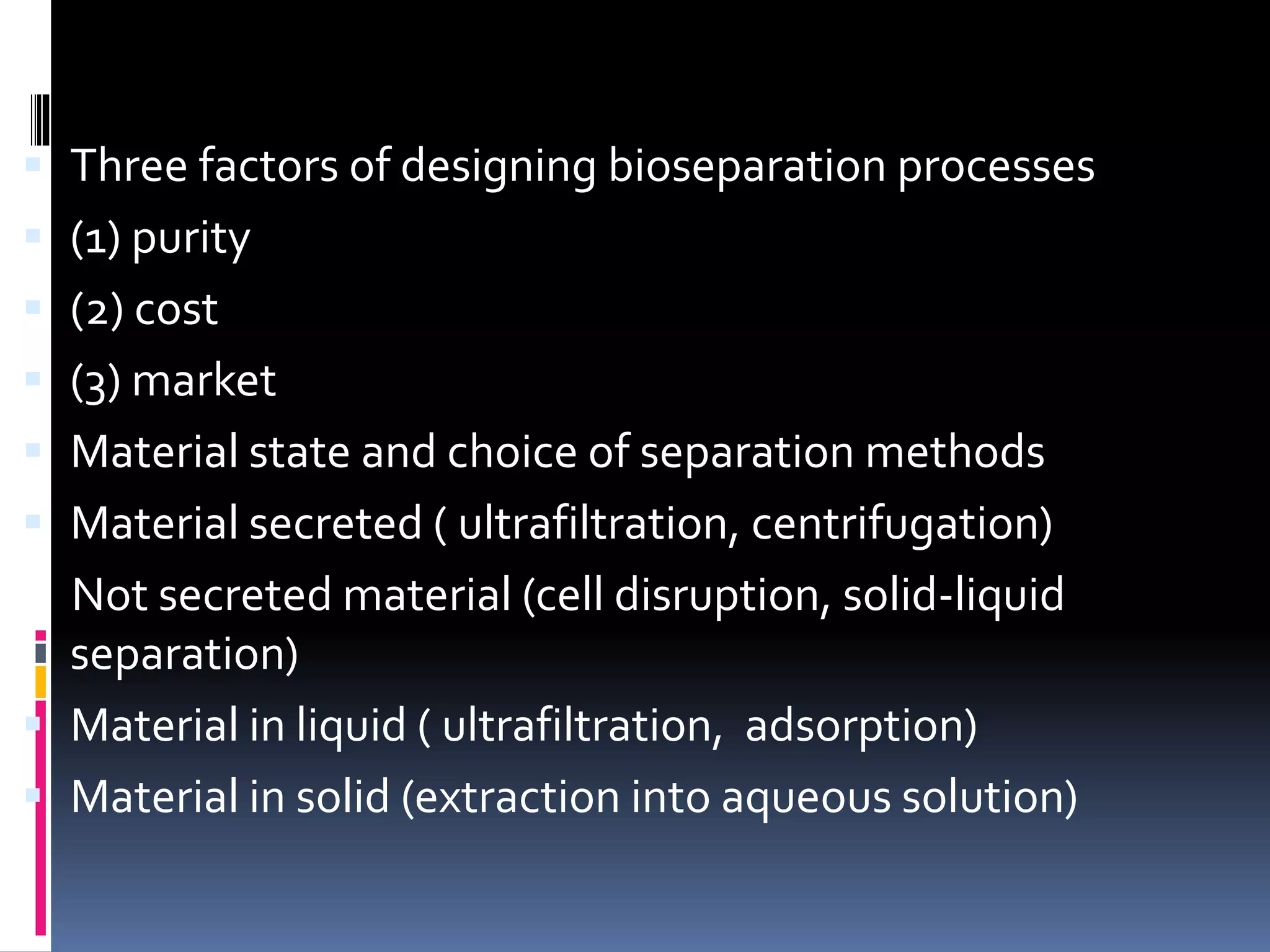
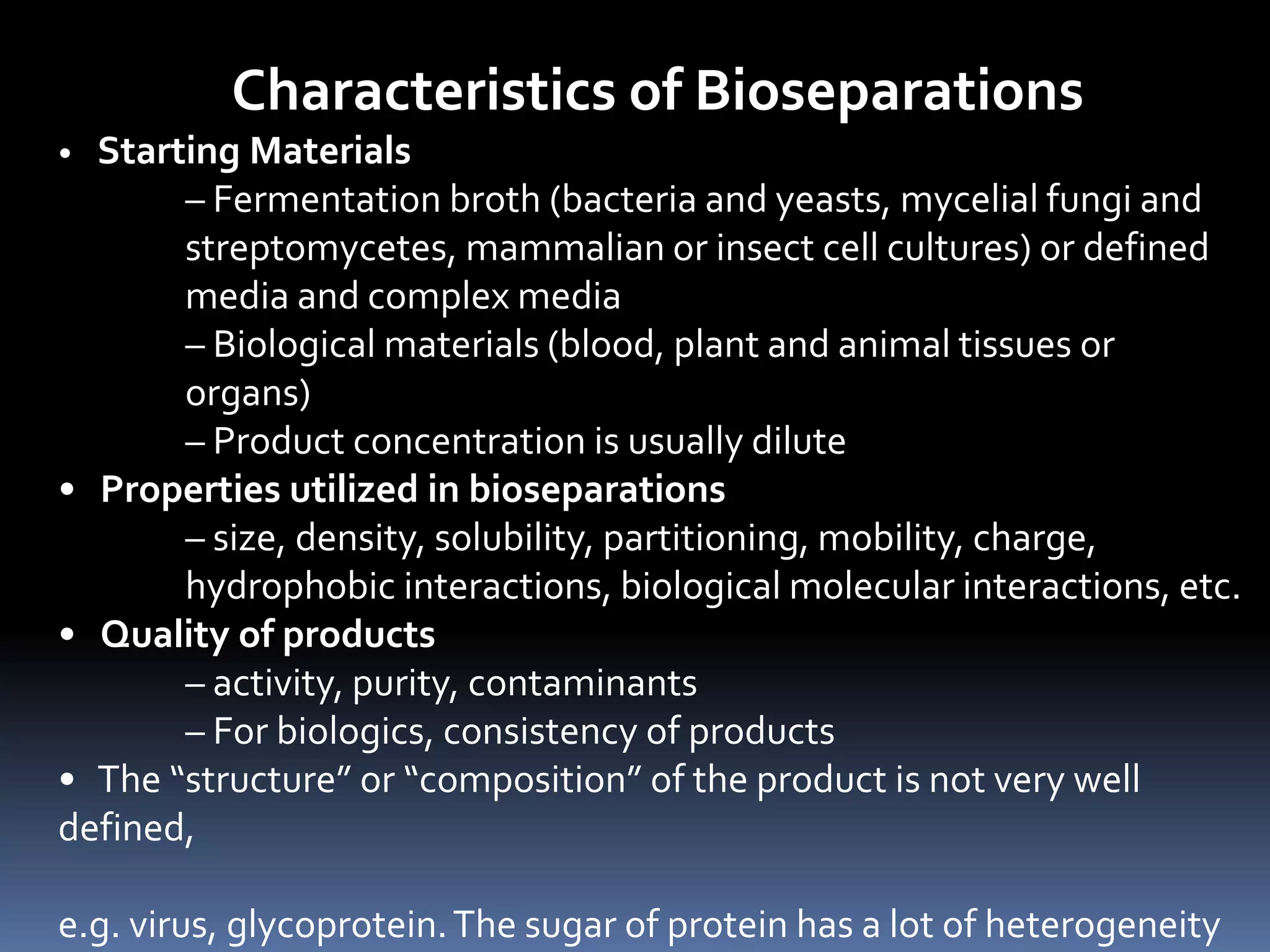
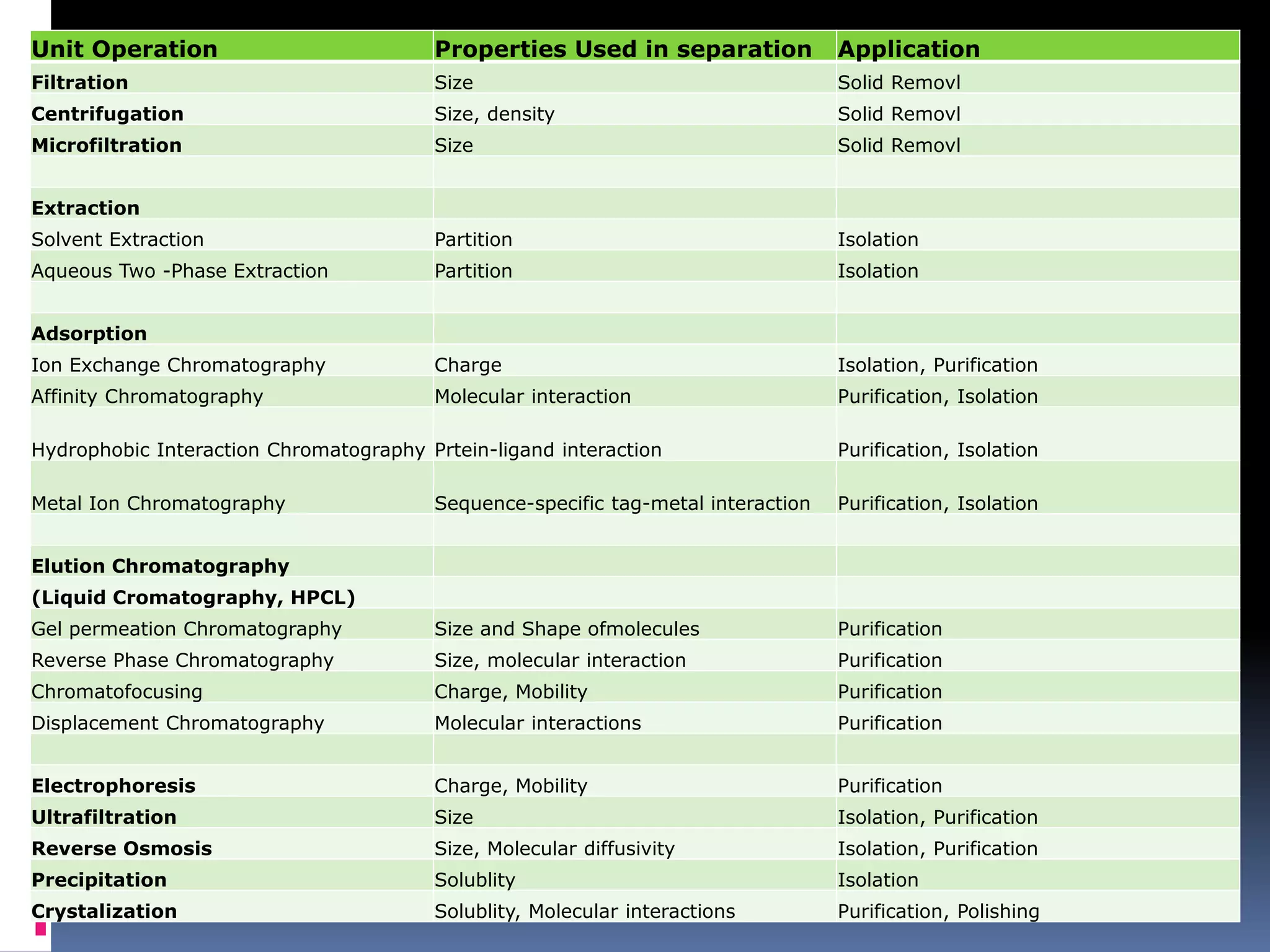
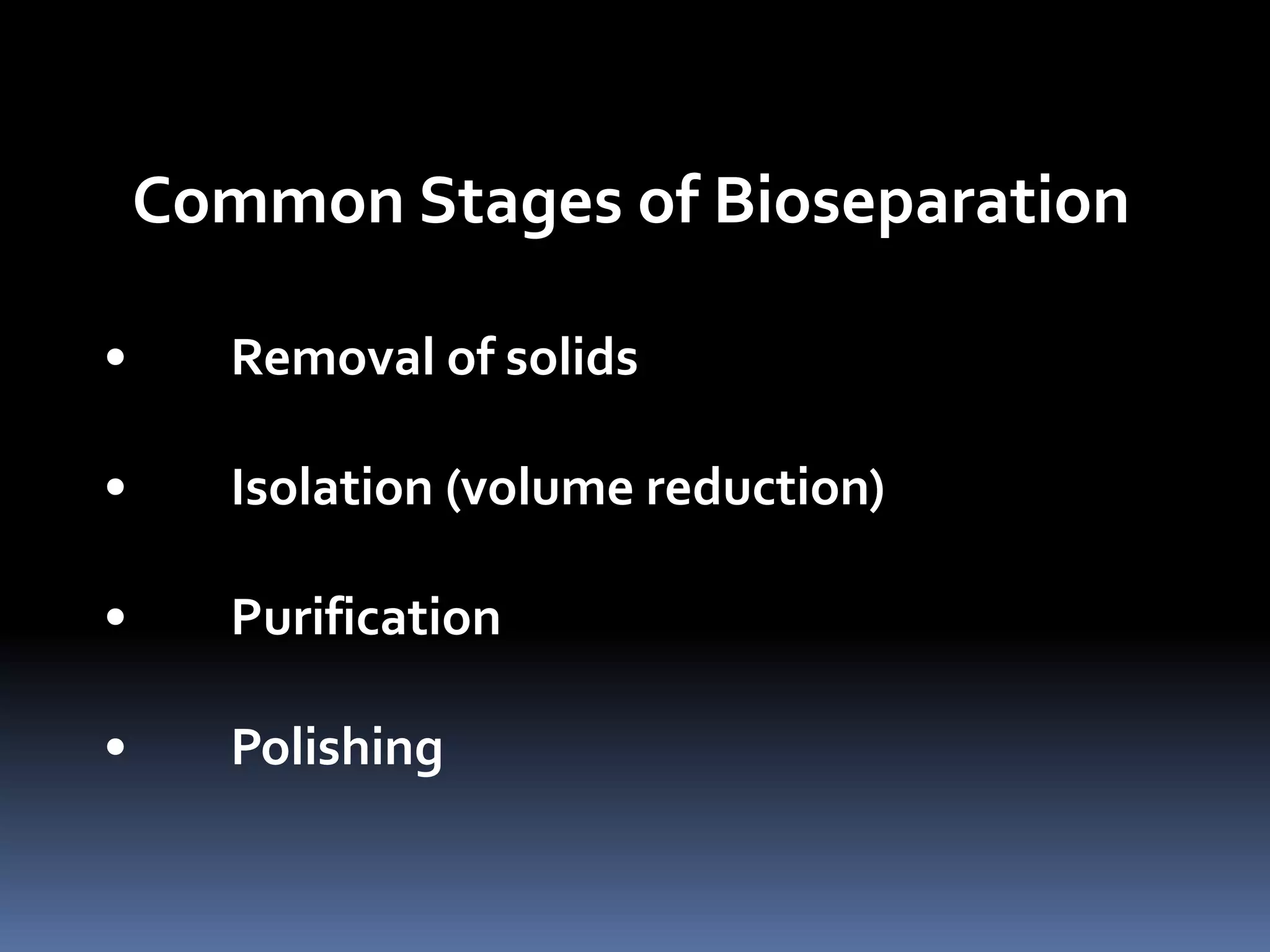
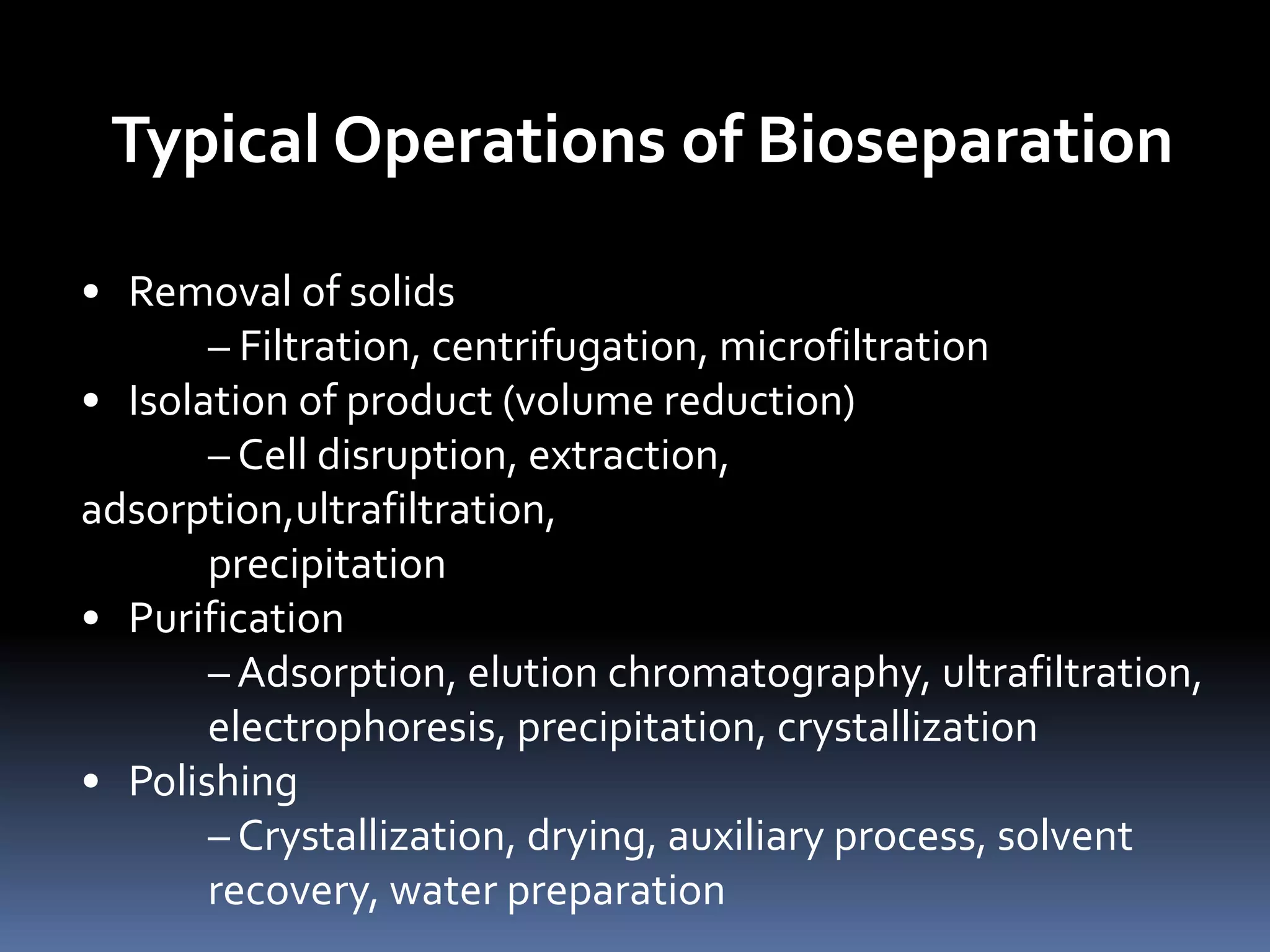
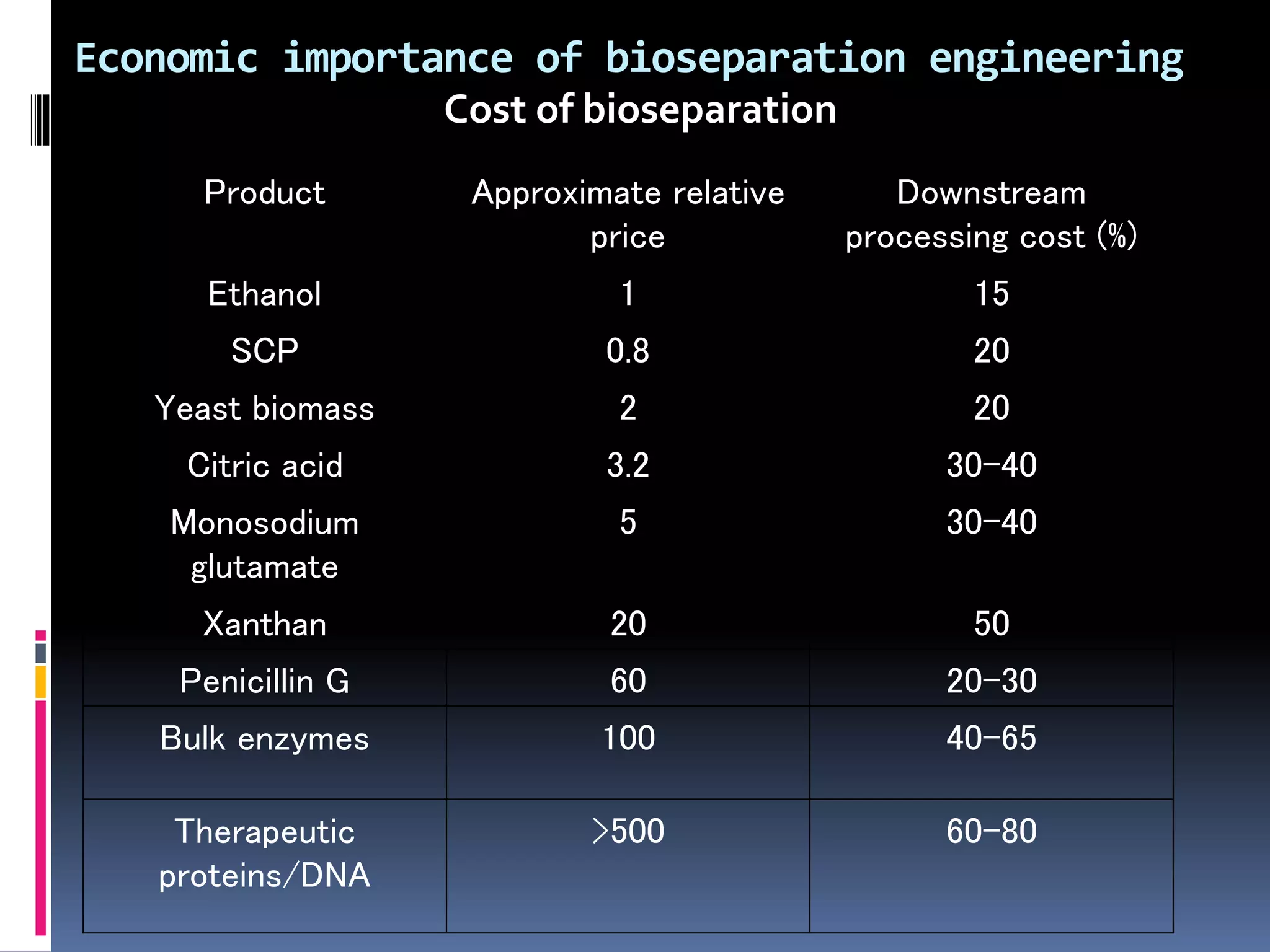
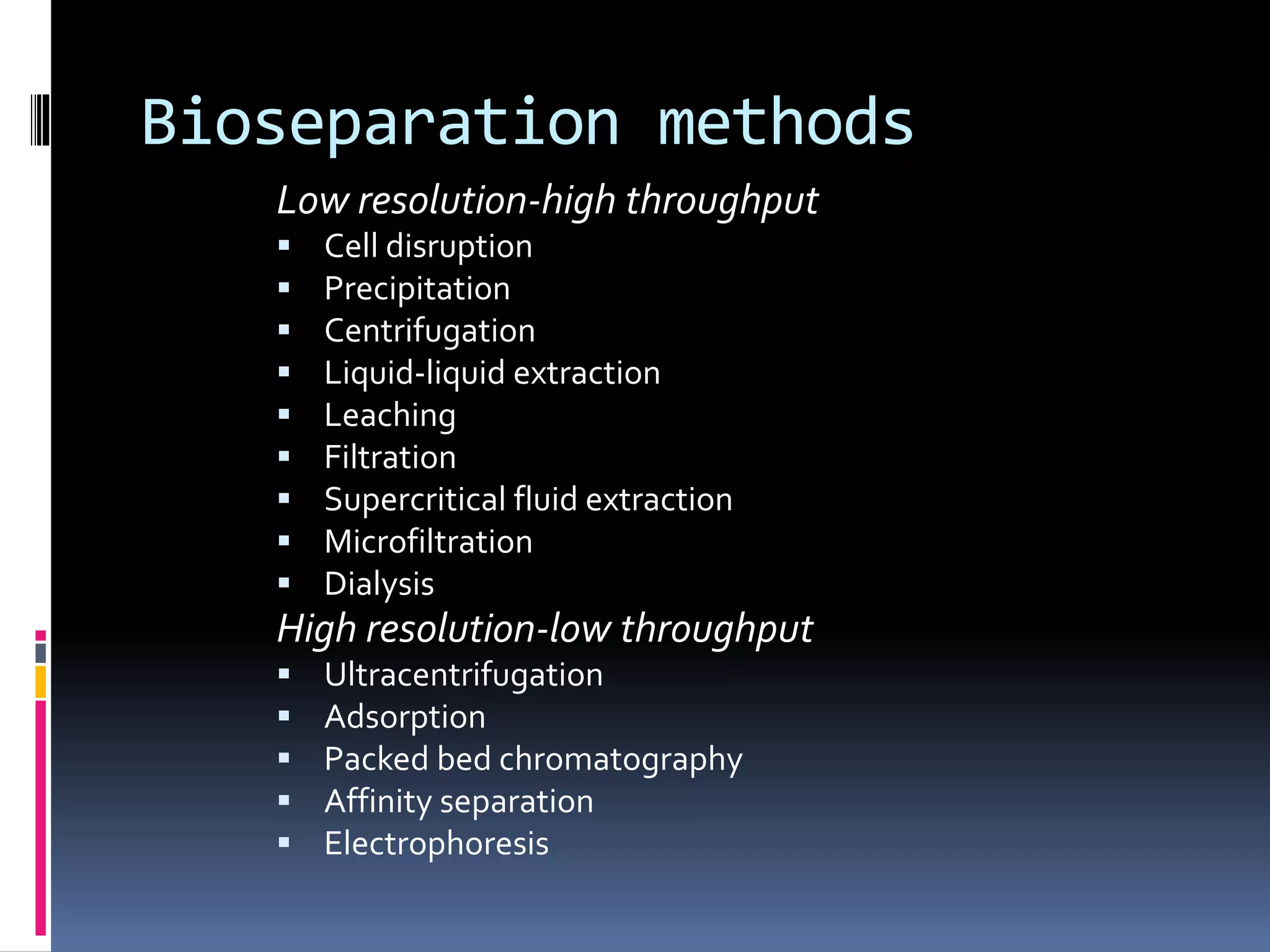
This document discusses downstream processing in biotechnology. It defines downstream processing as the steps occurring after fermentation to recover and purify products. The key unit operations in downstream processing include cell removal, concentration, and purification techniques like chromatography. The level of purification required depends on the intended use and market for the product. Common downstream processing techniques are outlined along with considerations for designing efficient bioseparation processes.