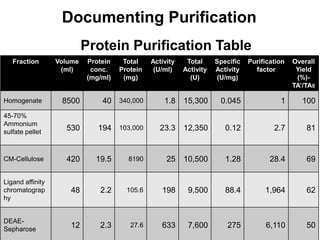
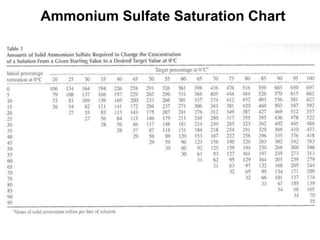
Native and recombinant sources can be used to produce enzymes. Preparation of crude extracts involves homogenizing or lysing the source cells or tissues and preventing proteolysis. Various techniques can then be used to separate and purify proteins based on exploiting differences in their solubility, charge, size, or ability to bind specifically. Key steps include precipitation with ammonium sulfate or organic solvents, ion exchange chromatography, size exclusion chromatography, and affinity chromatography. Fractional precipitation provides a simple initial concentration and enrichment of proteins.