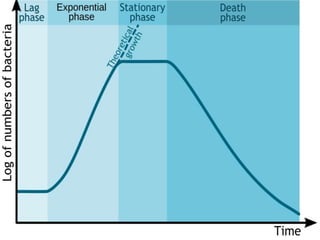
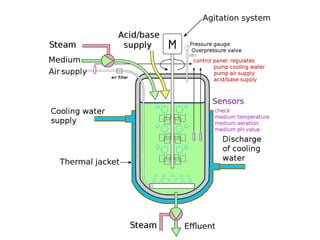
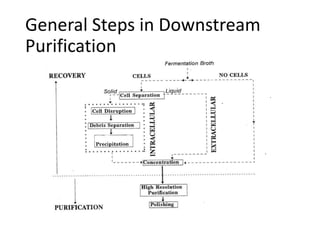
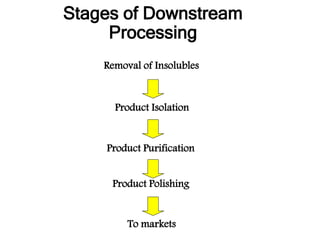
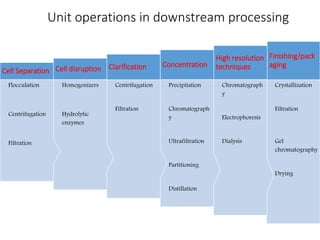
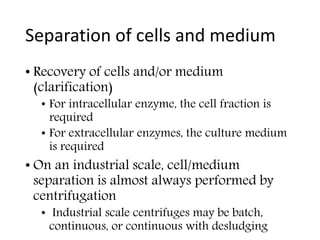
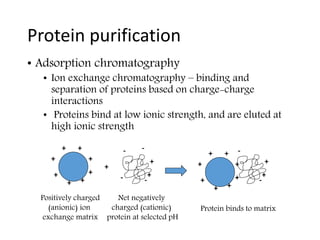
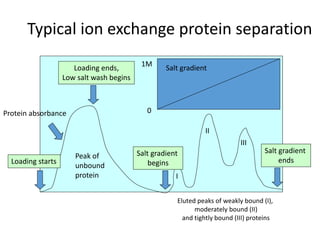
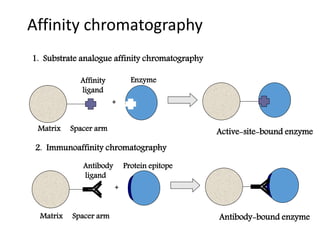
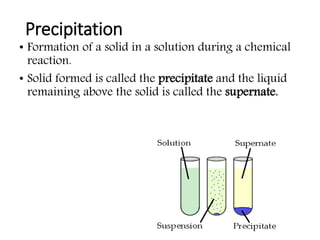
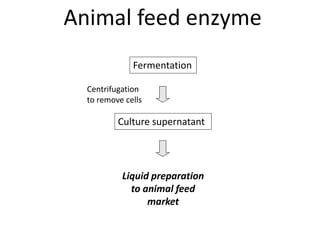
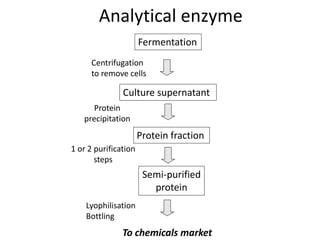
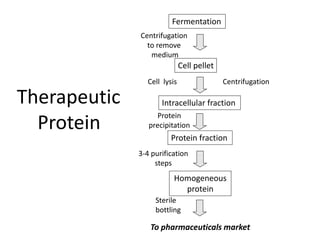
This document provides an overview of fermentation technology and downstream processing. It defines fermentation as the production of a product by microorganism mass culture. It describes the basic stages of batch fermentation including lag, log, stationary and death phases. It then outlines the main steps in downstream processing including removal of insolubles, product isolation, purification, polishing and packaging. Specific unit operations used at each stage like centrifugation, filtration, chromatography are also explained. The document emphasizes that the level of downstream processing depends on the target product and its end use.