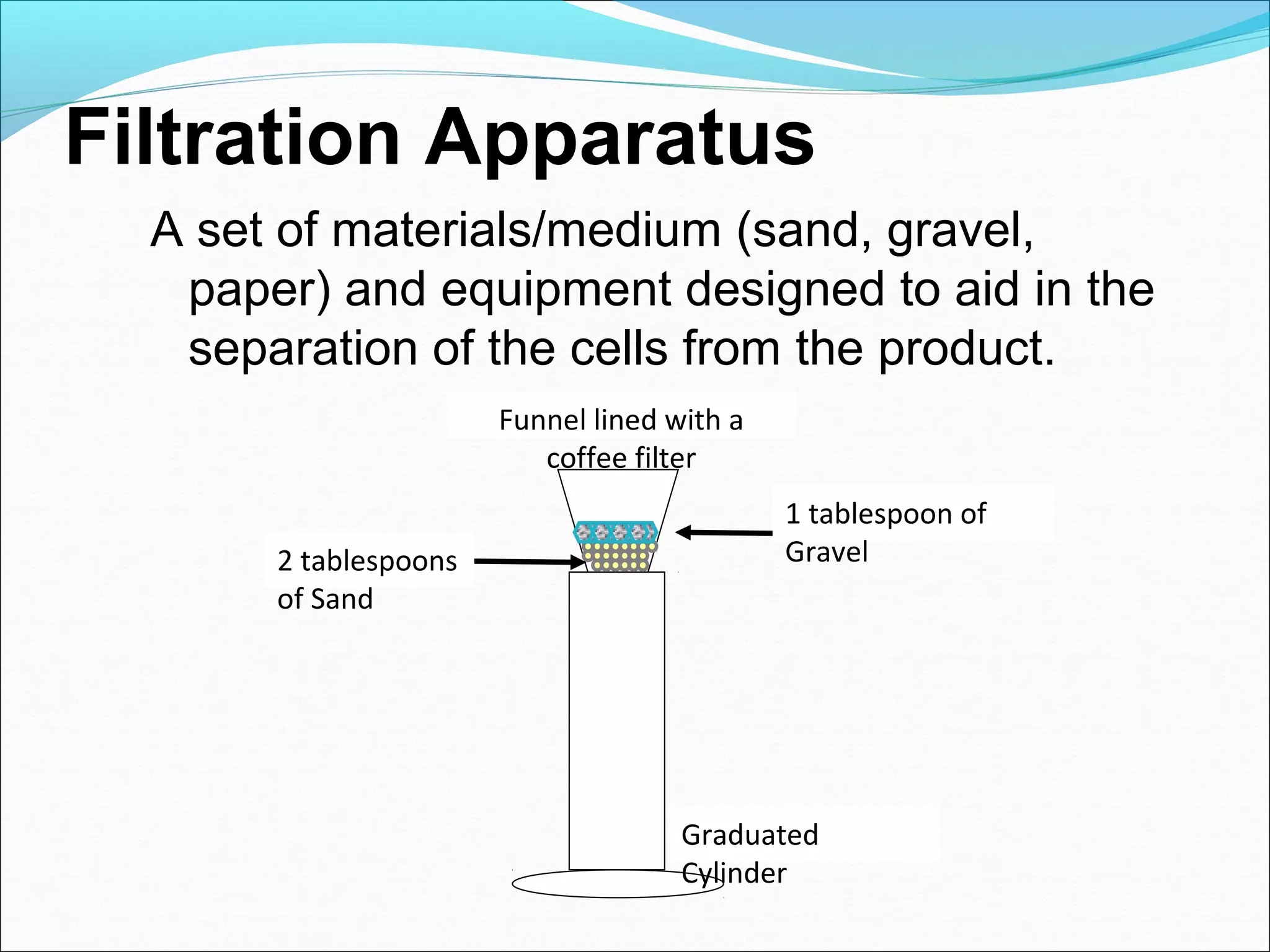
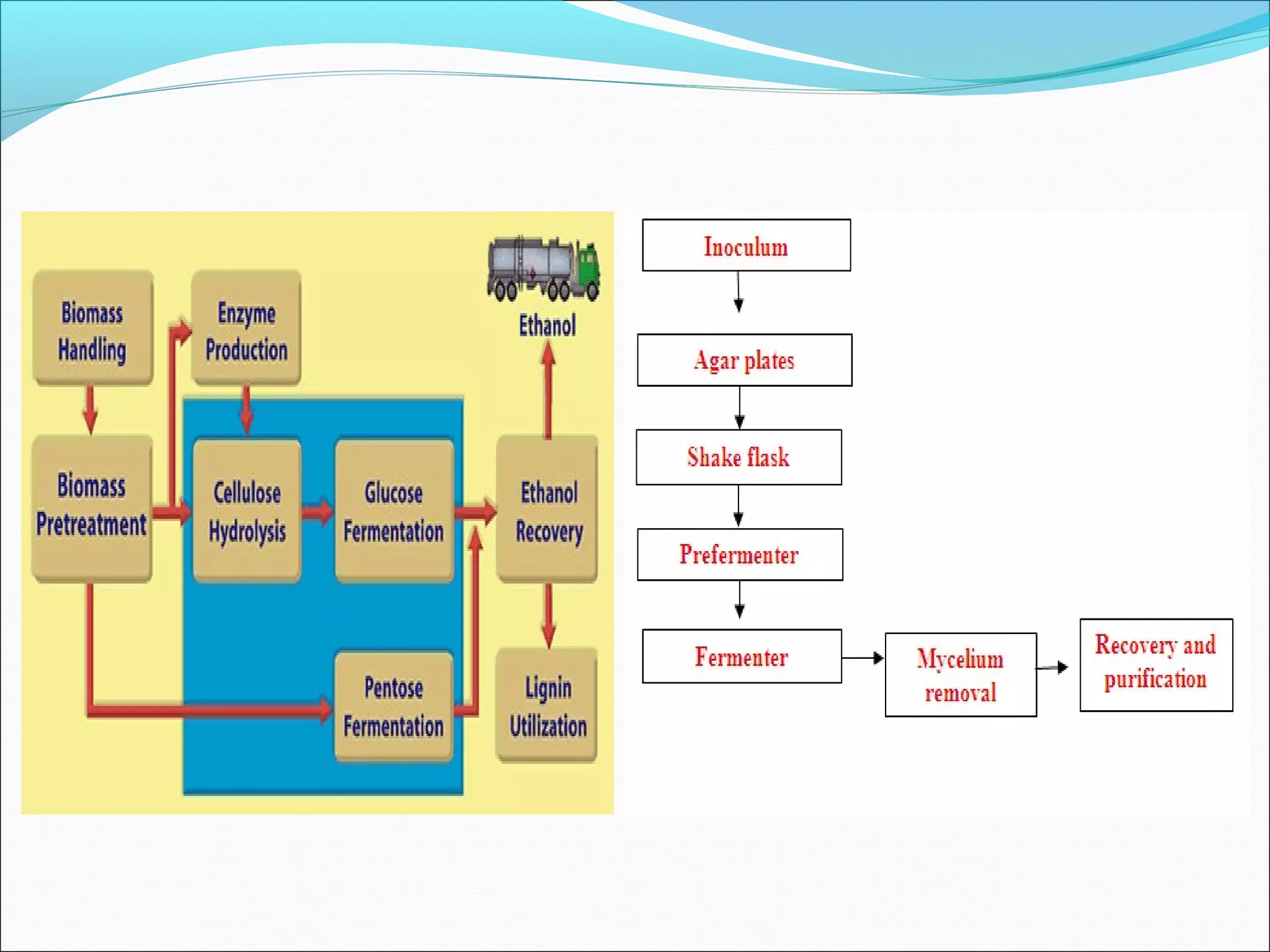
The document discusses the key stages in downstream processing as part of bio manufacturing or biosynthesis of products. It describes how downstream processing involves removing cells and impurities from fermentation broth to produce the final product. The main stages discussed are removal of insolubles, product isolation, product purification, and product polishing. Key operations at each stage include filtration, centrifugation, precipitation, crystallization, and lyophilization.