The document summarizes the urea cycle and protein catabolism. It discusses:
1) Proteins are constantly degraded and resynthesized to remove damaged, unneeded, defective, or old proteins.
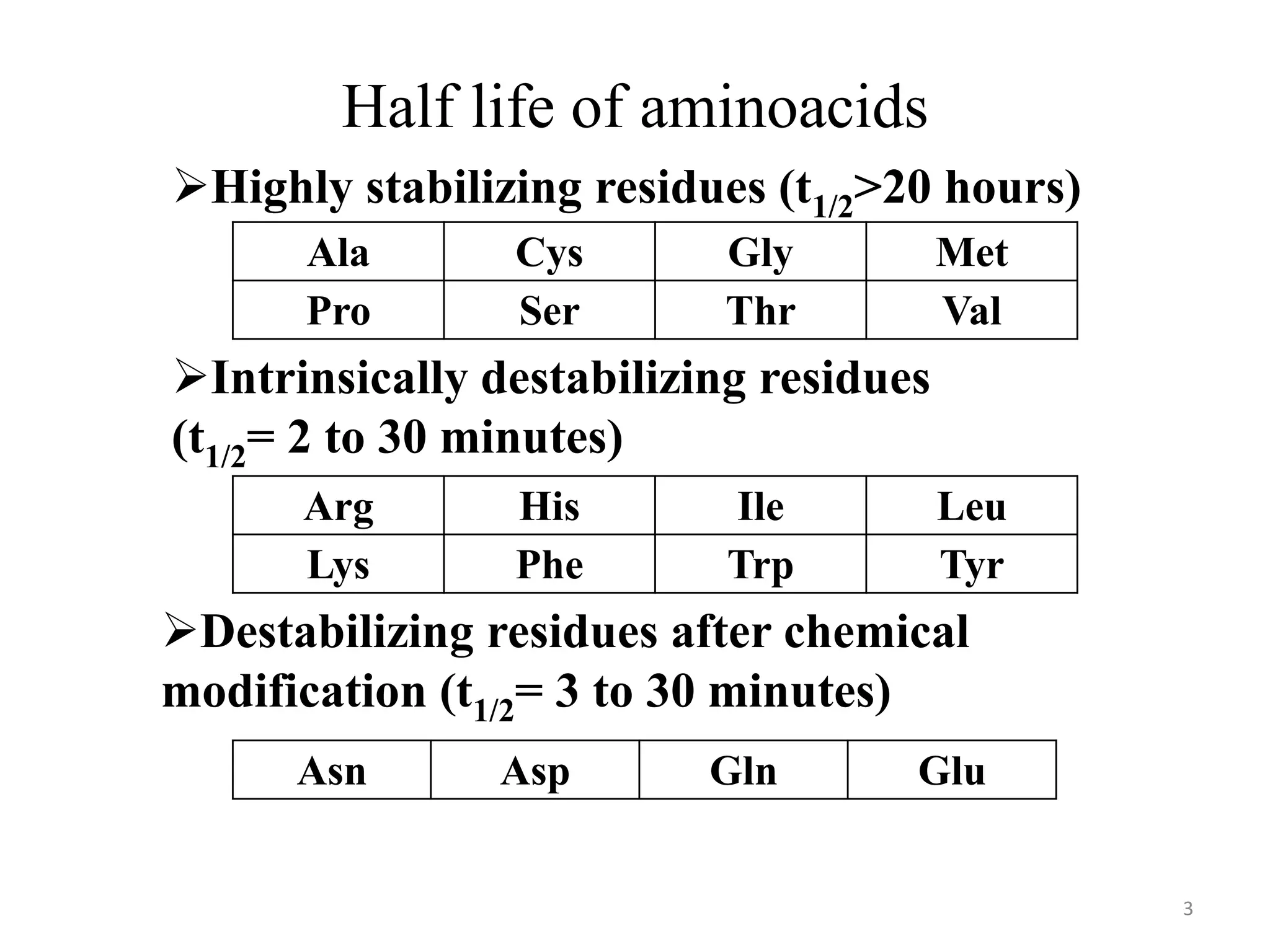
2) Amino acids have varying half-lives, and some residues are more stabilizing while others are destabilizing.
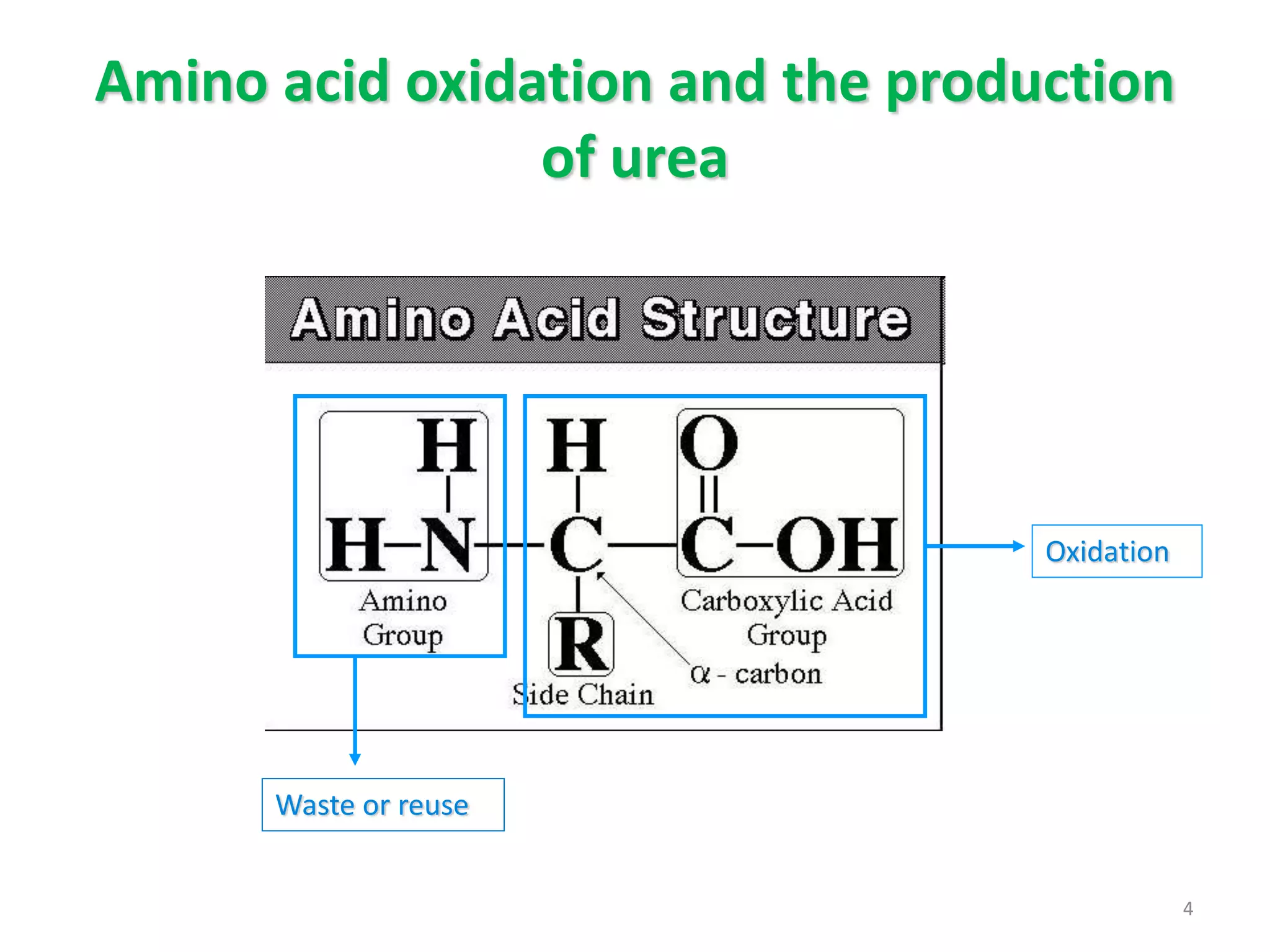
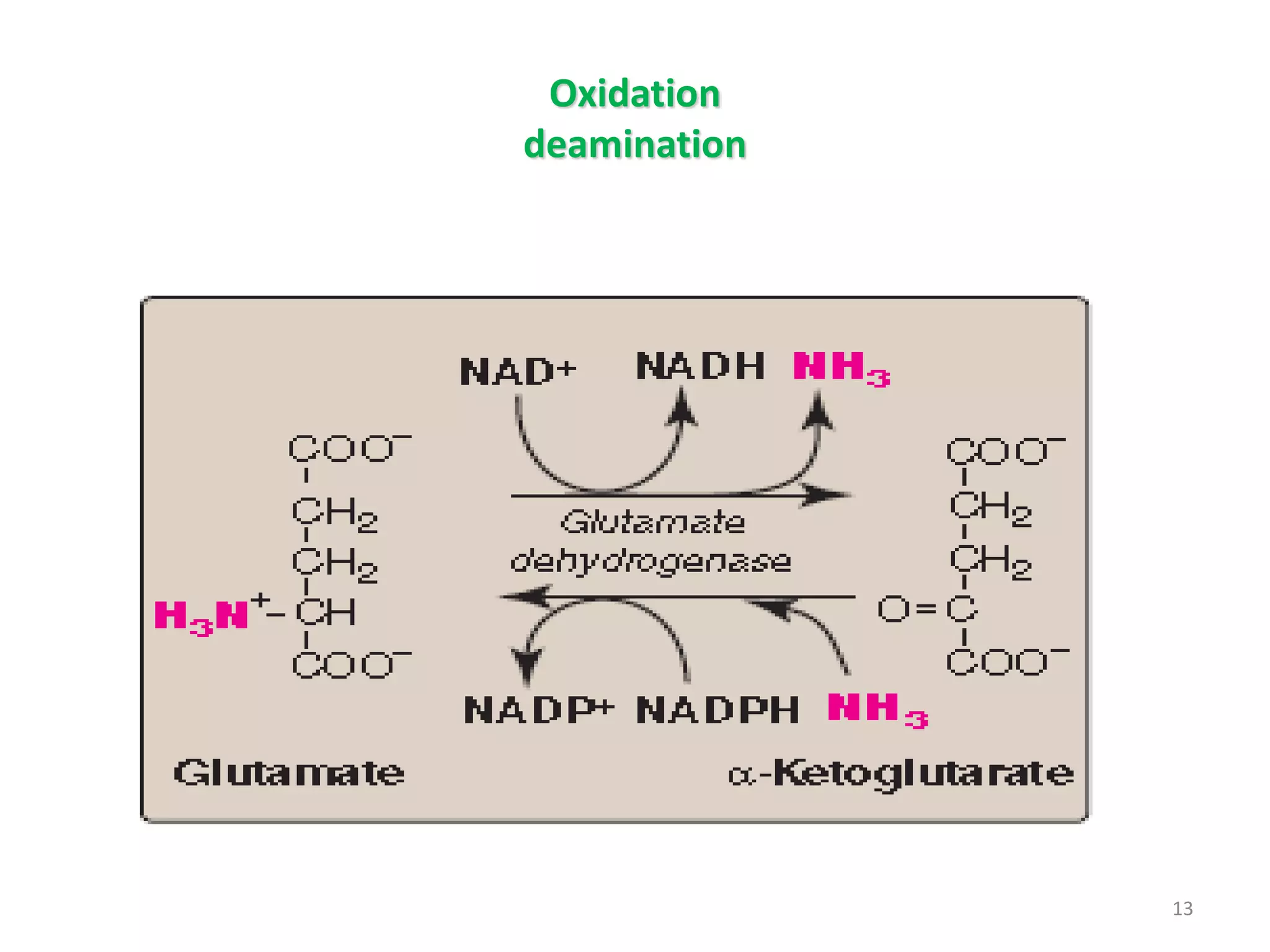
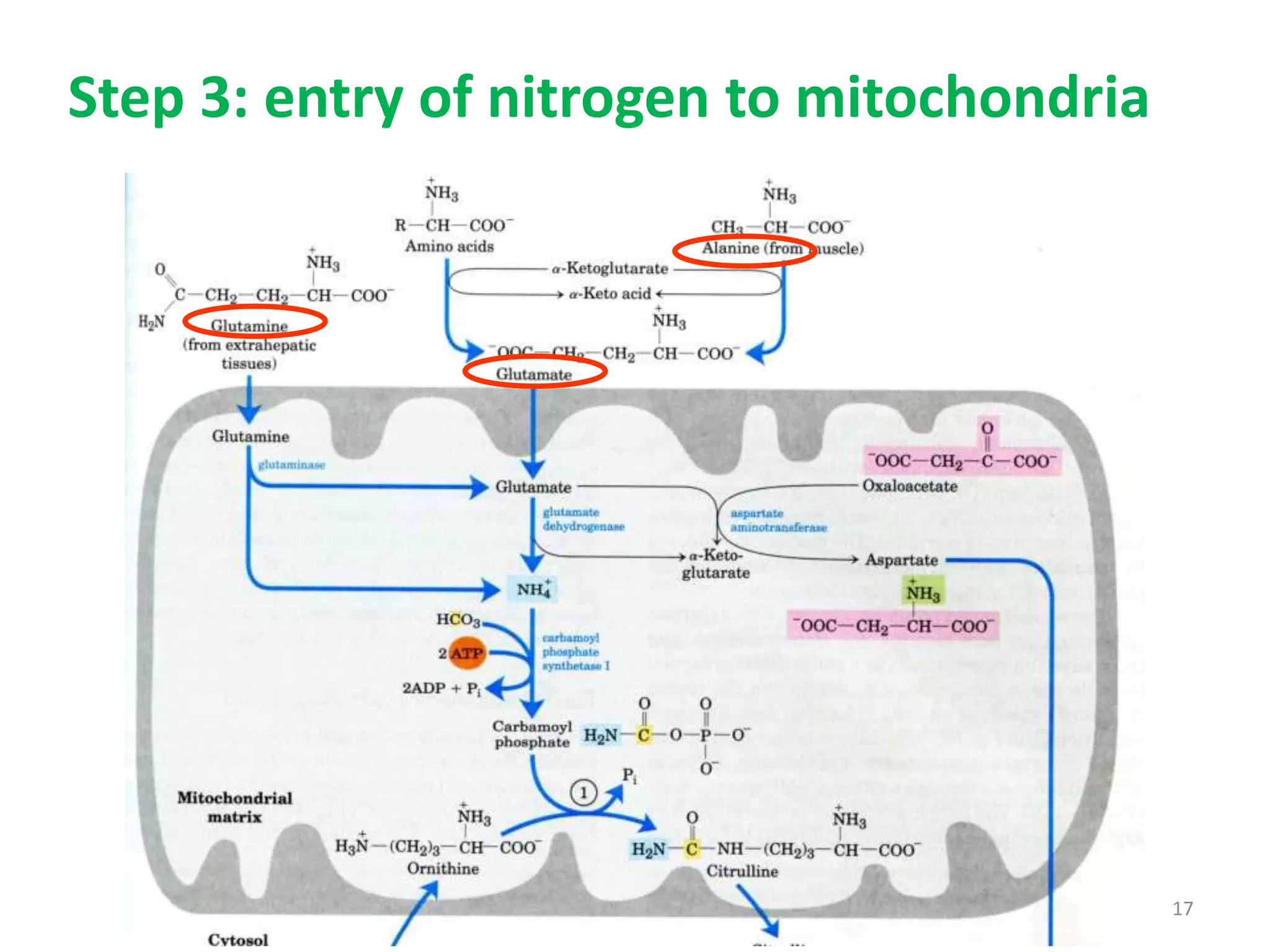
3) Amino acids are oxidized or reused. Ammonia produced from amino acid catabolism must be eliminated as it is toxic, especially to the central nervous system.
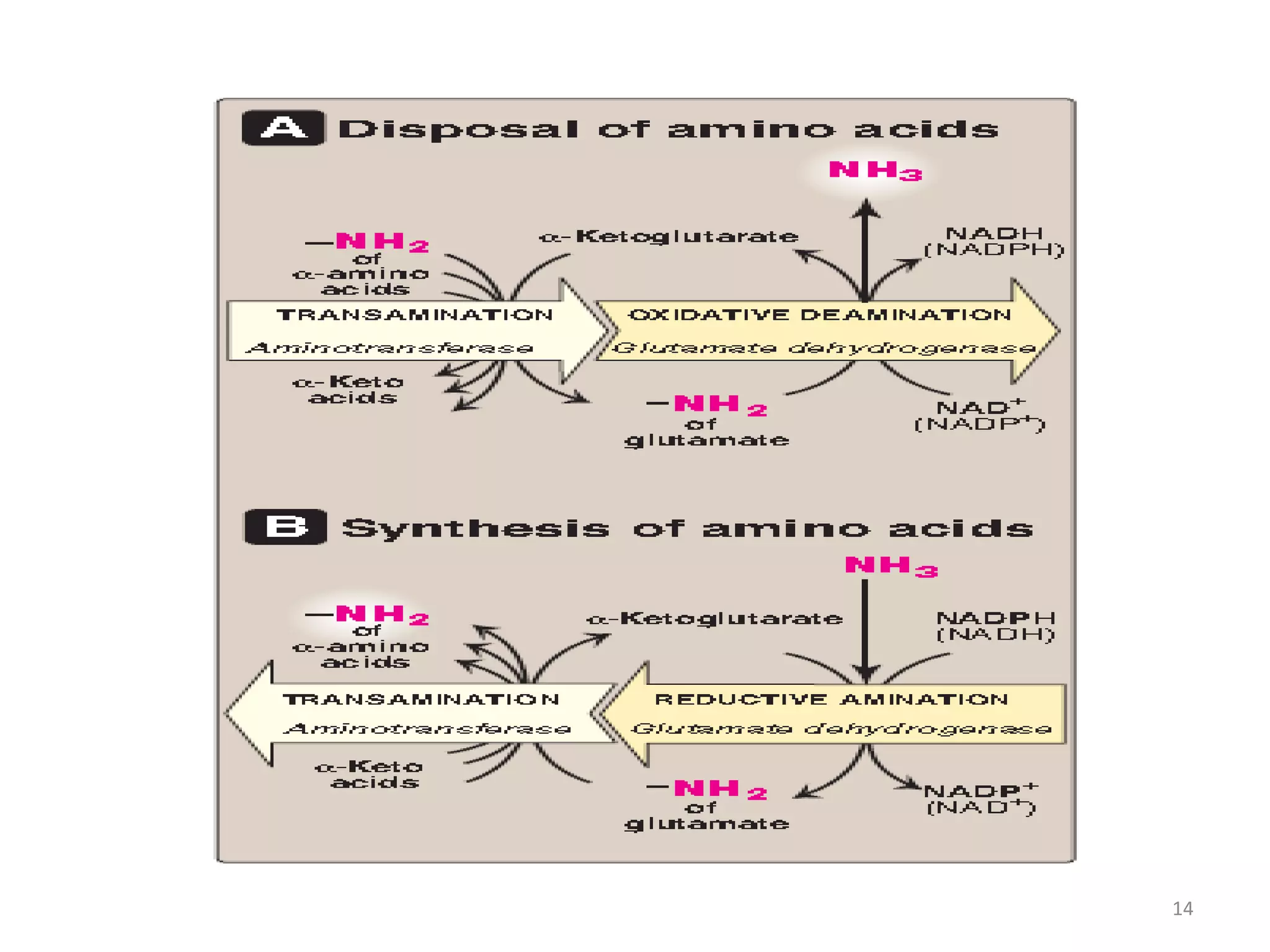
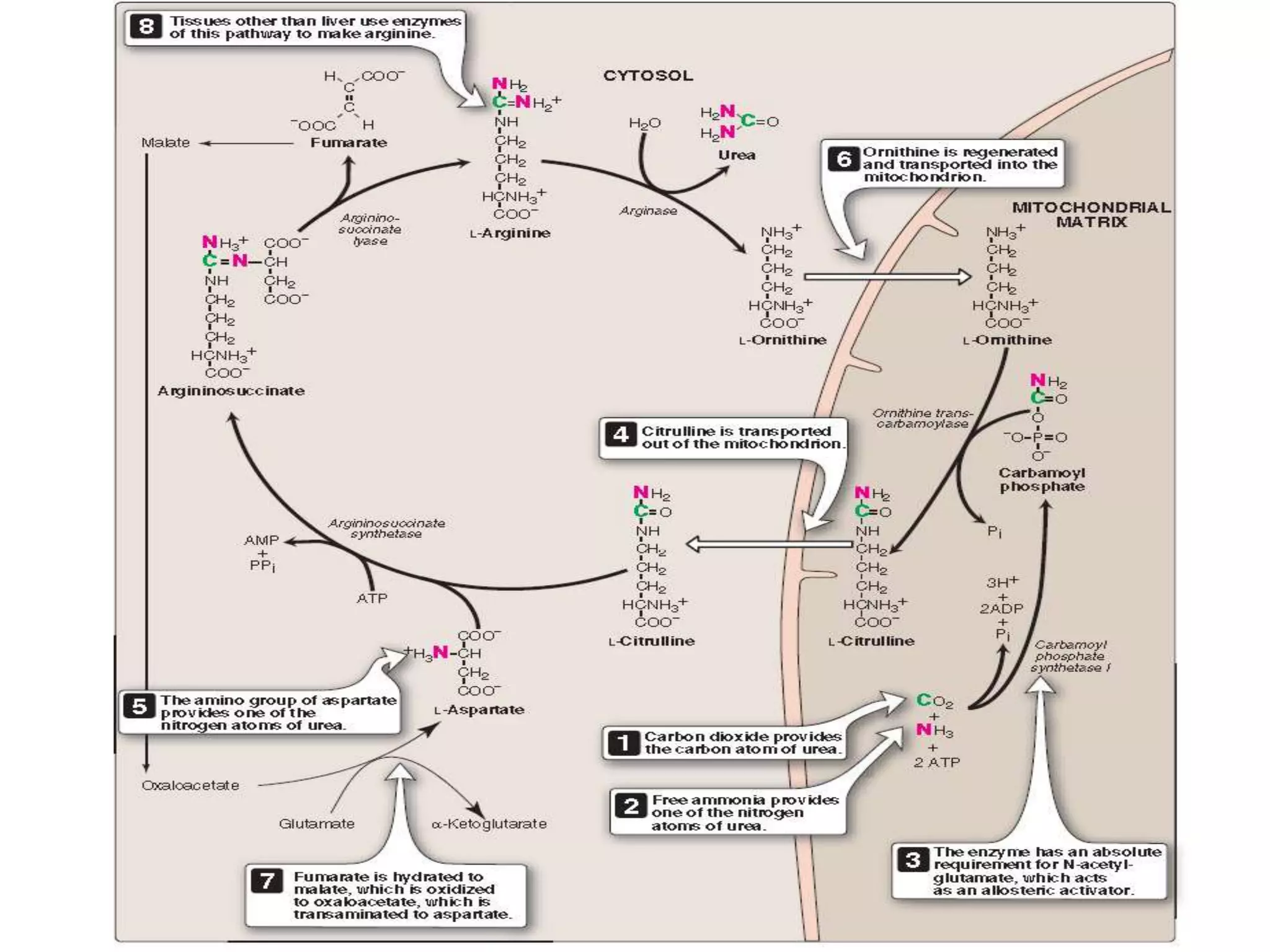
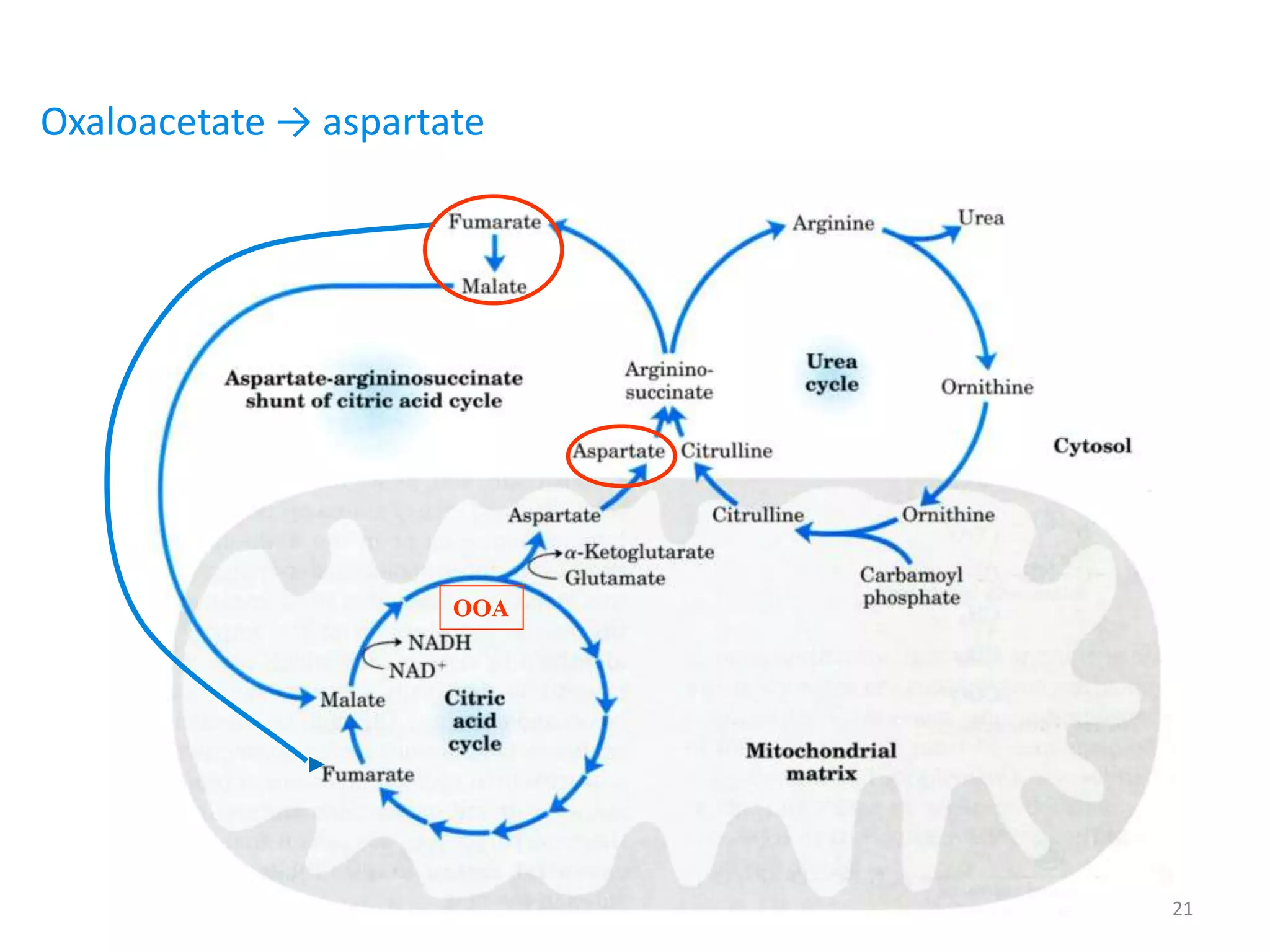
4) The urea cycle in the liver involves several steps to convert ammonia to less toxic urea for excretion, including transamination to shuttle amino groups to glutamate