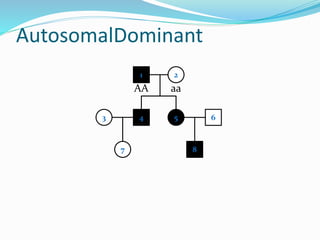
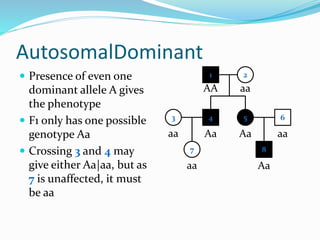
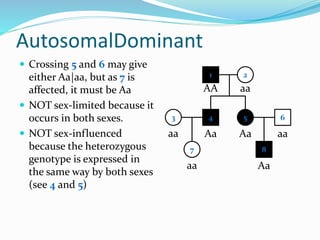
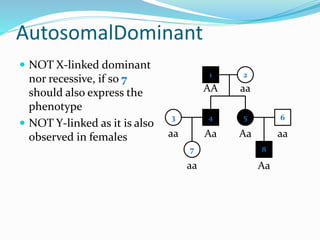
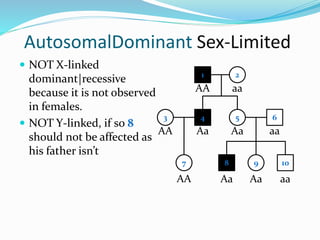
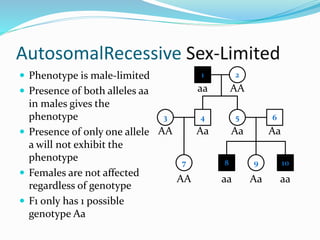
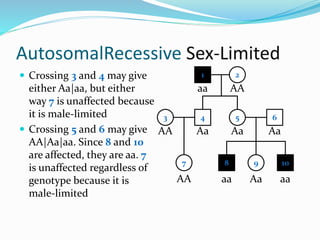
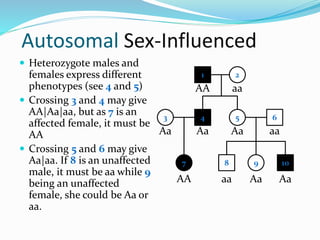
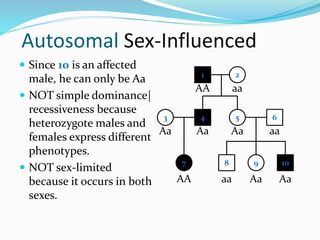
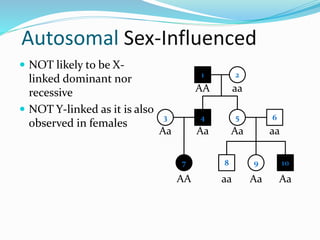
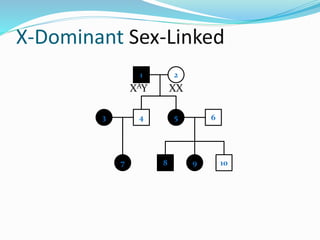
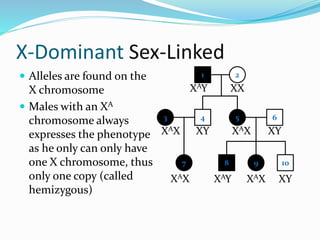
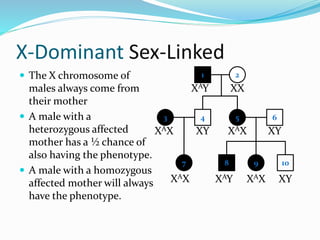
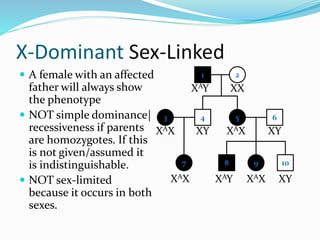
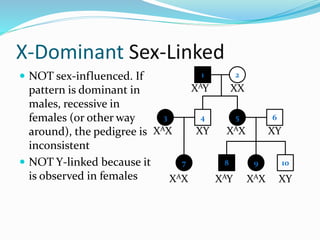
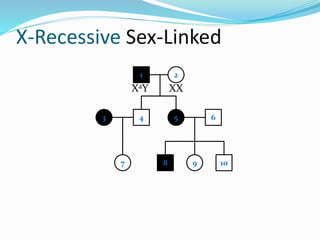
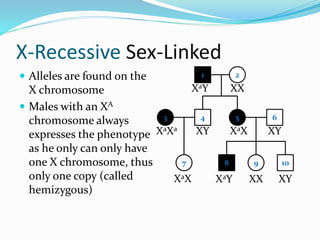
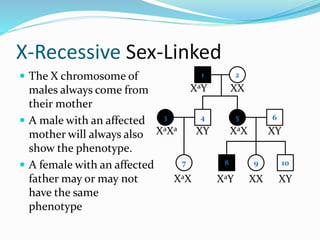
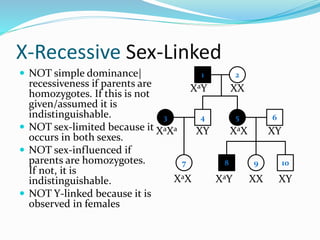
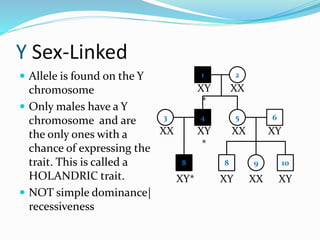
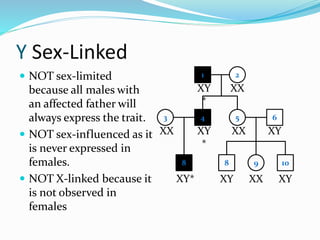
The document discusses various patterns of inheritance through analysis of pedigrees, including:
- Autosomal dominant inheritance where one copy of the dominant allele results in the phenotype.
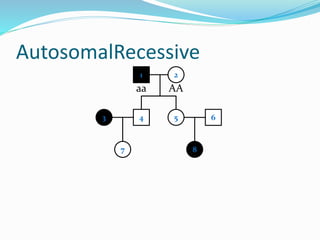
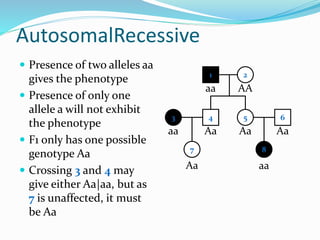
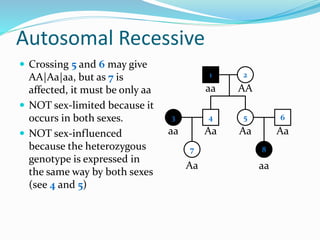
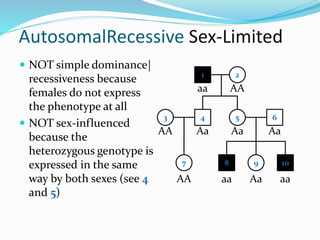
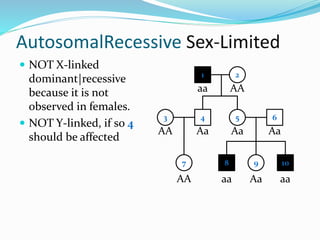
- Autosomal recessive inheritance where two copies of the recessive allele are required to manifest the phenotype.
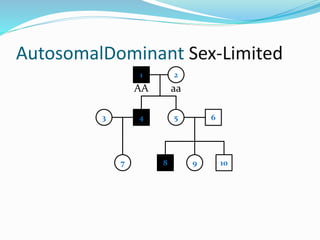
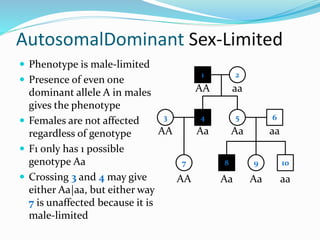
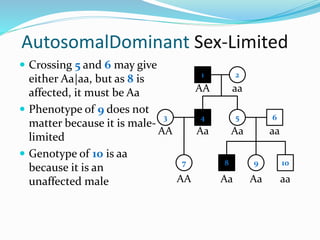
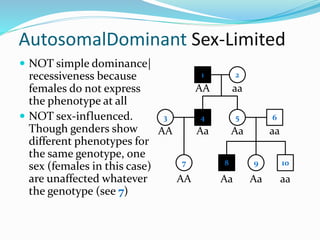
- Sex-limited traits where the phenotype is expressed in only one sex.
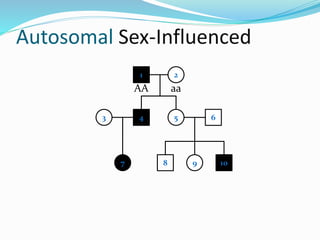
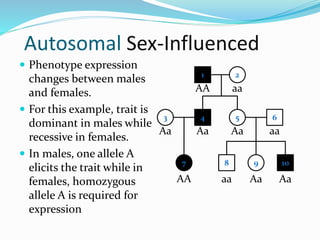
- Sex-influenced traits where the same genotype results in different phenotypes between males and females.
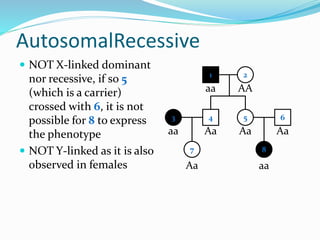
- X-linked traits where the allele is located on the X chromosome and follows patterns of X-linked dominance or recessiveness.
- Y-linked traits which are expressed only in males since they possess the Y chromosome.