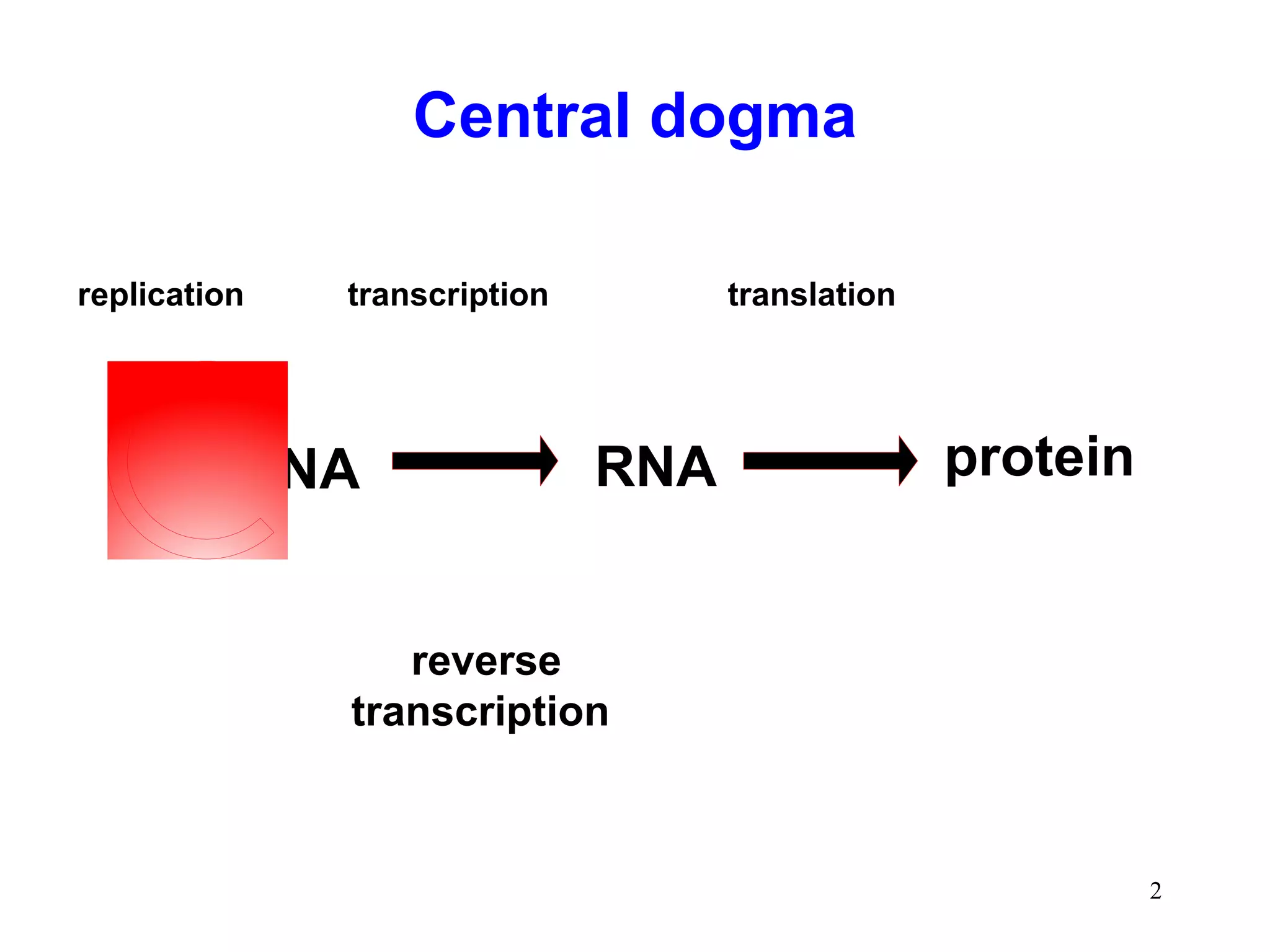
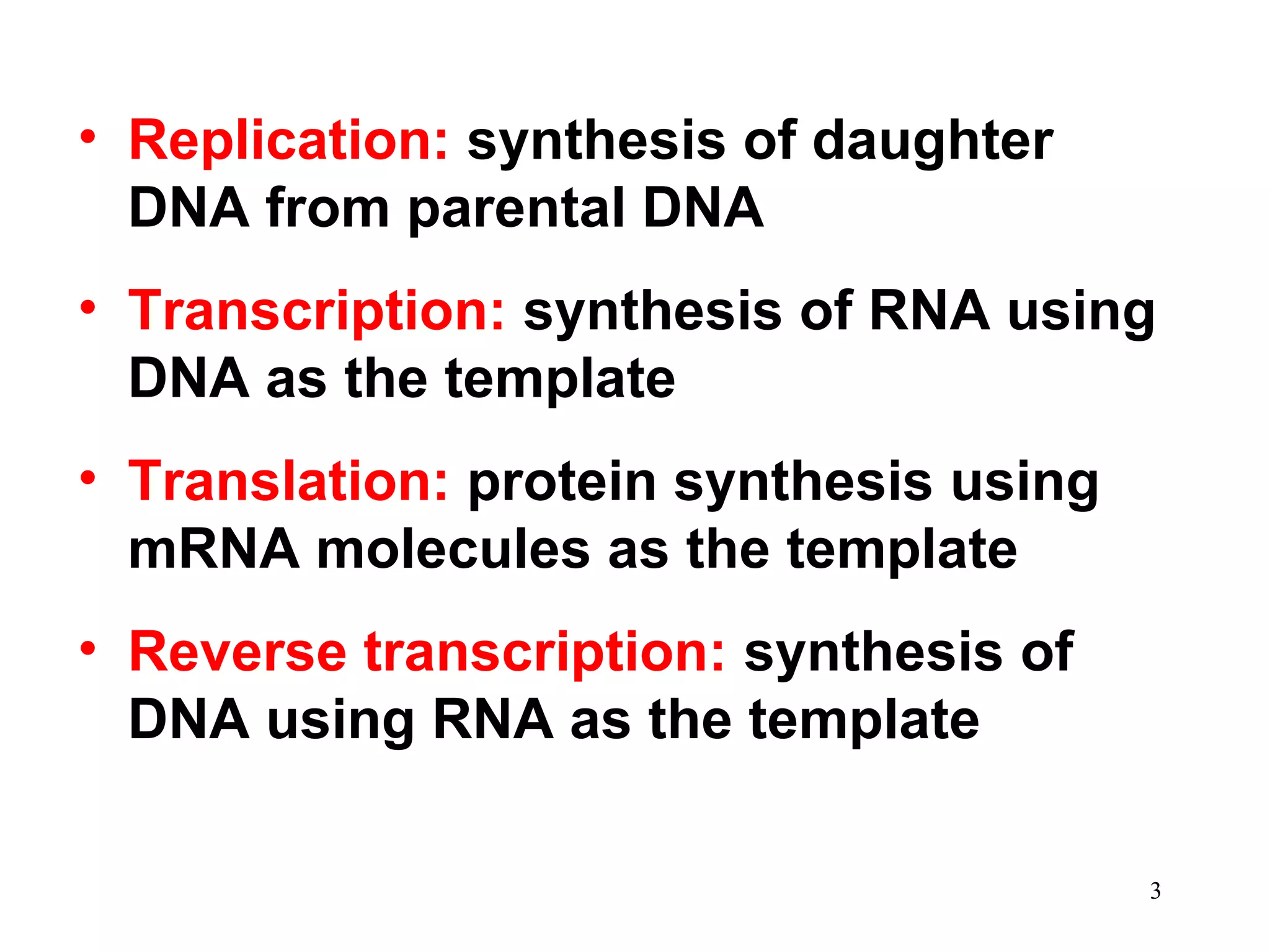
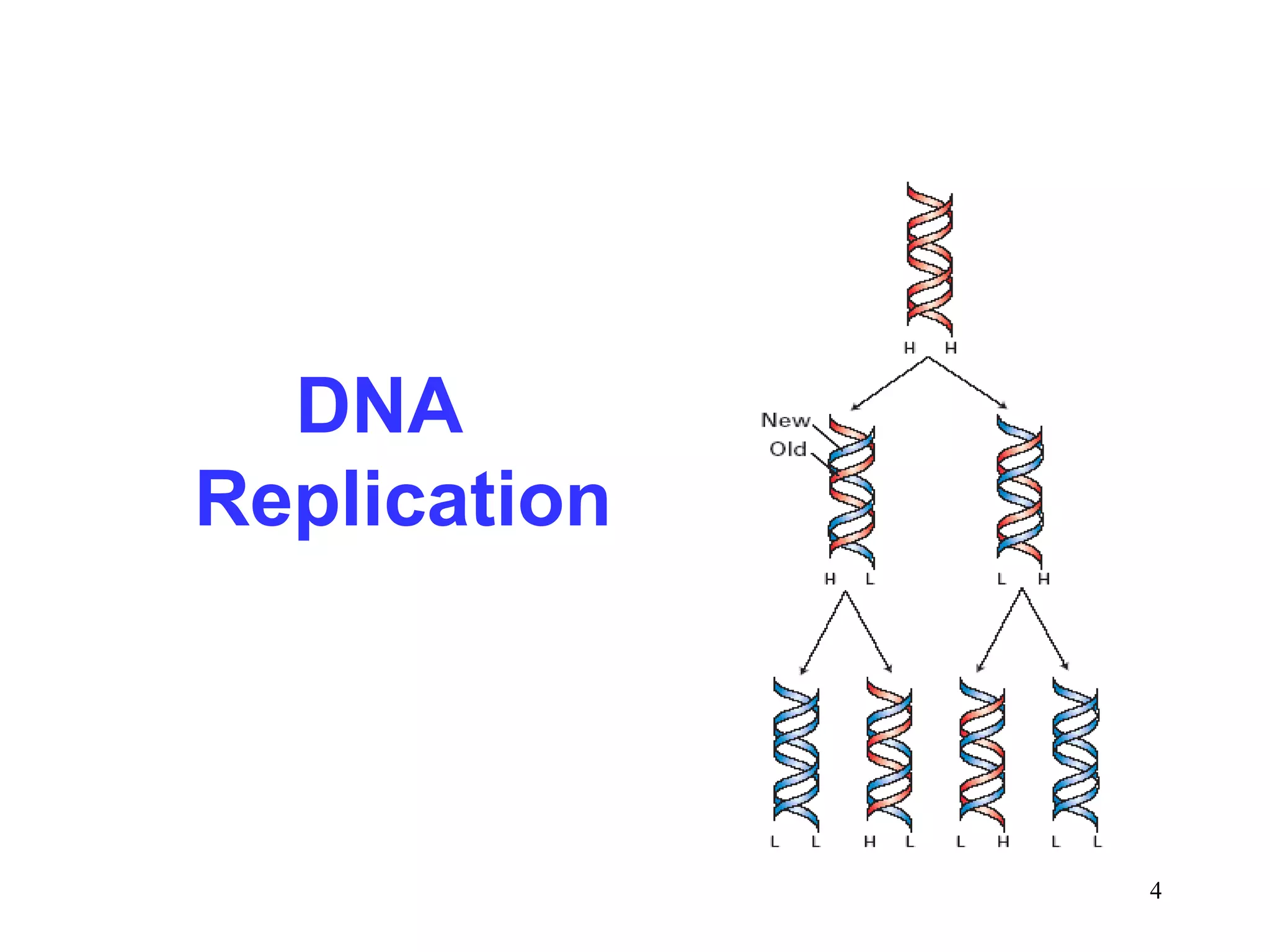
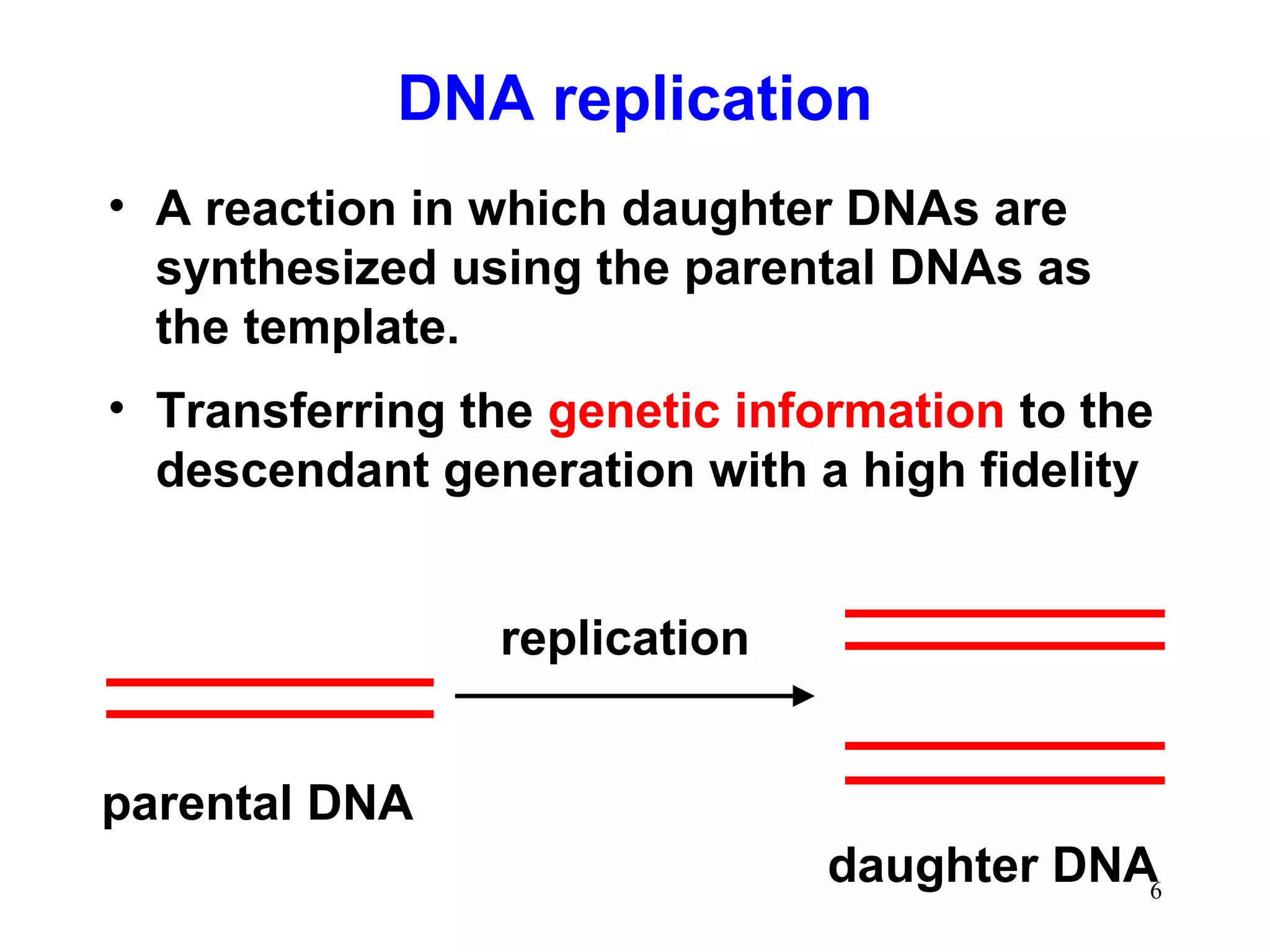
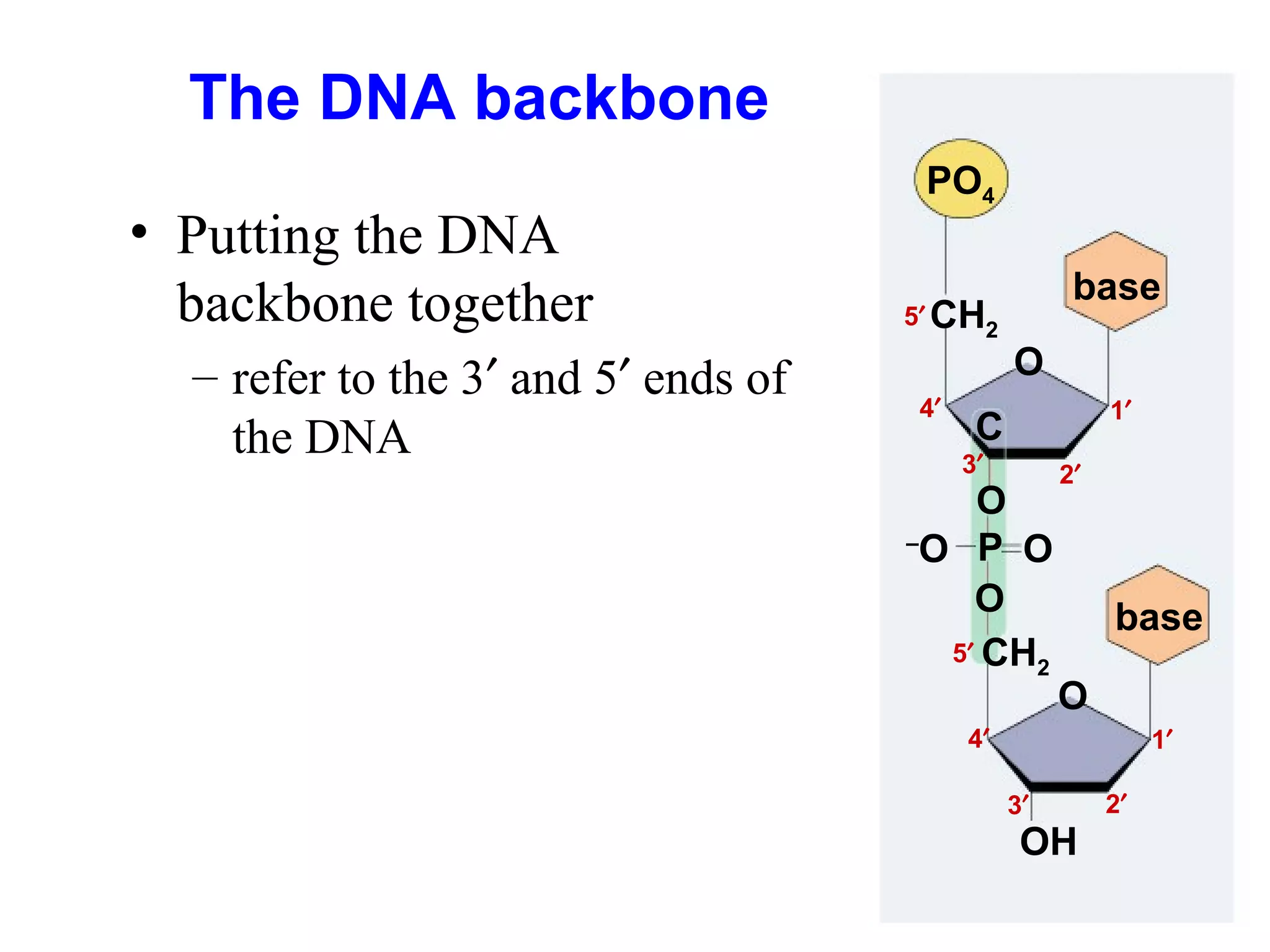
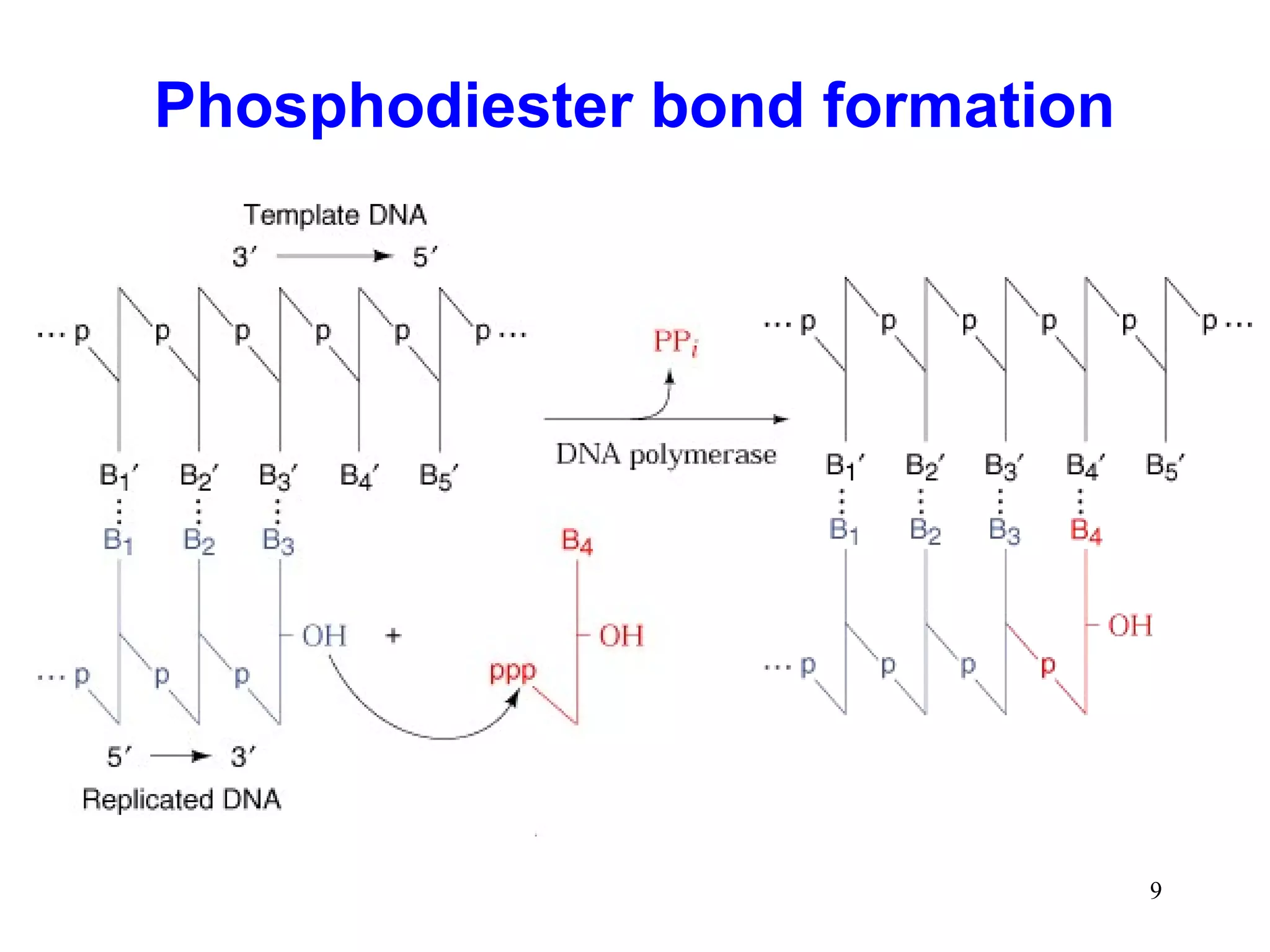
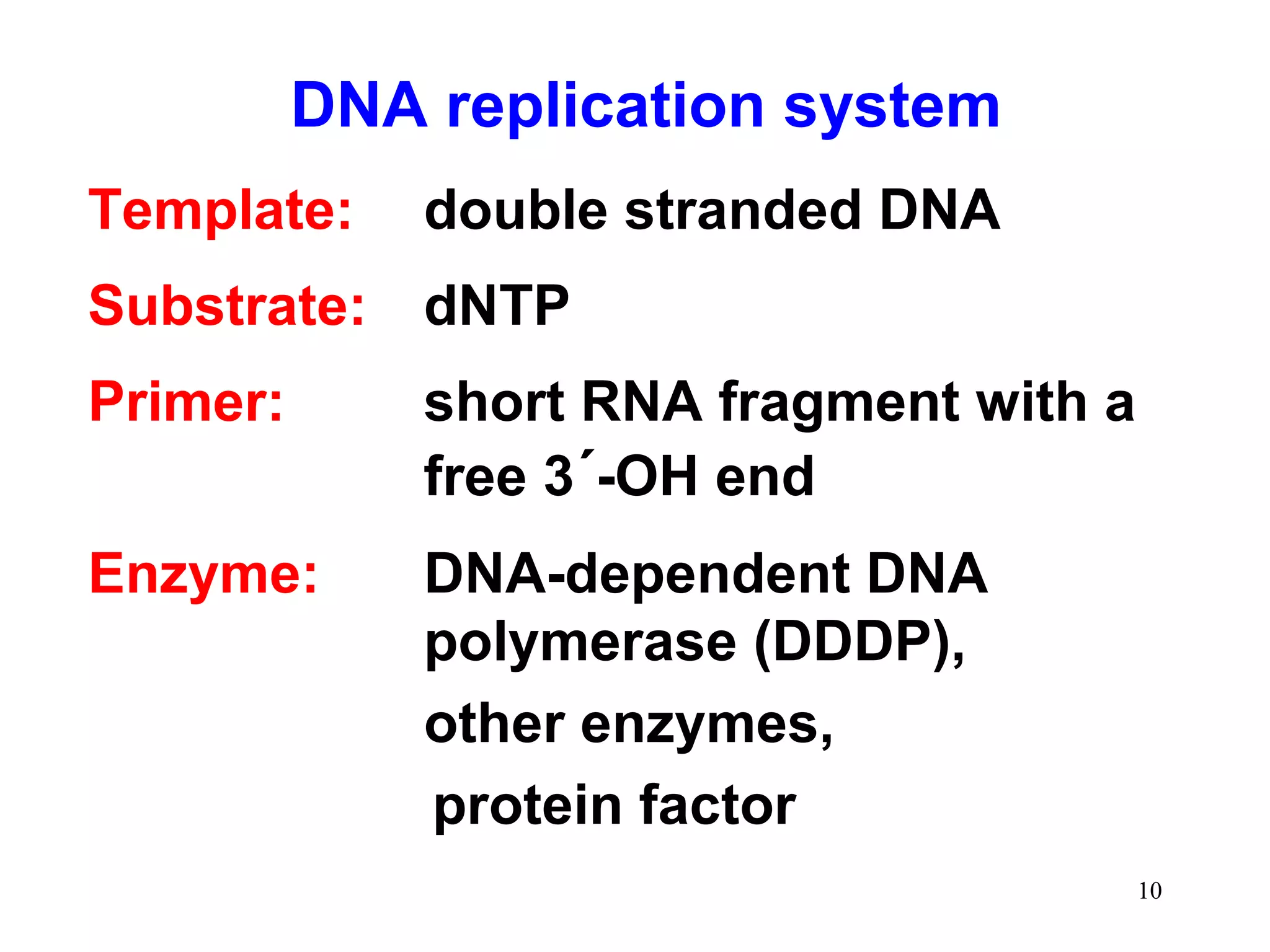
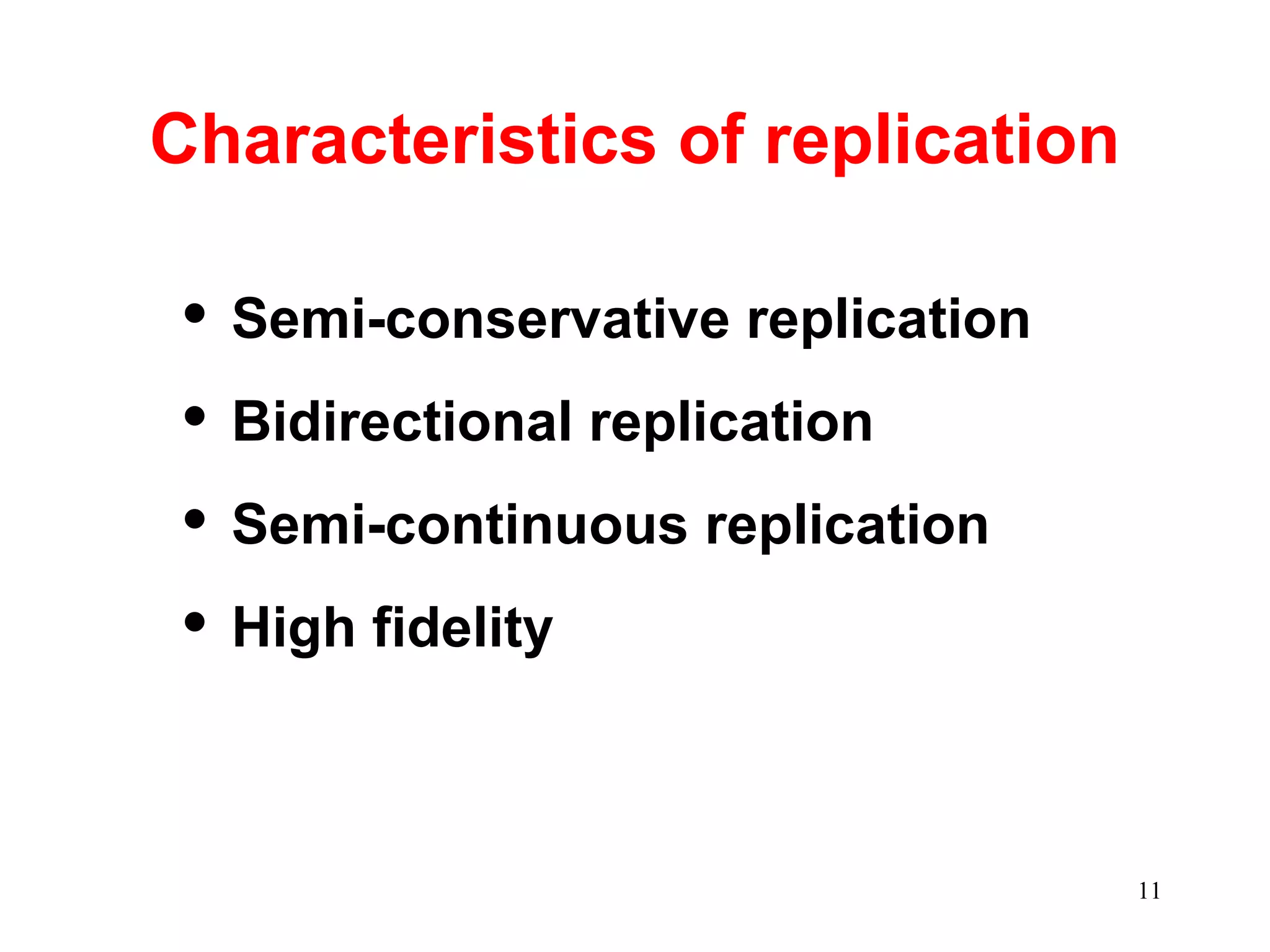
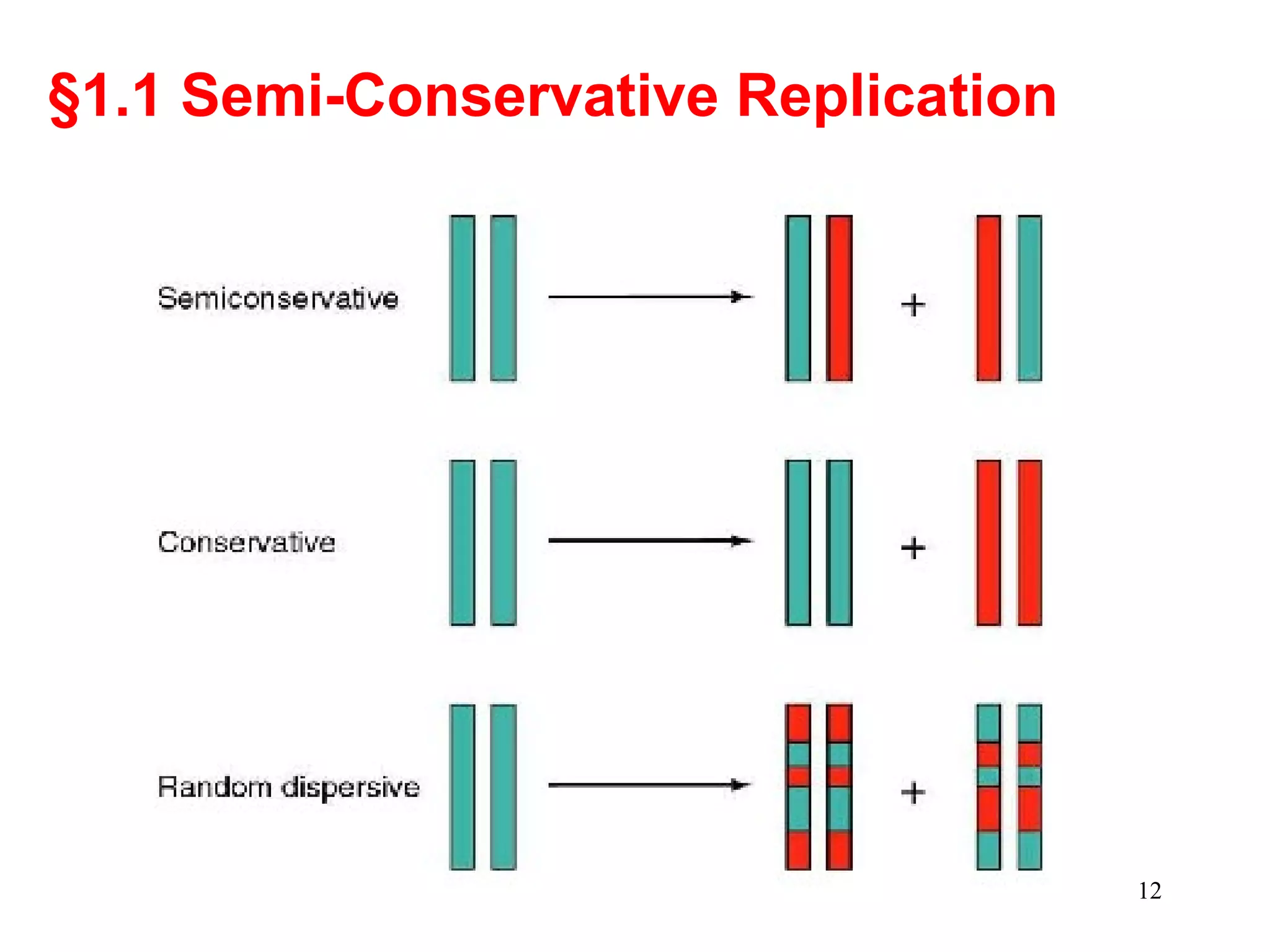
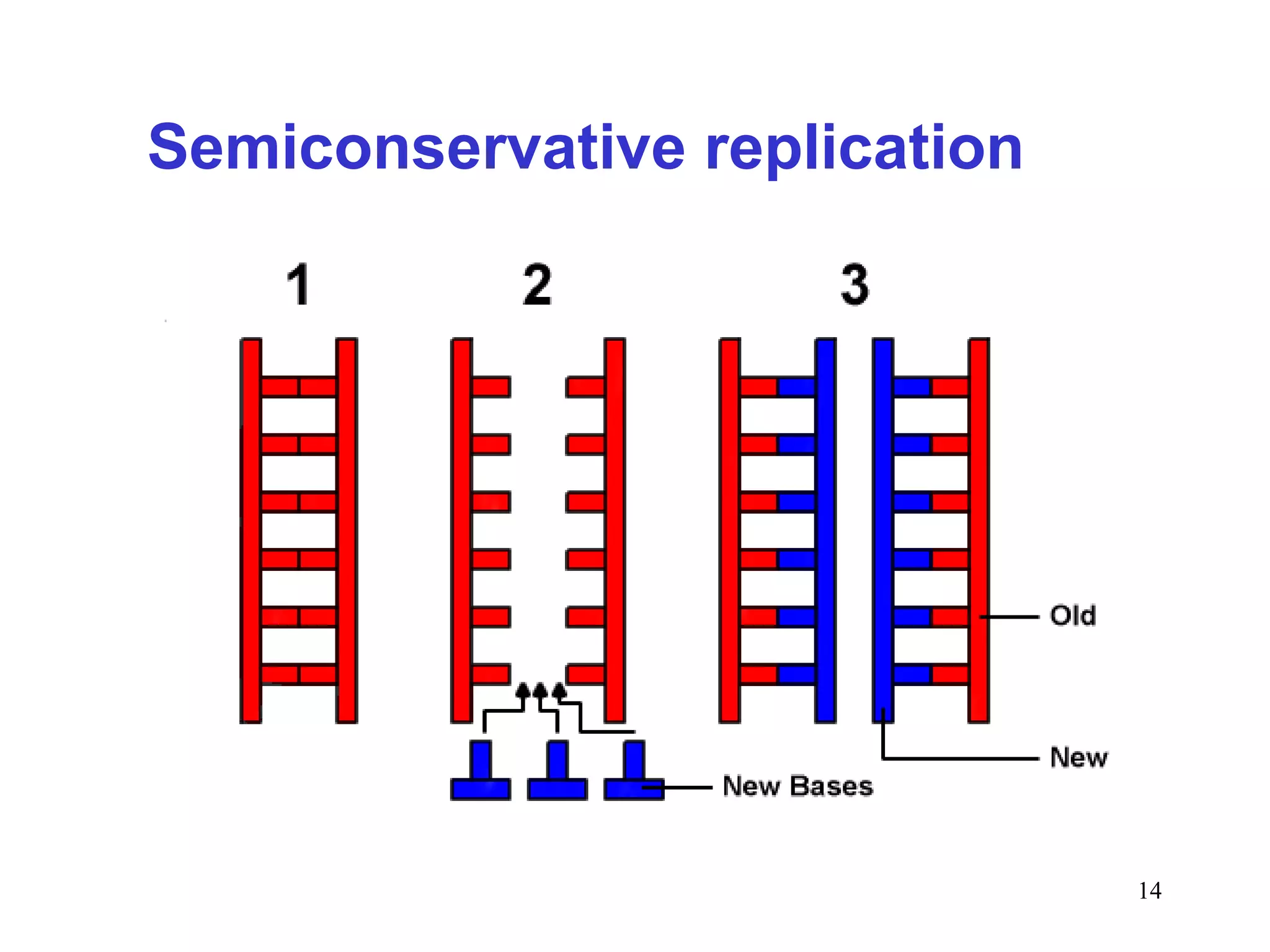
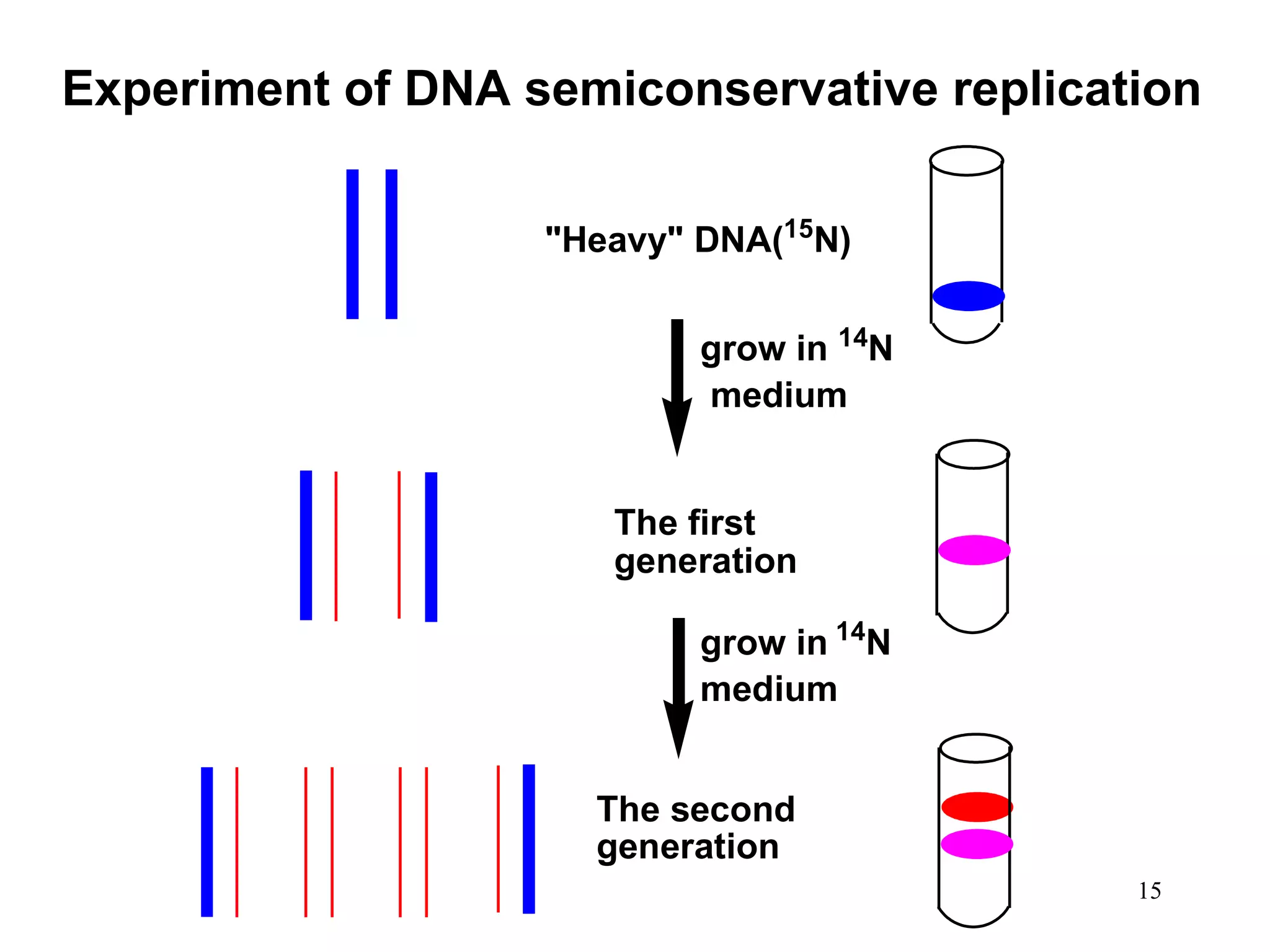
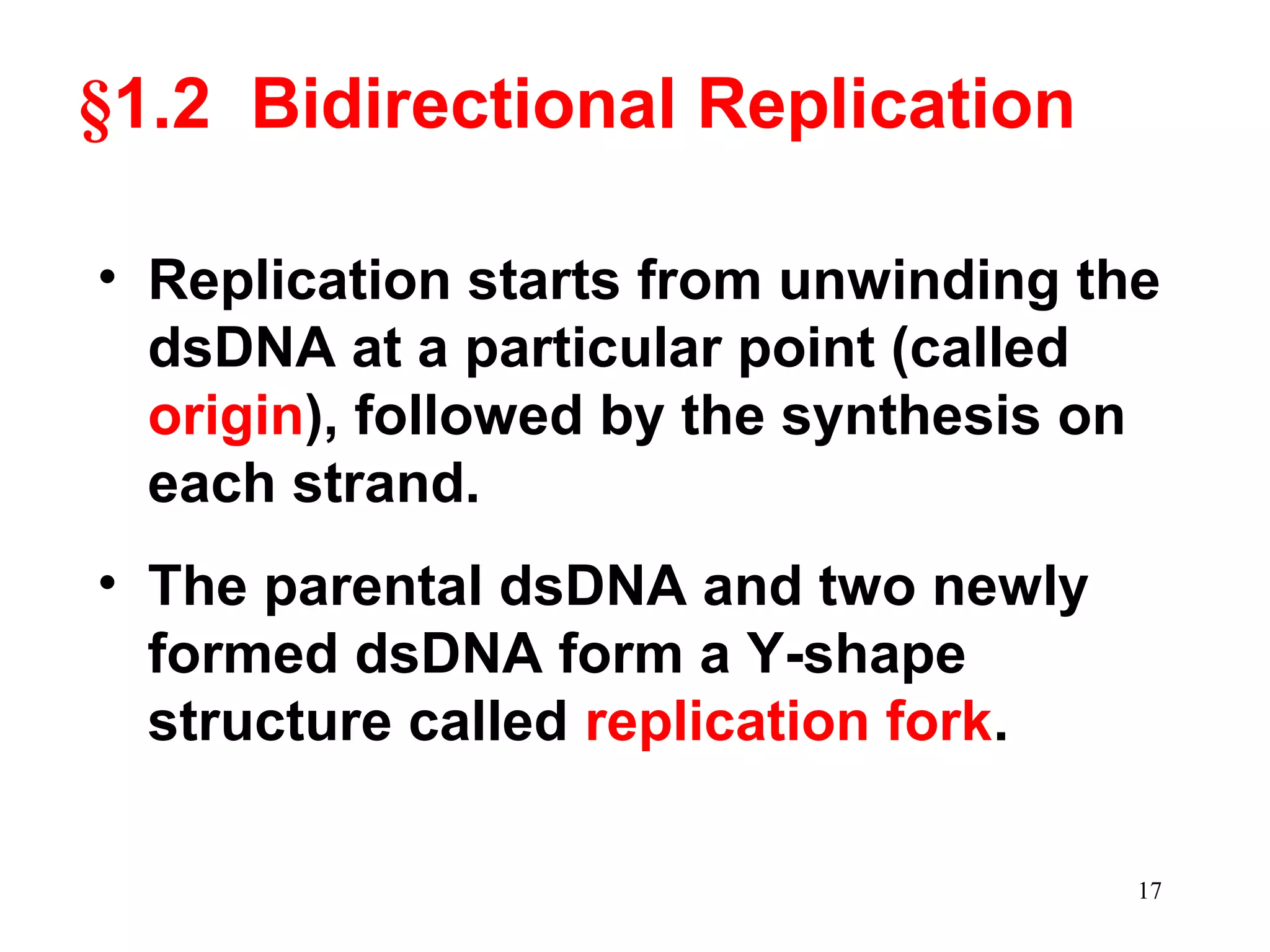
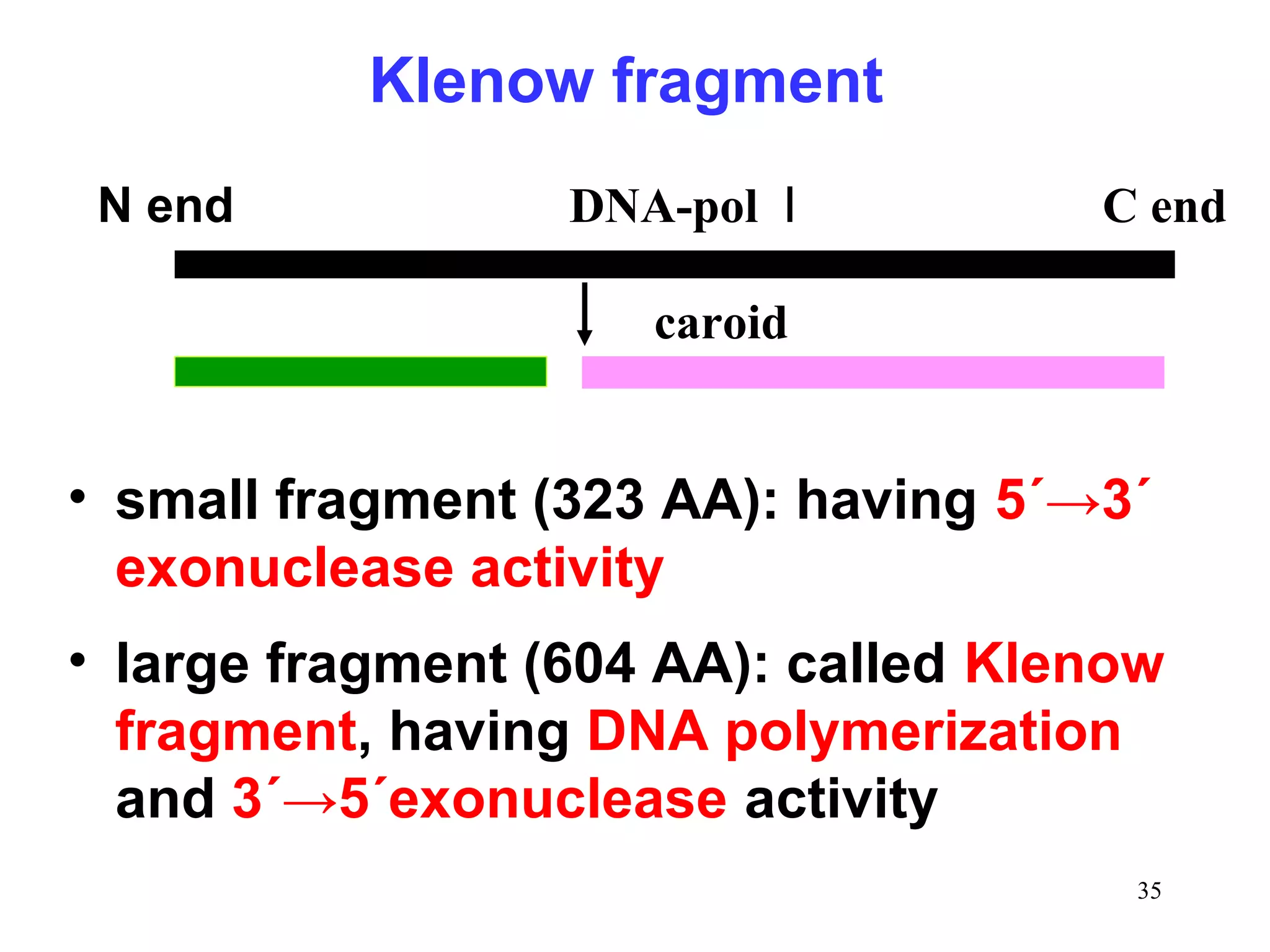
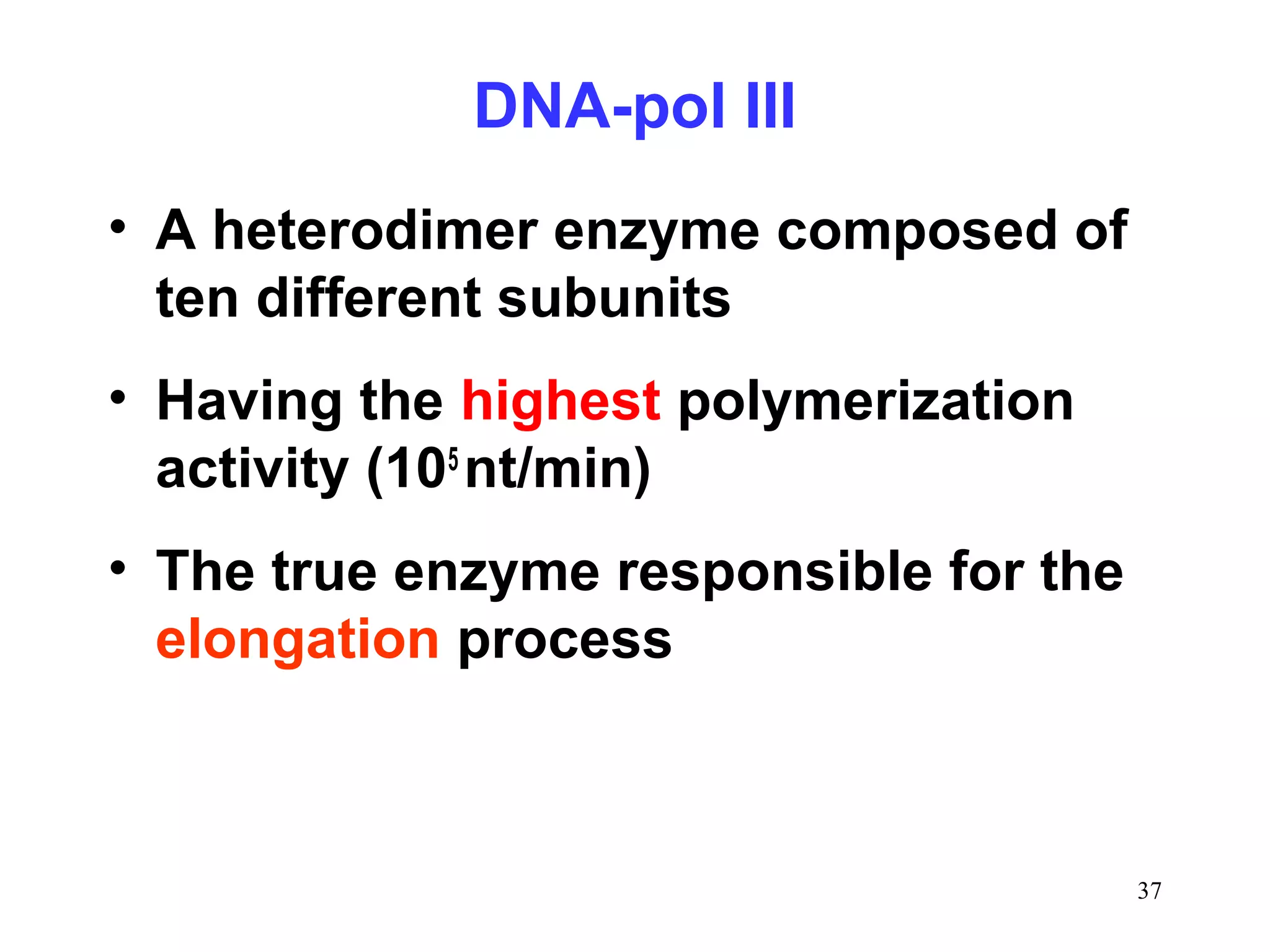
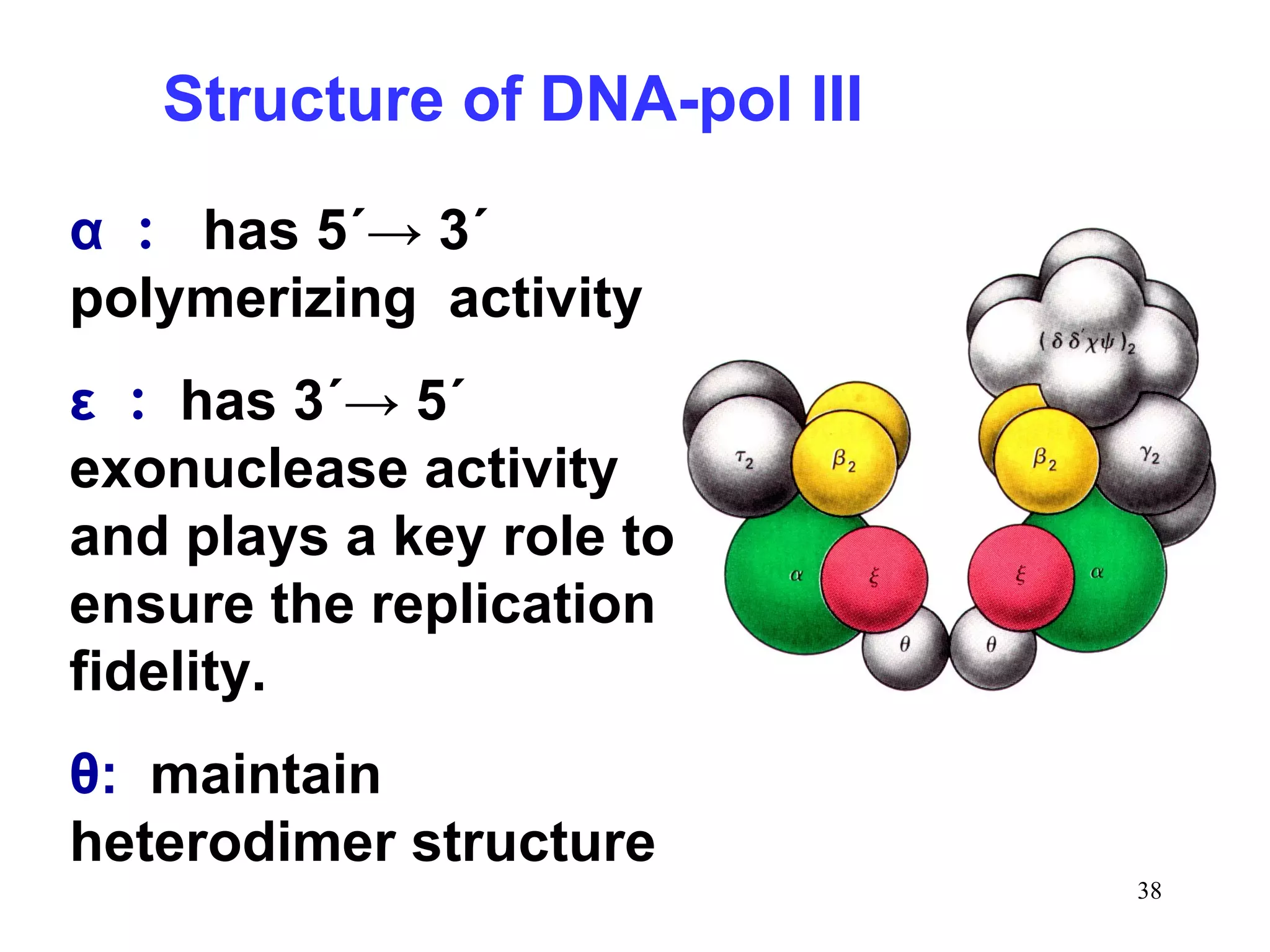
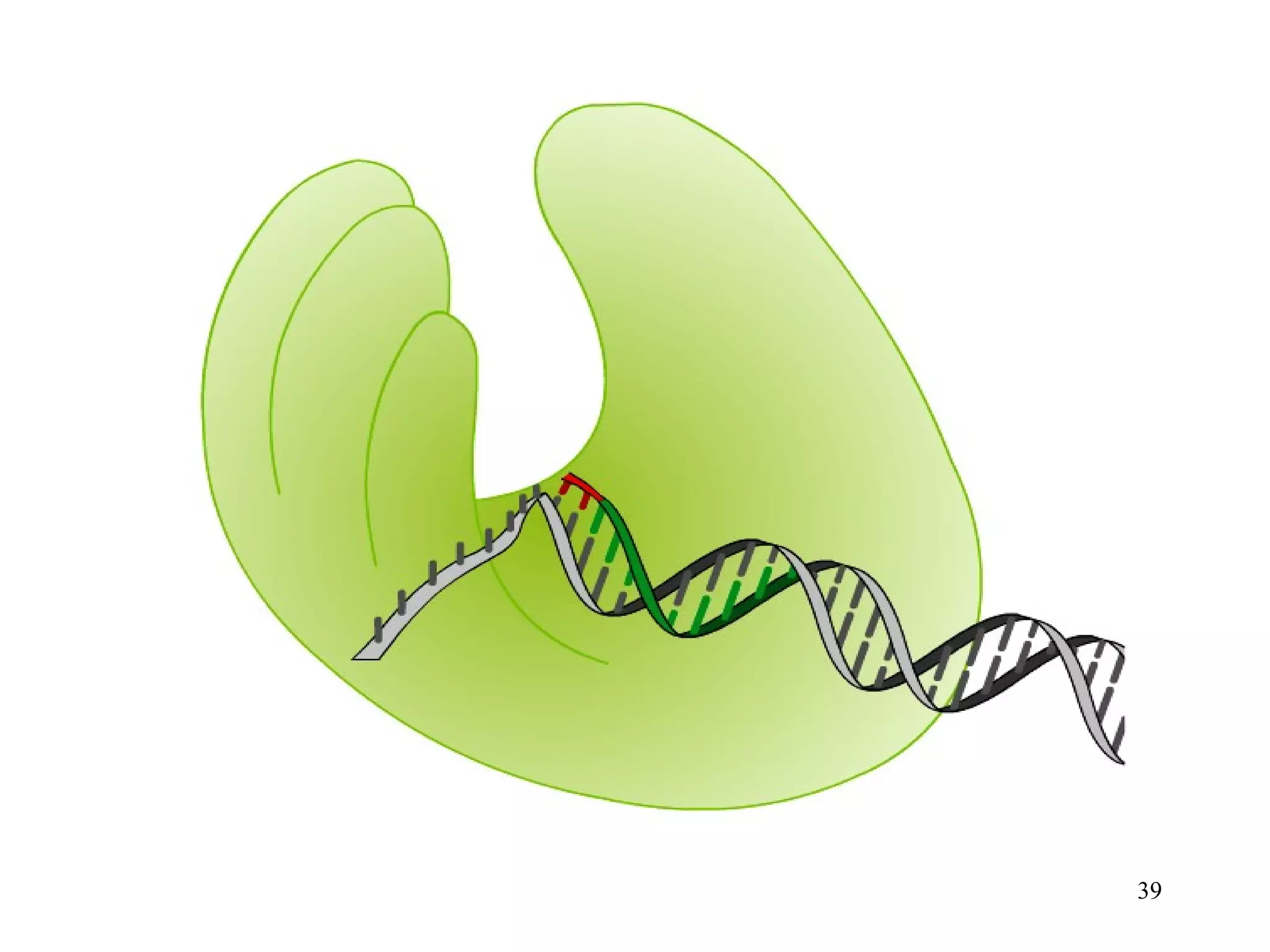
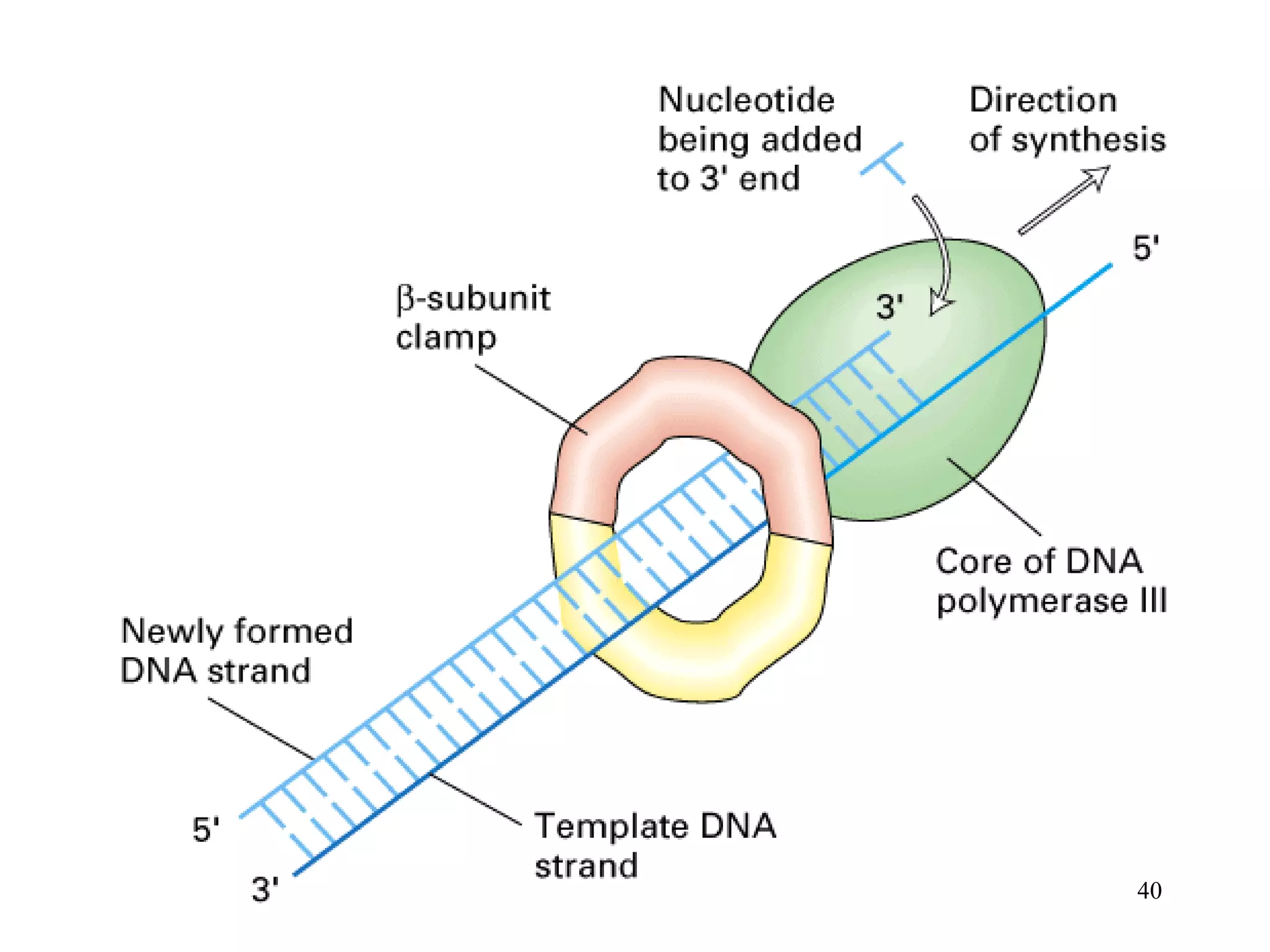
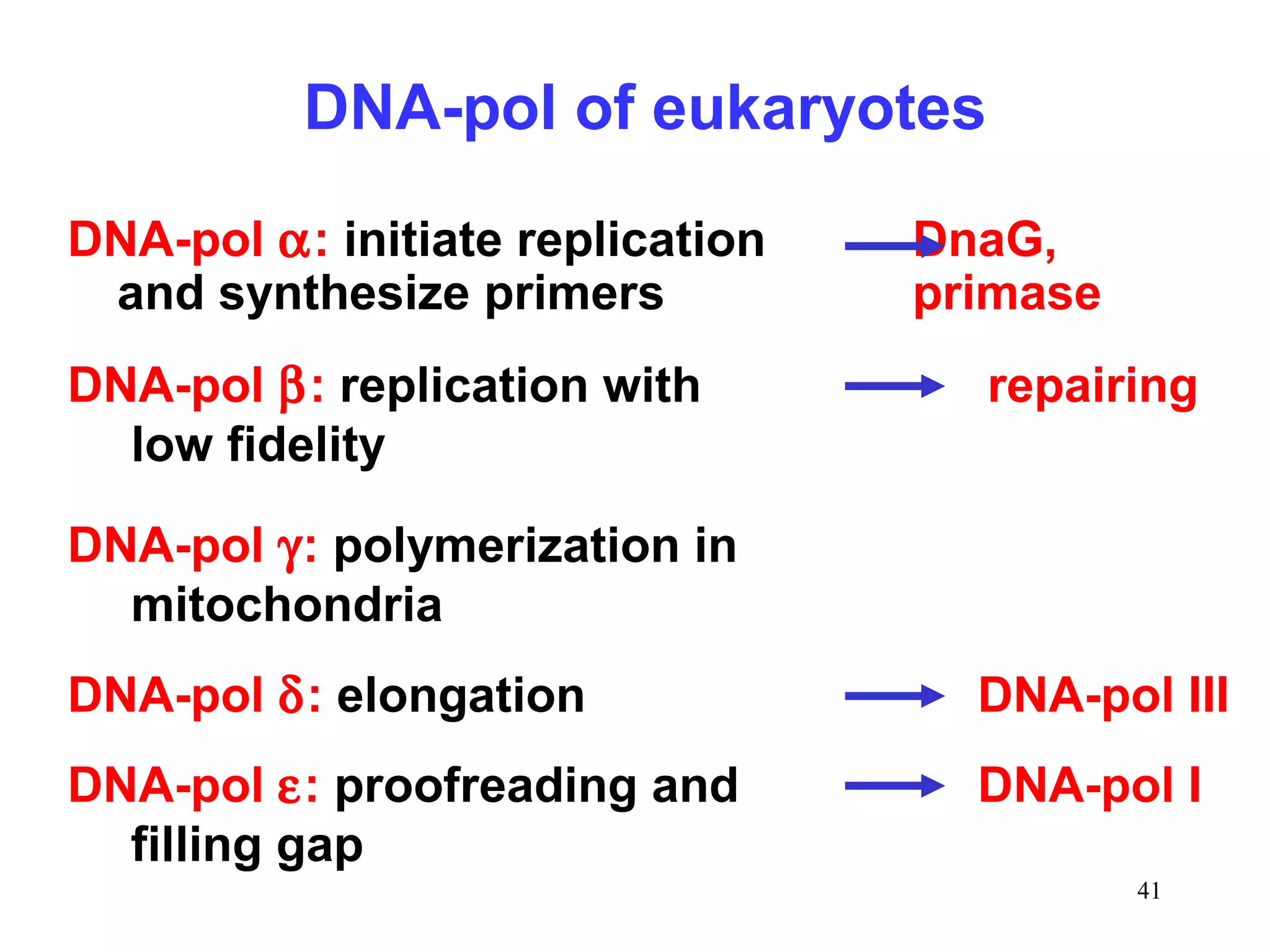
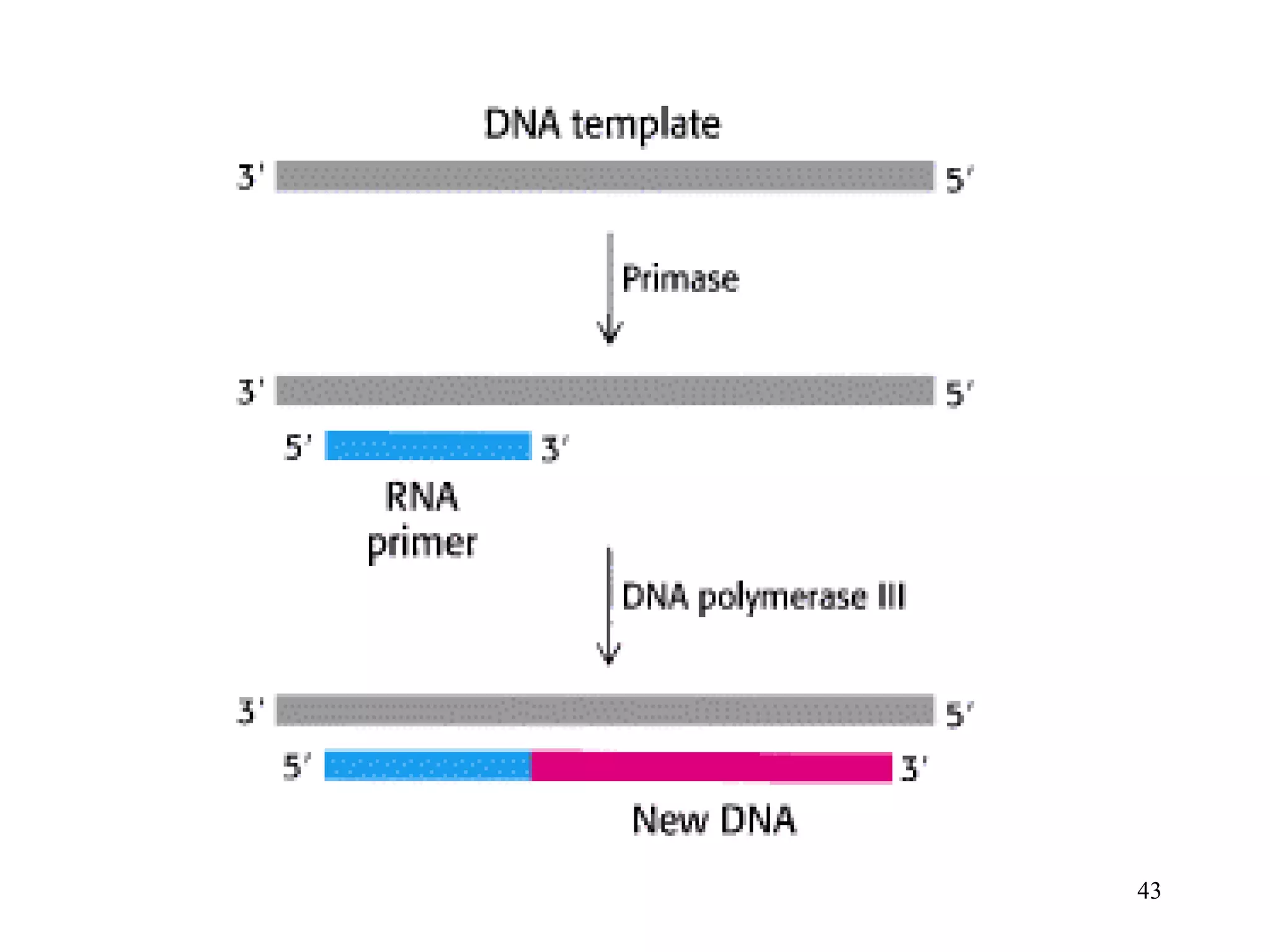
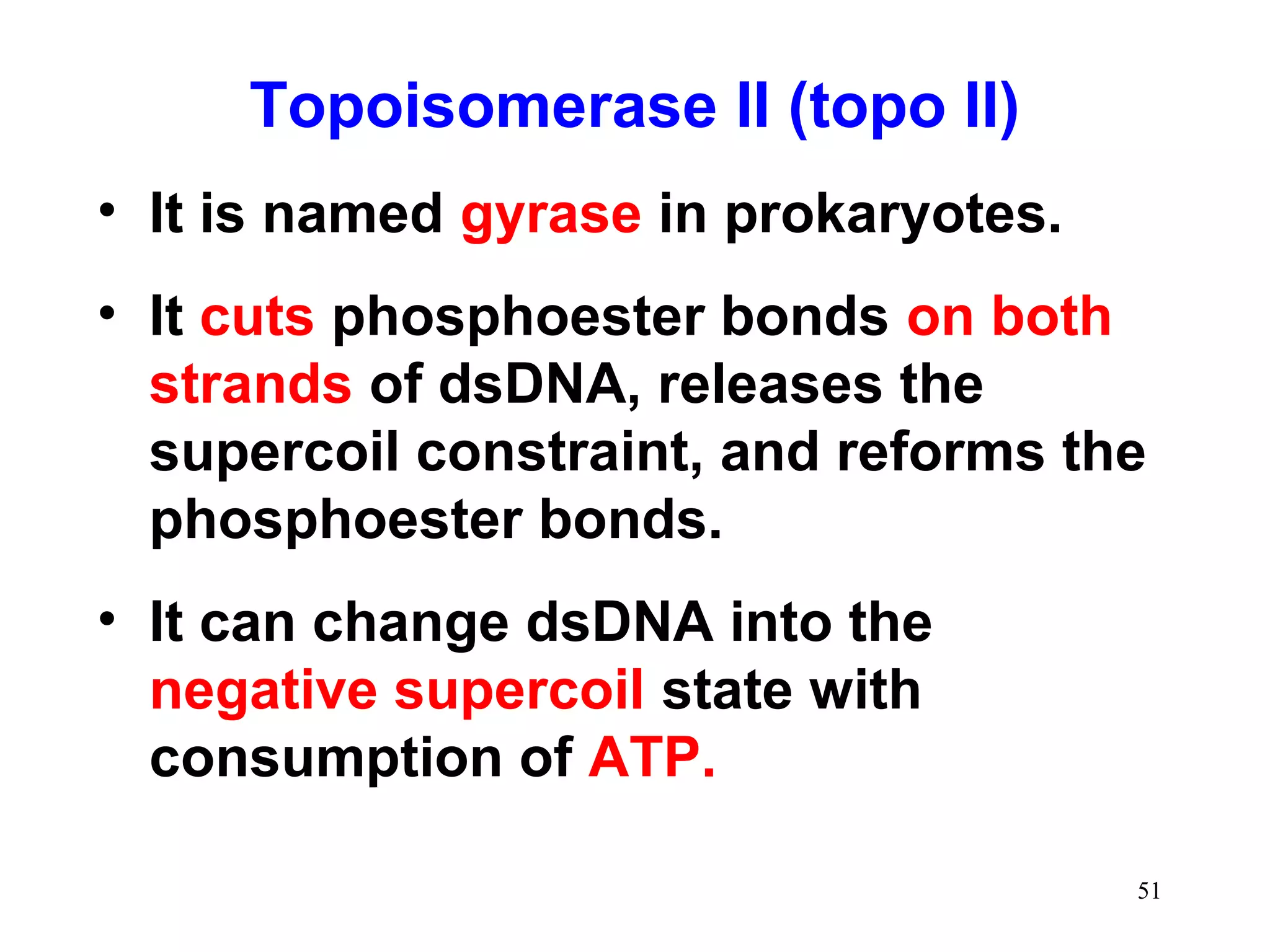
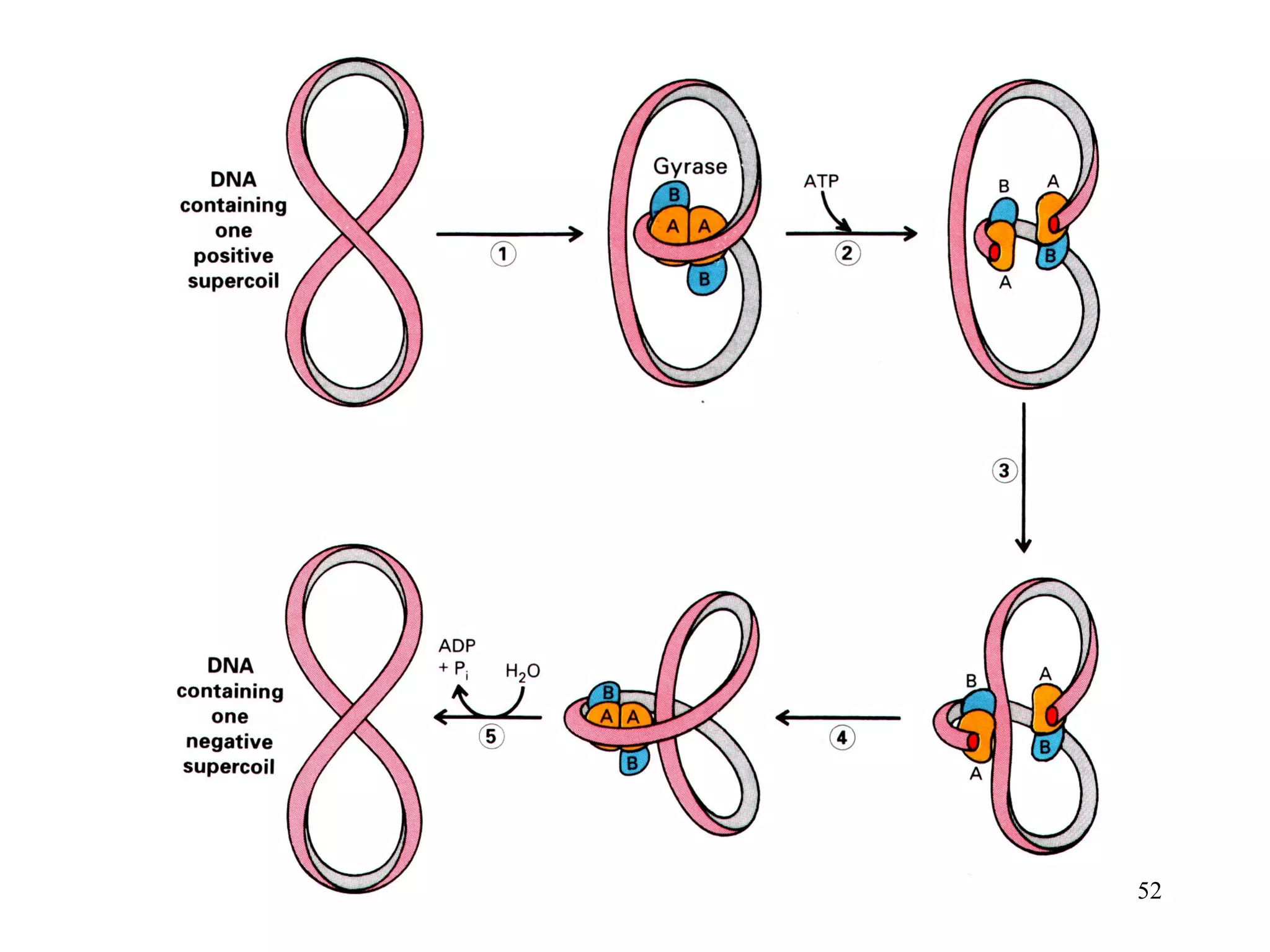
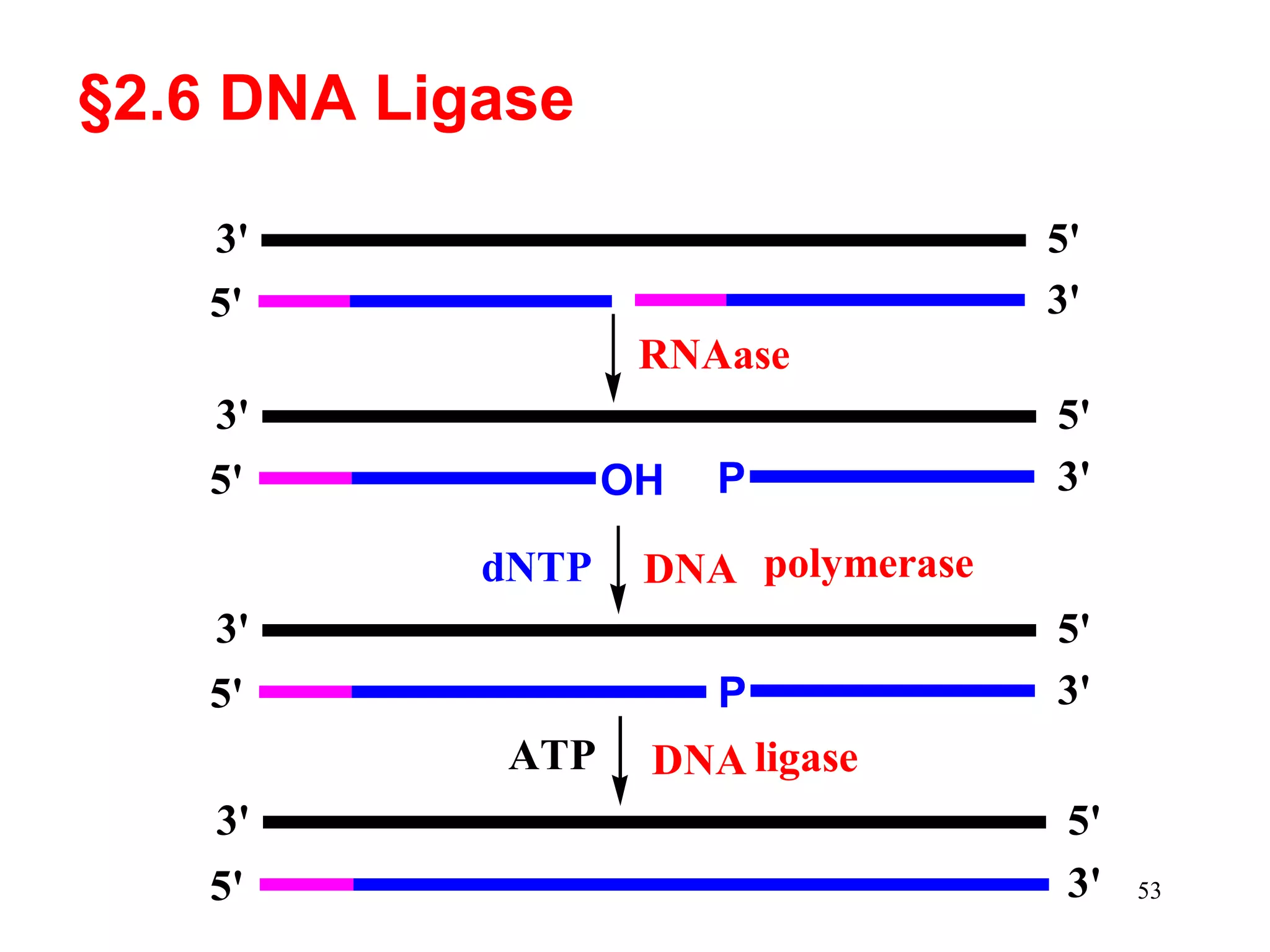
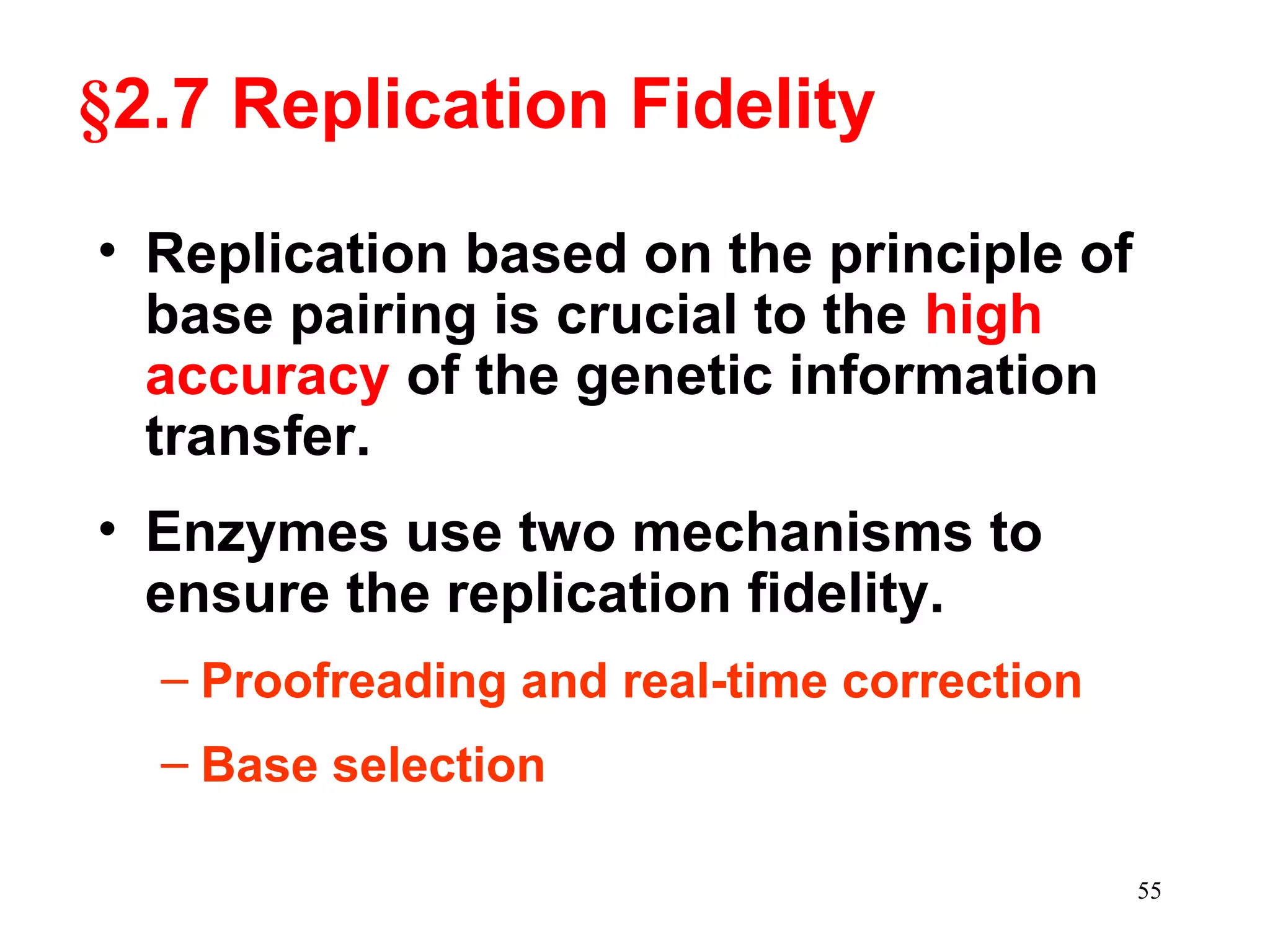
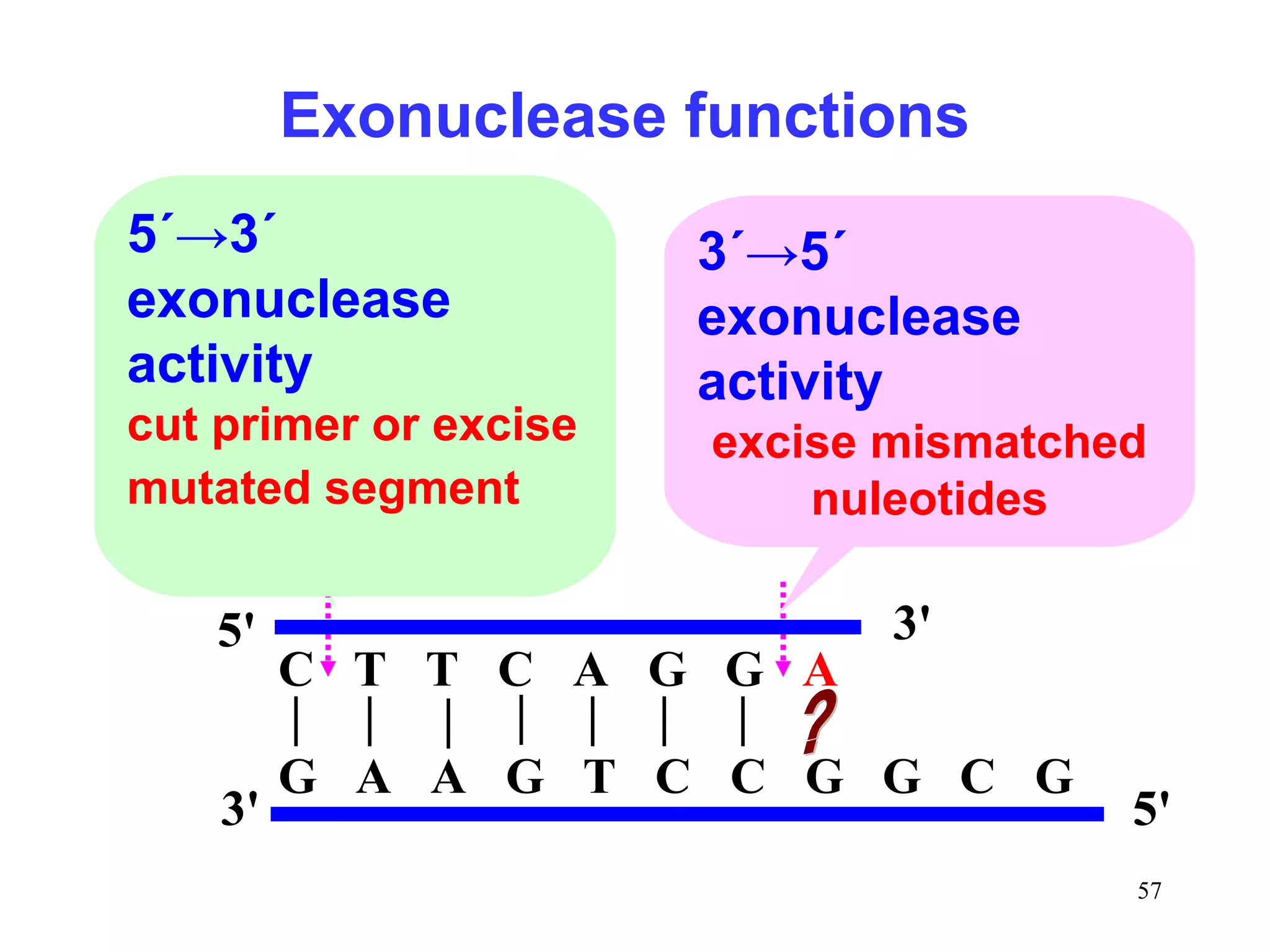
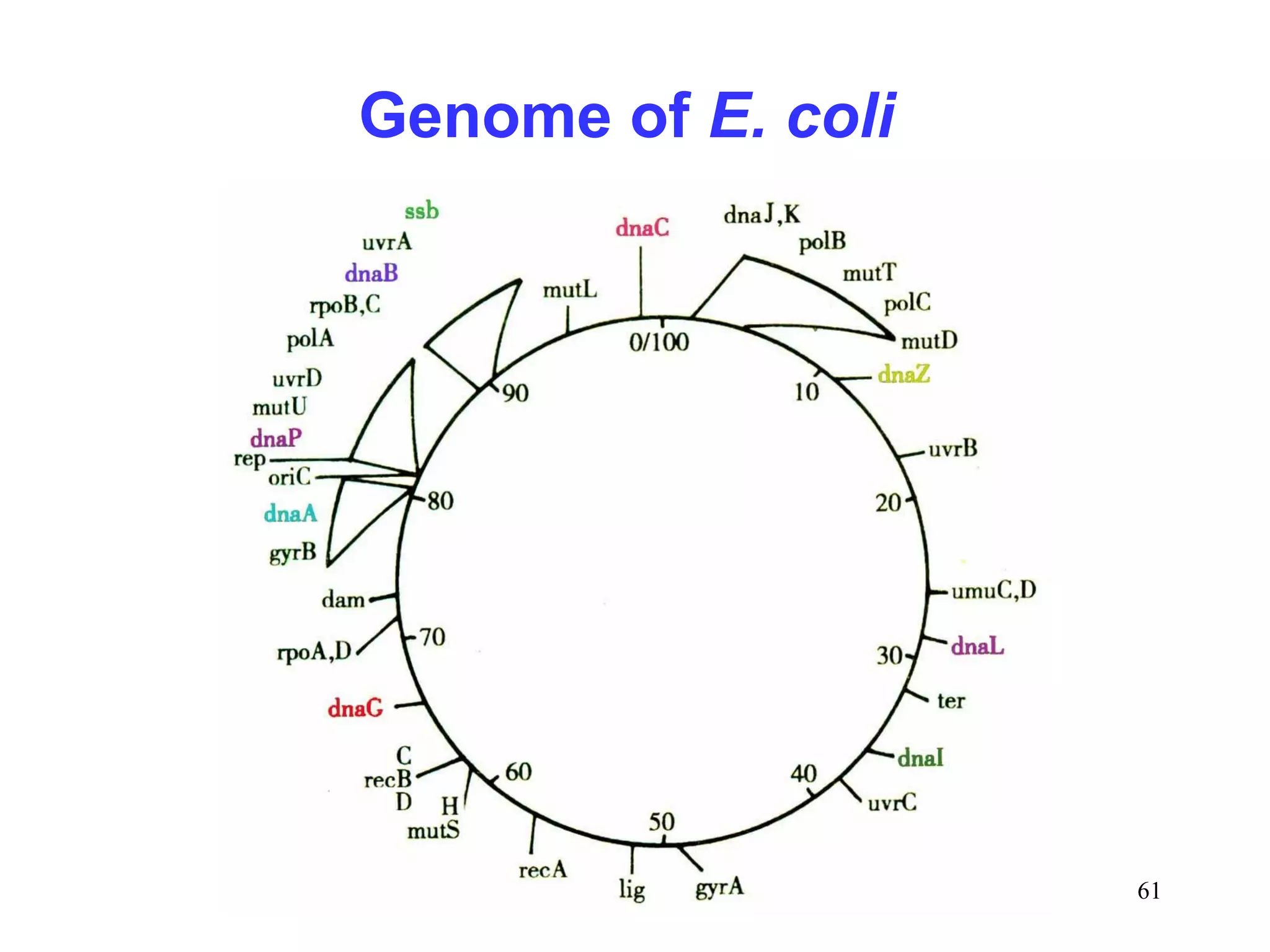
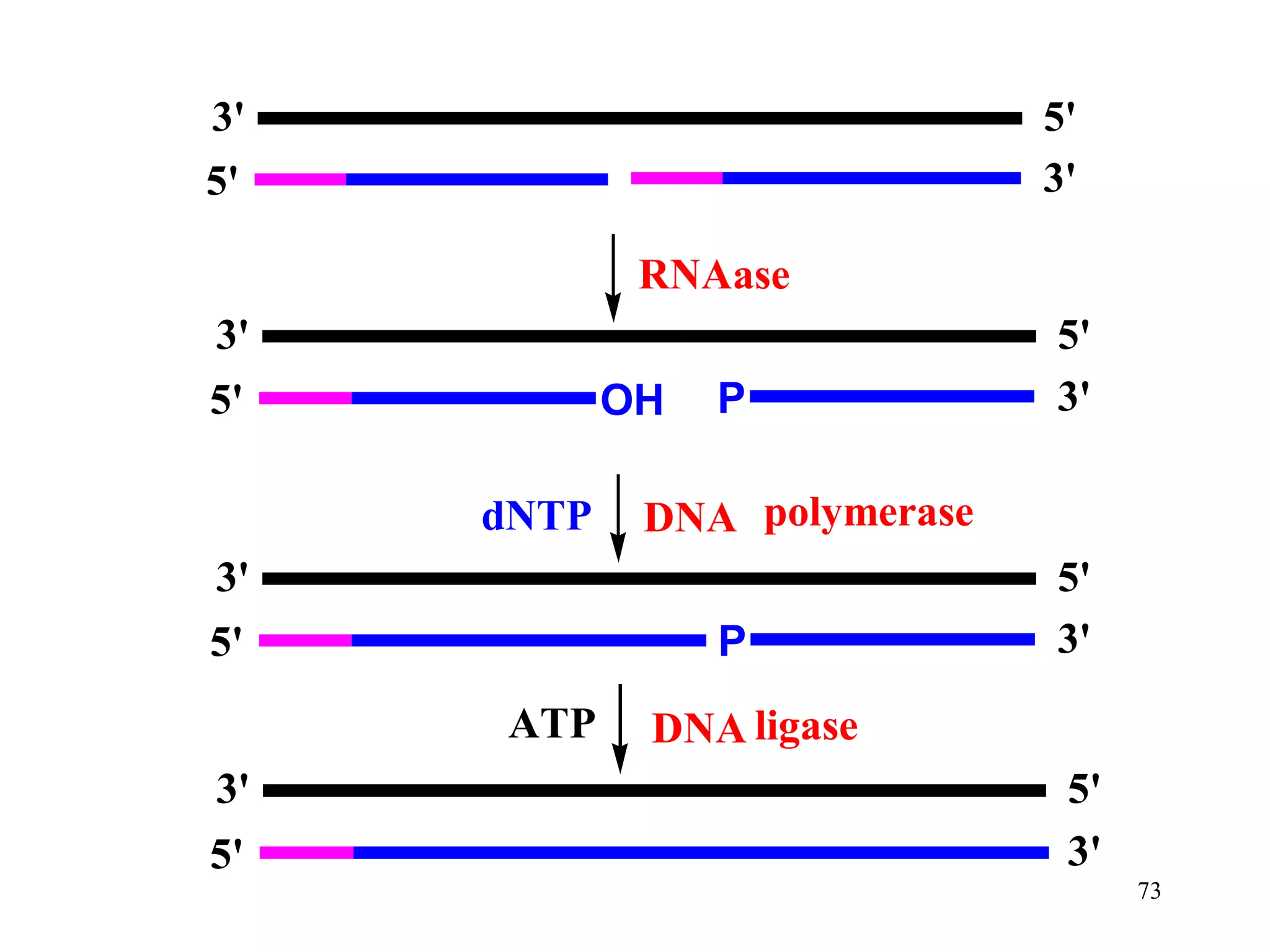
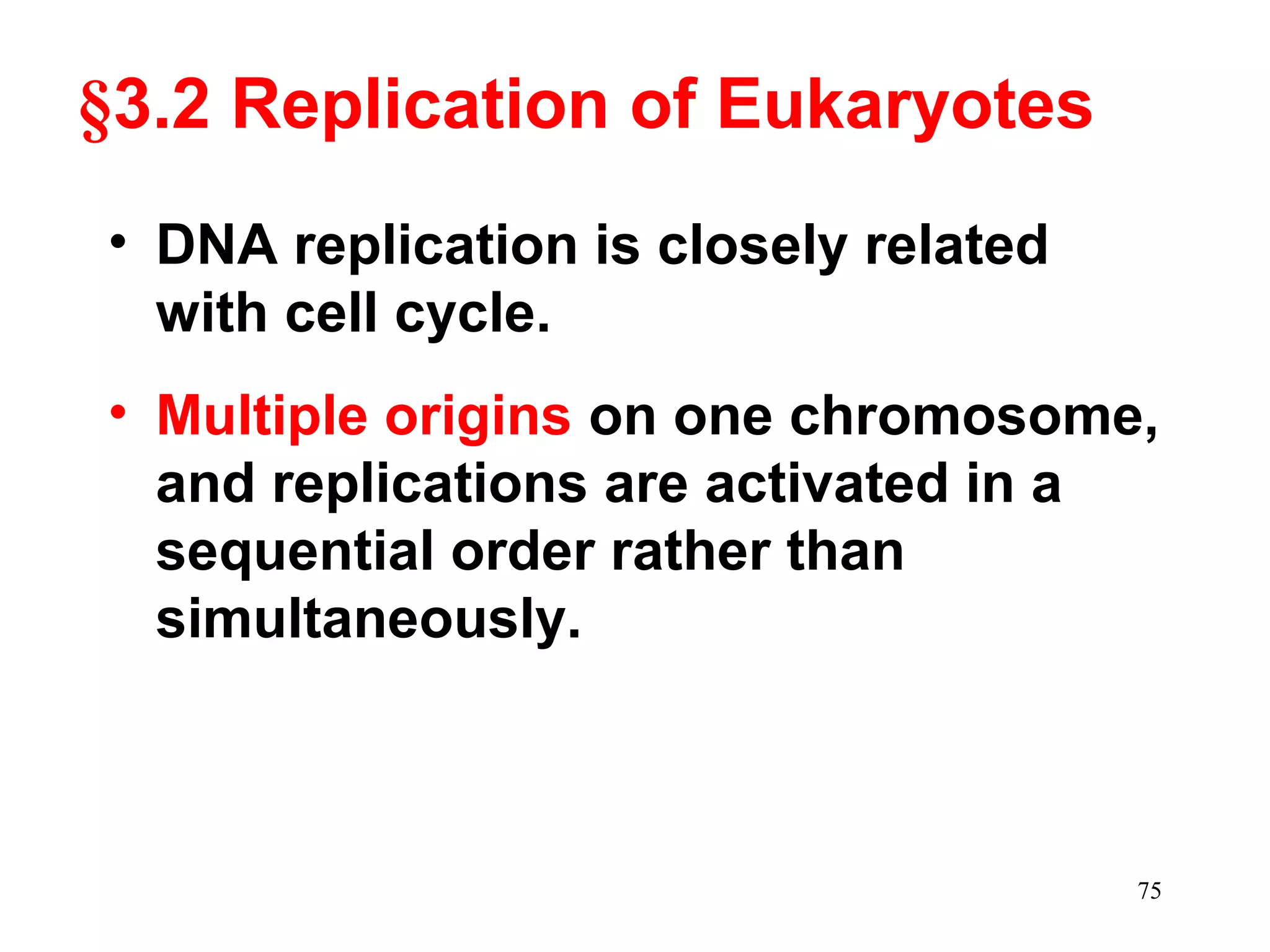
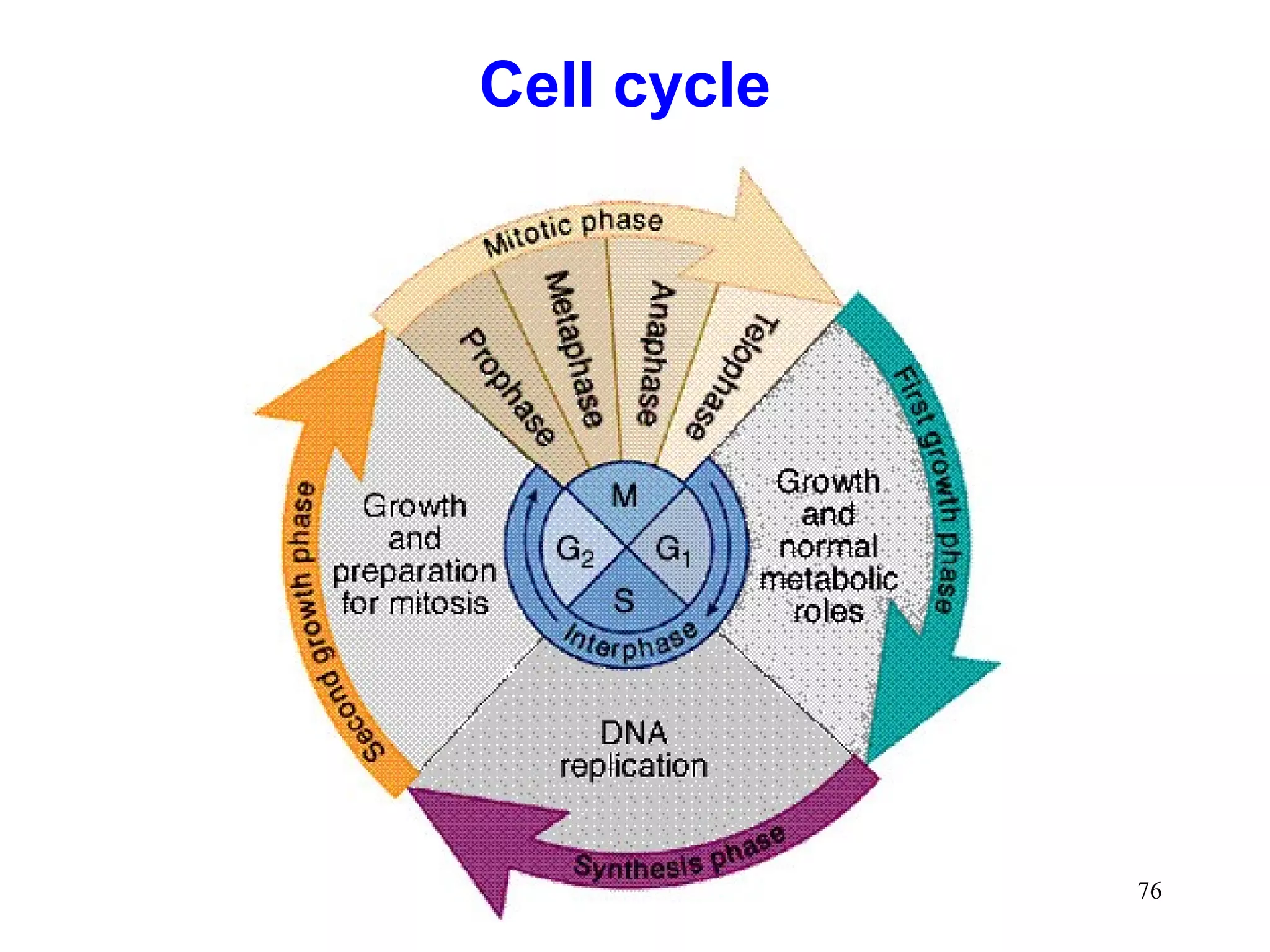
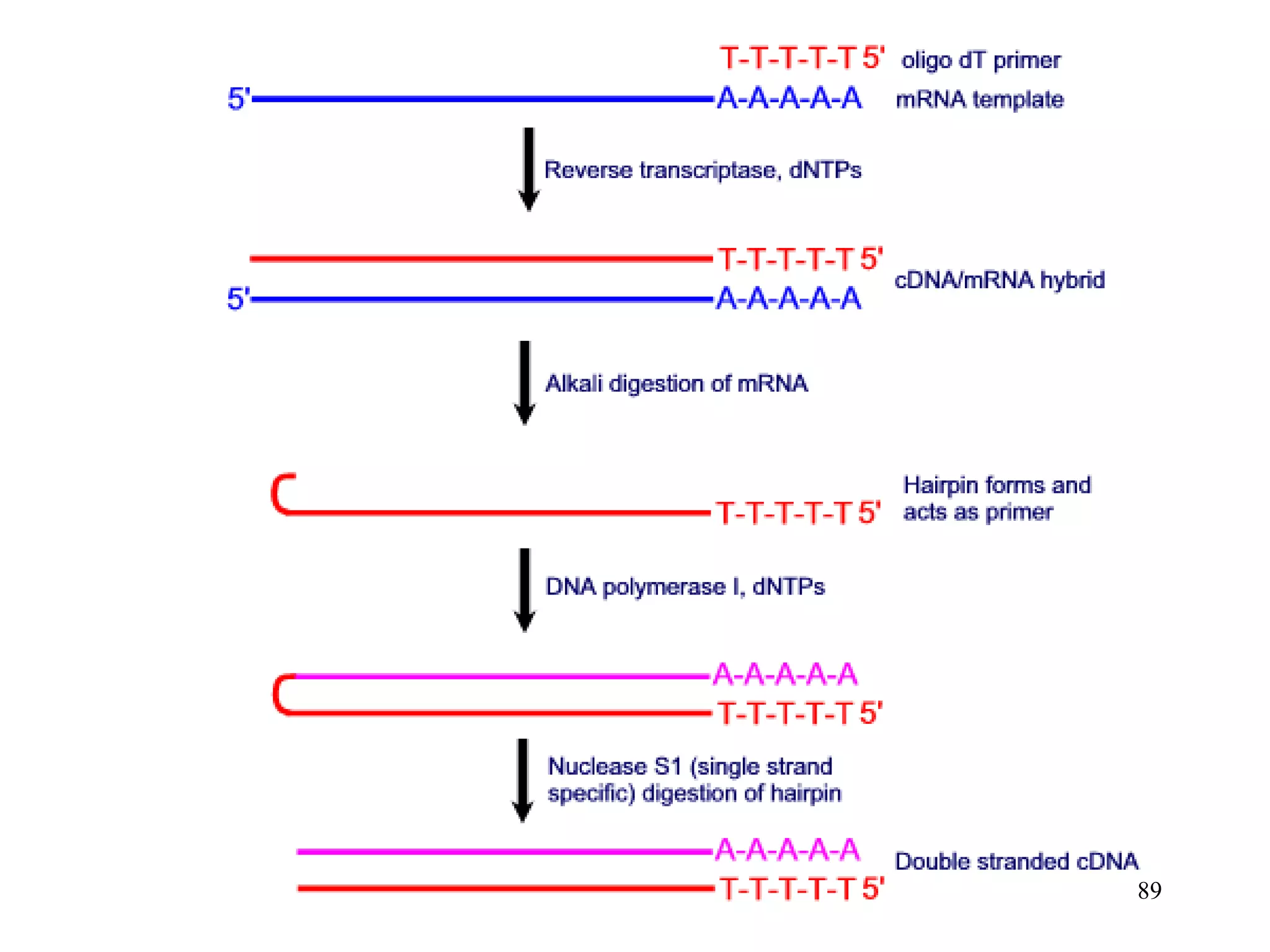
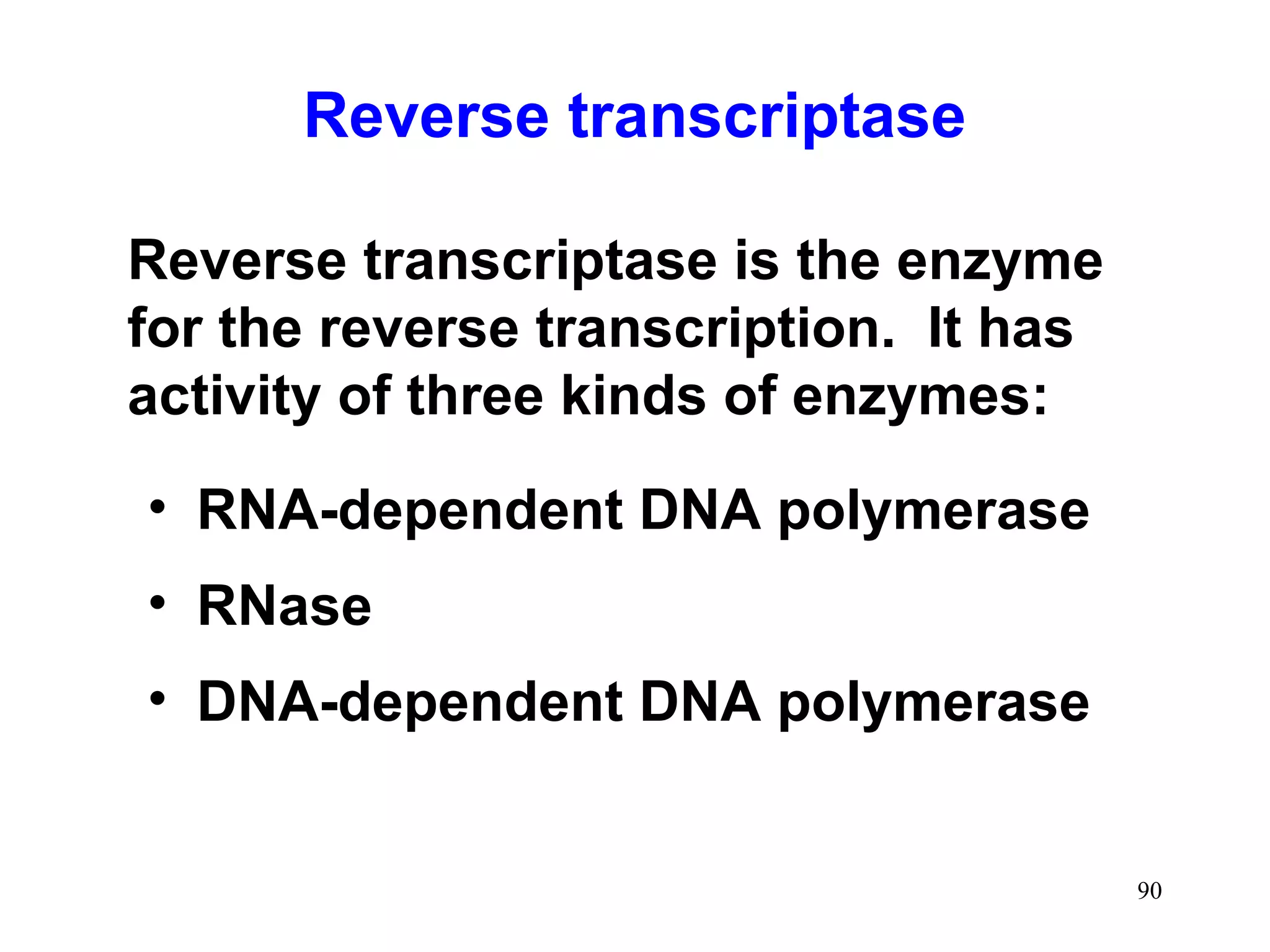
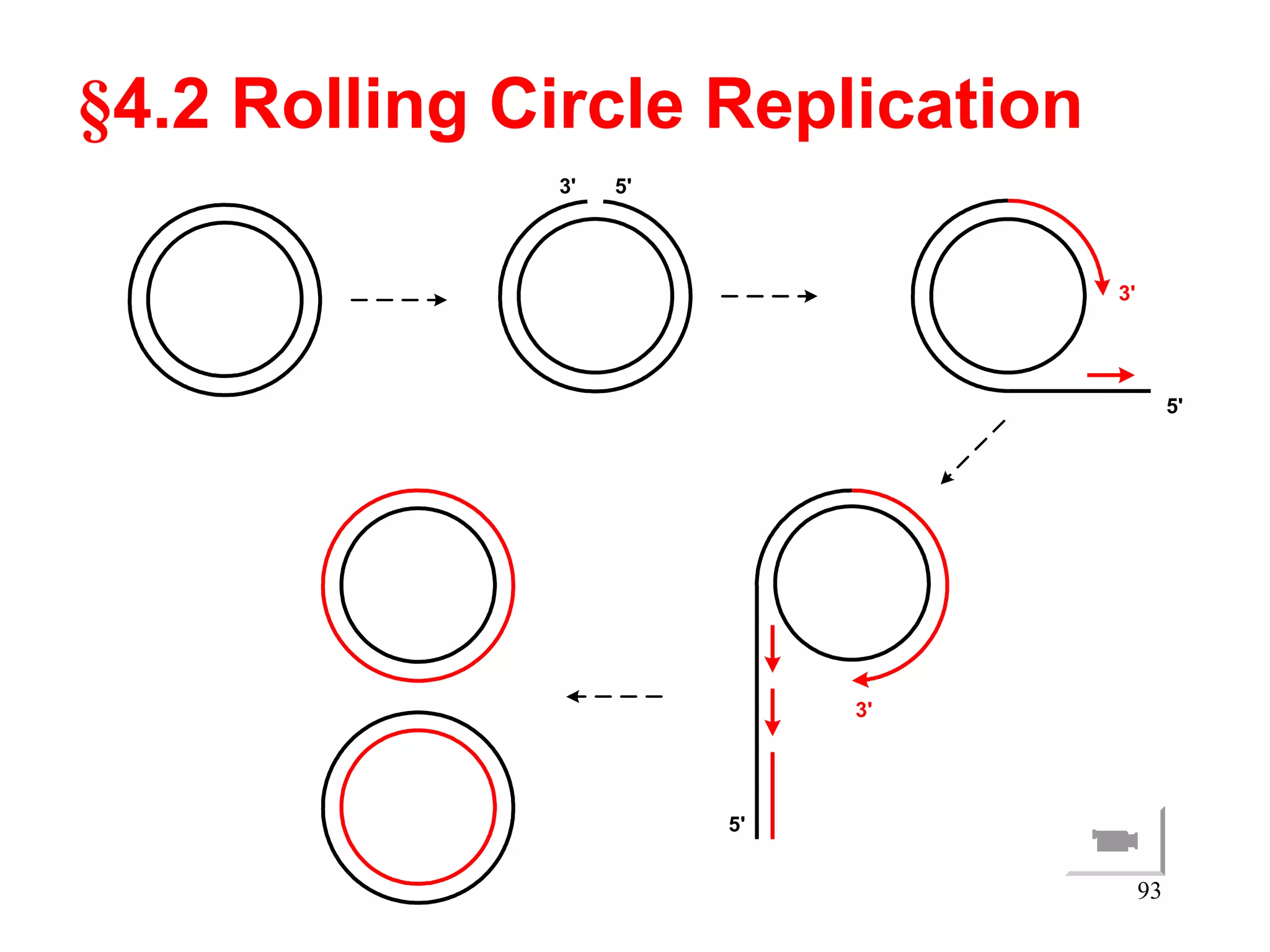
DNA replication is the process whereby a cell passes on its genetic material to its daughter cells. It involves DNA polymerase synthesizing new DNA strands using existing DNA as a template. There are several key steps and enzymes involved:
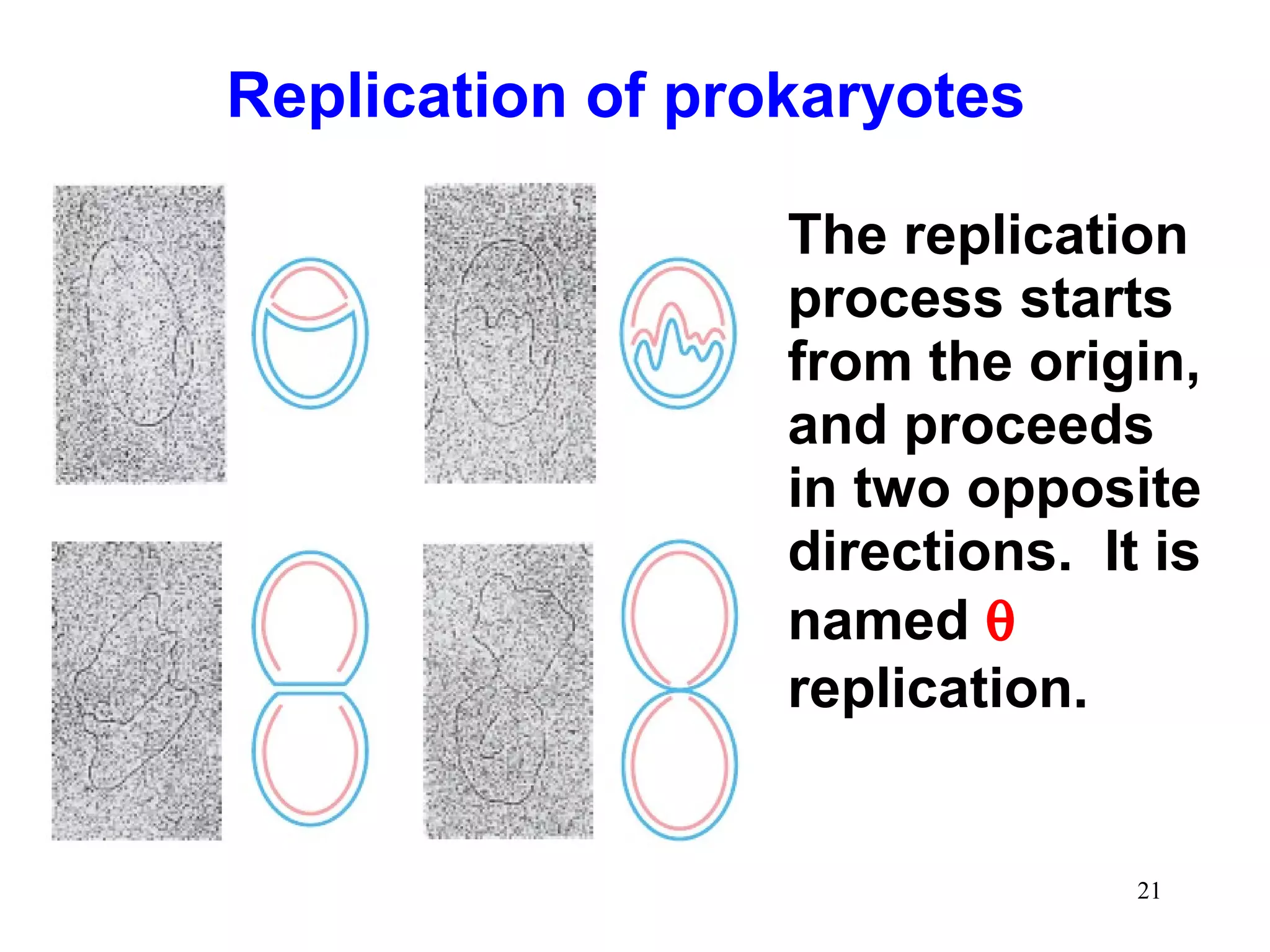
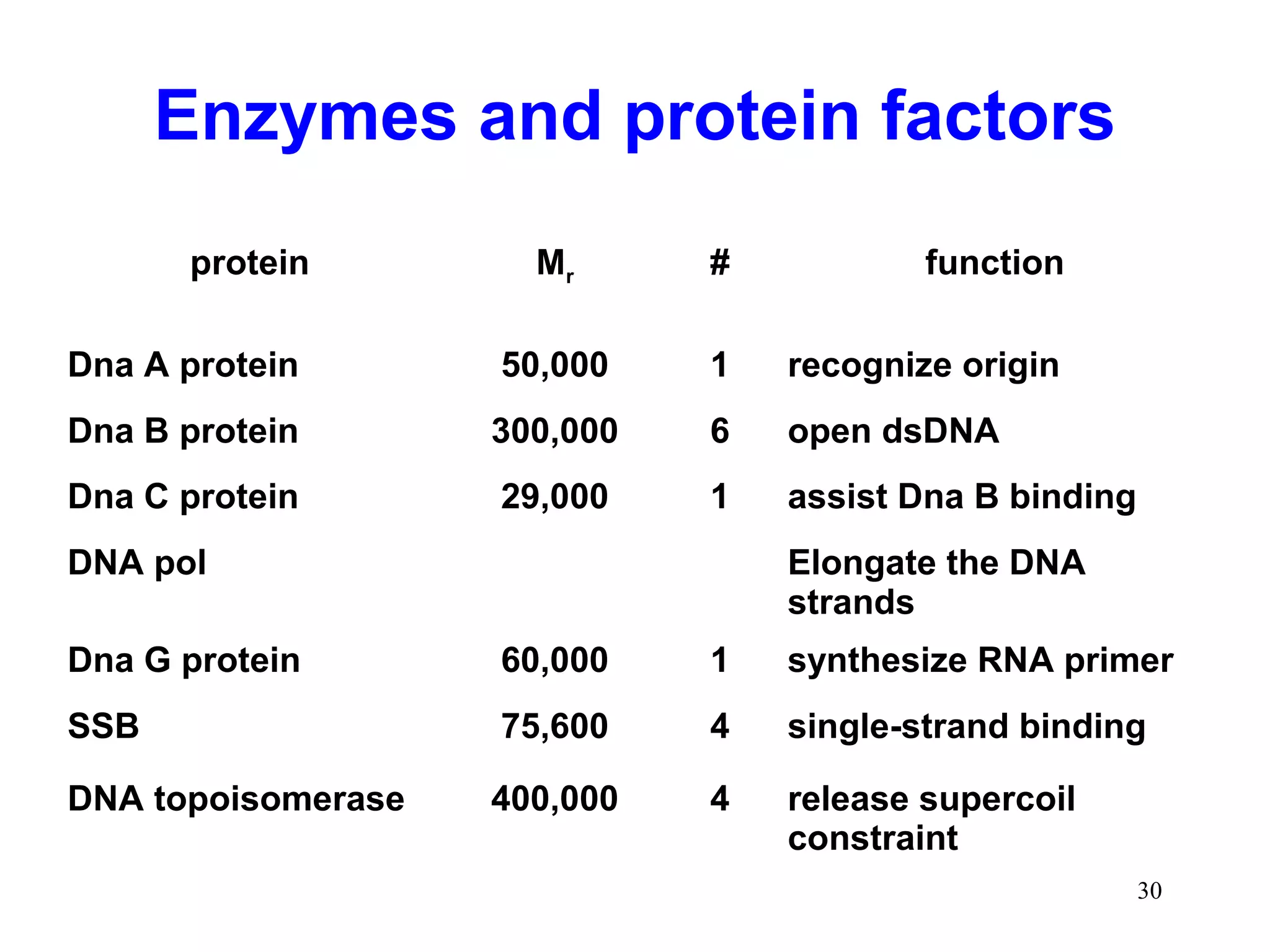
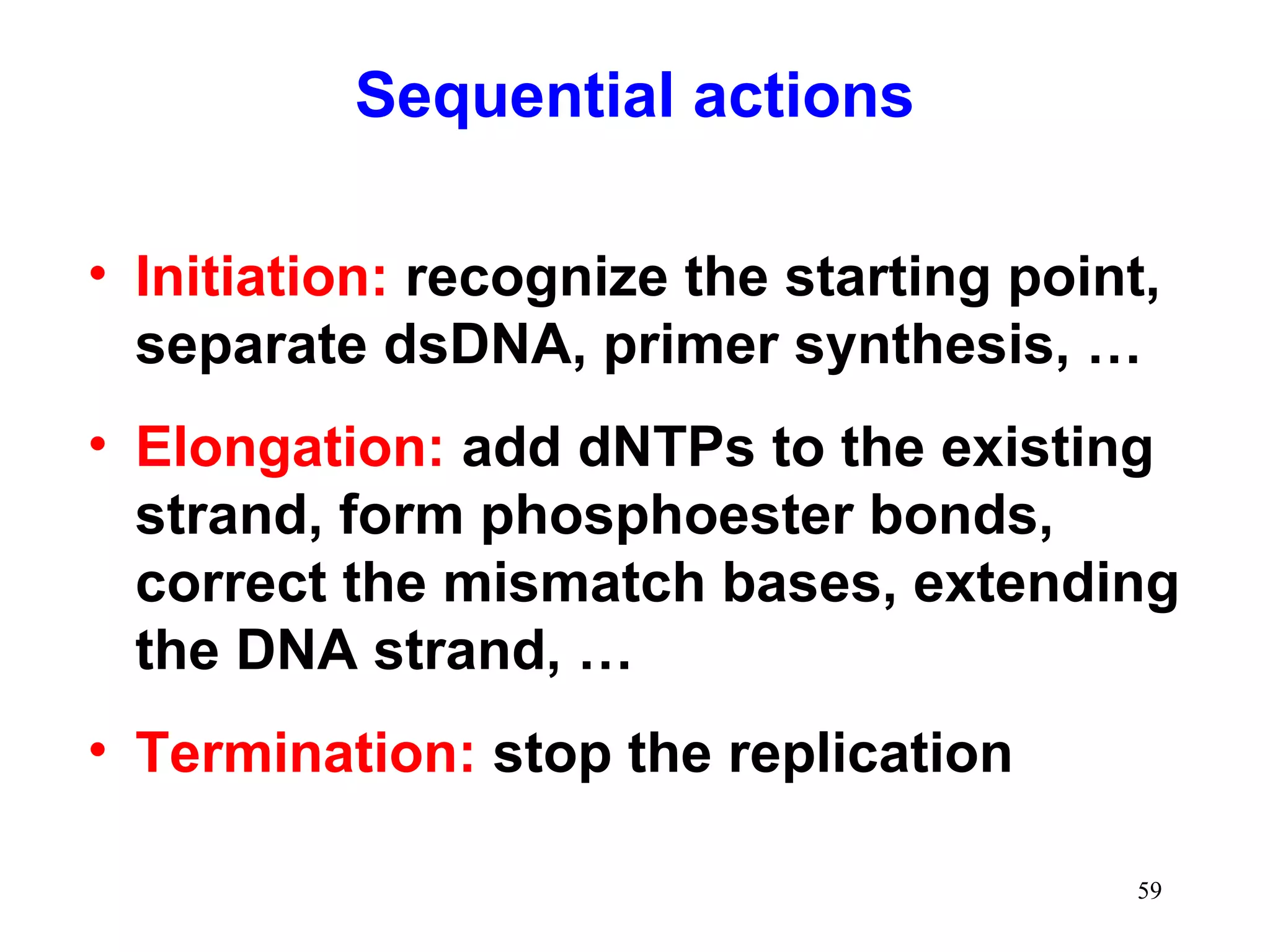
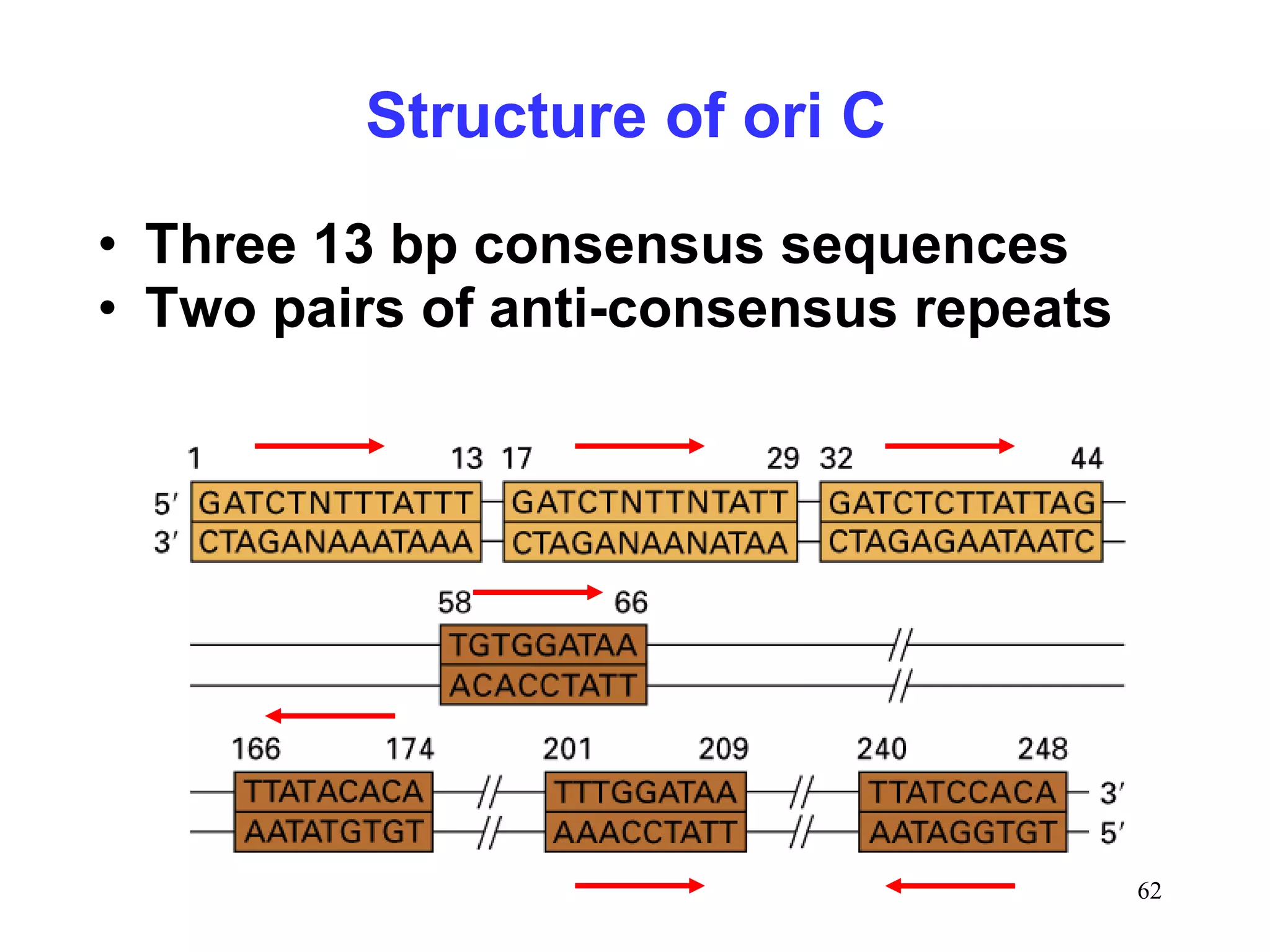
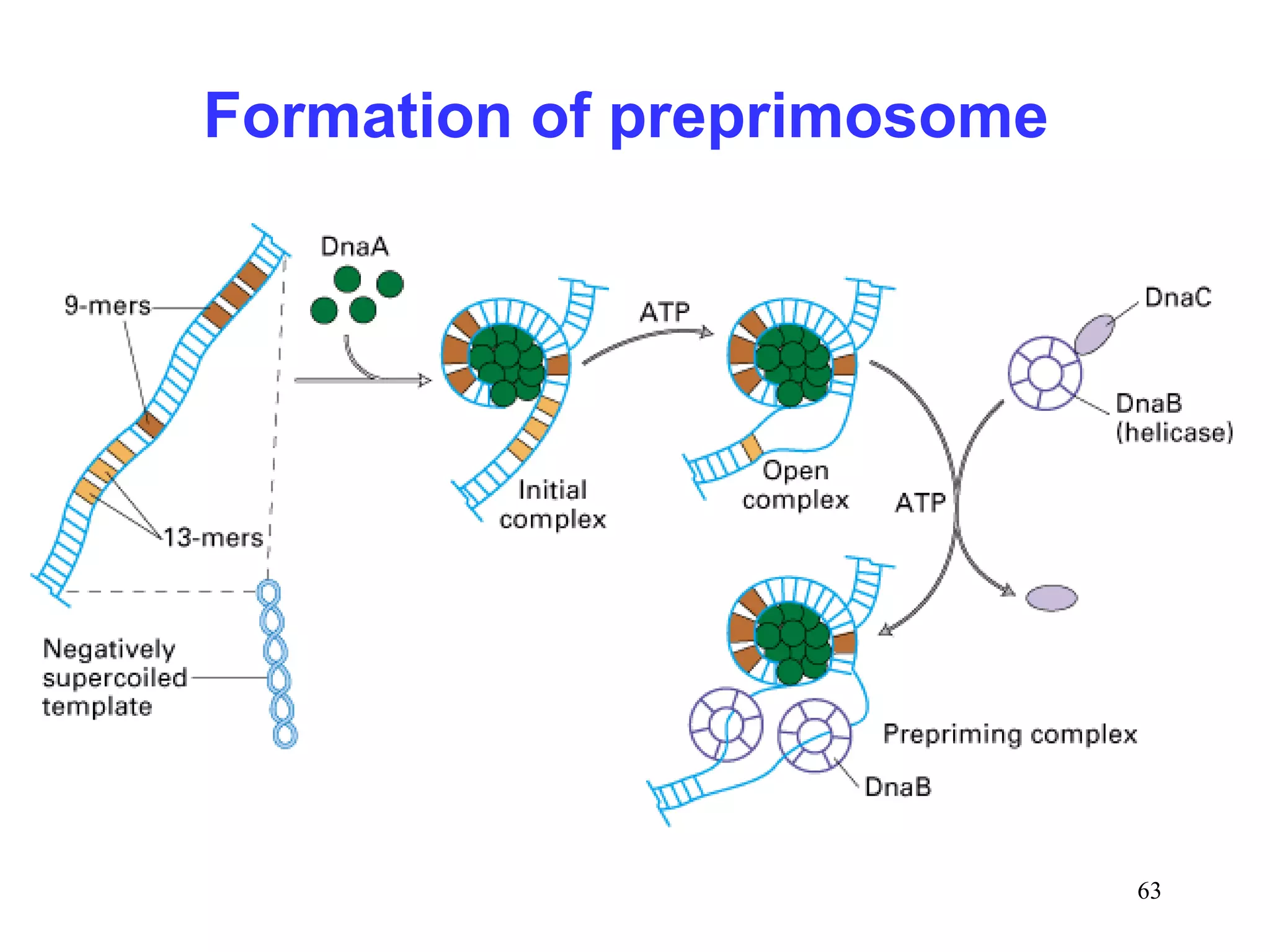
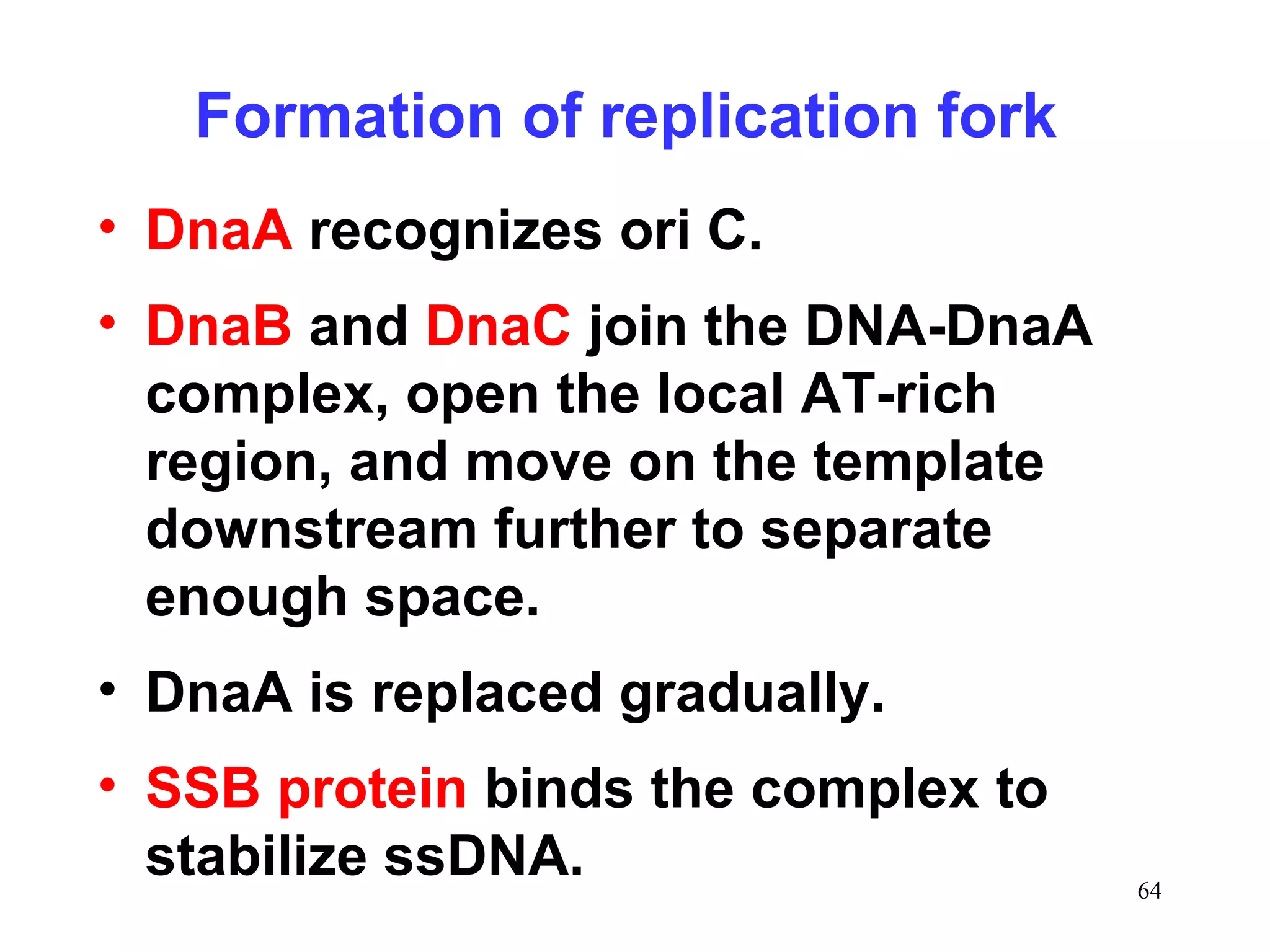
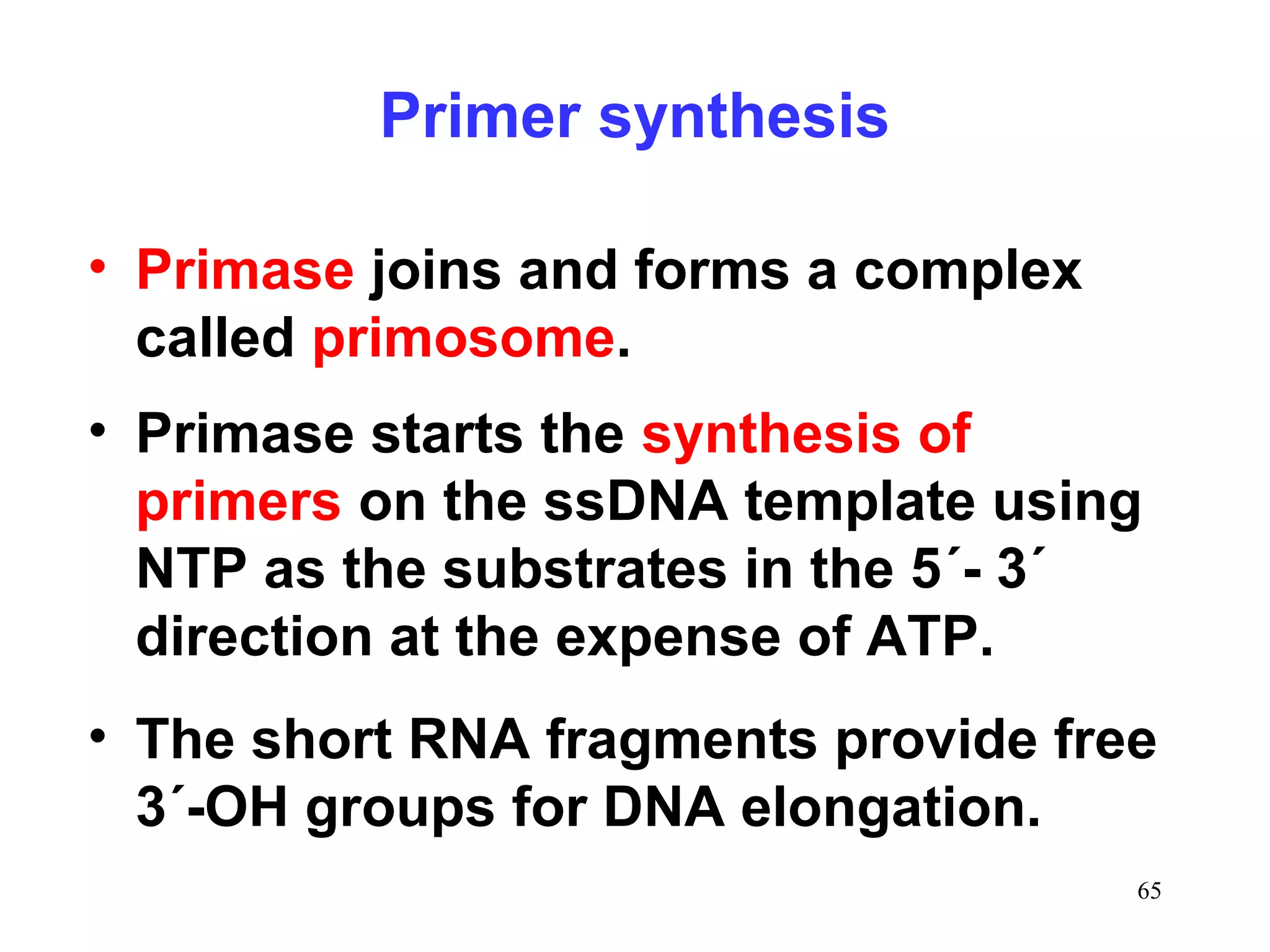
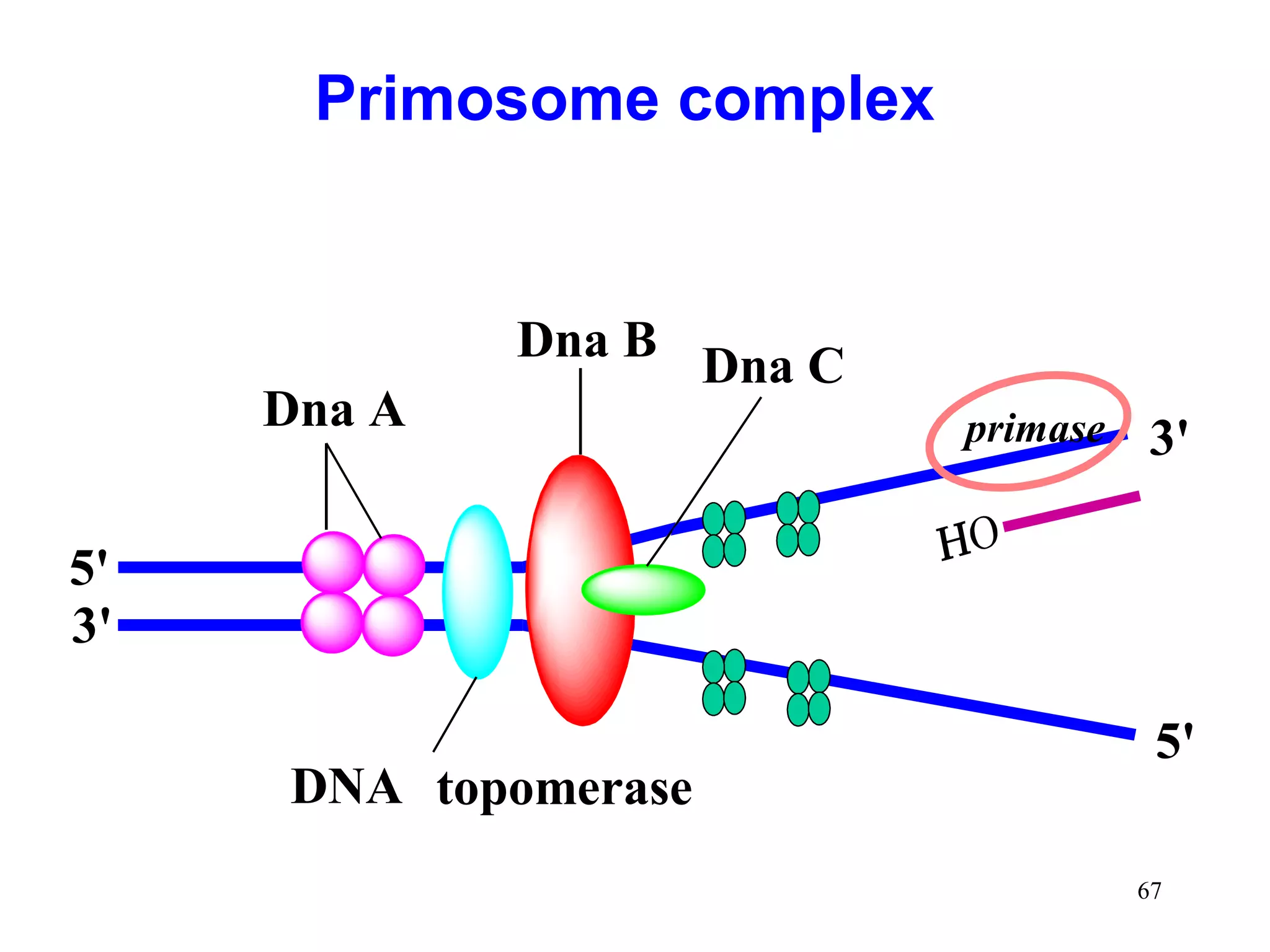
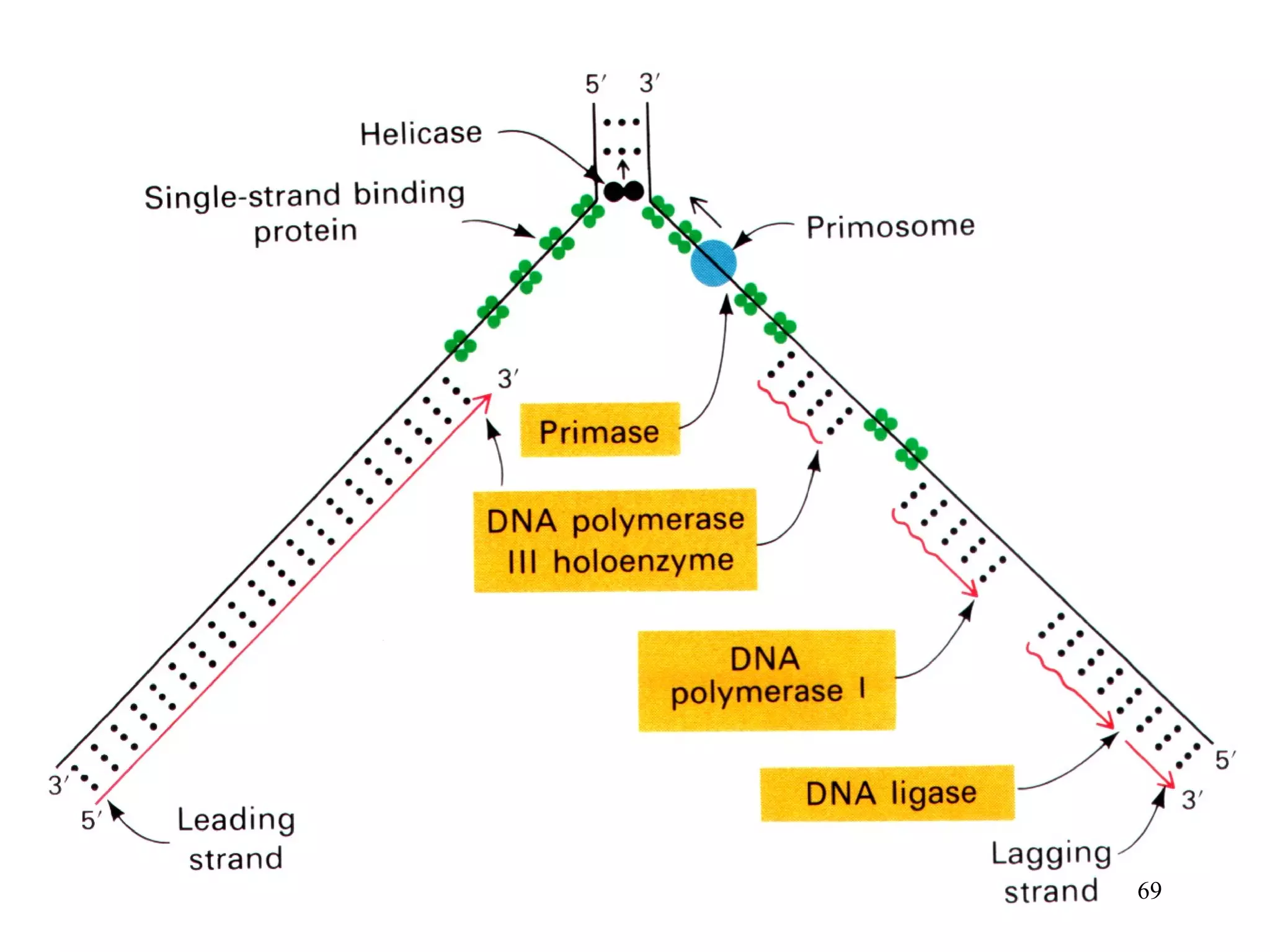
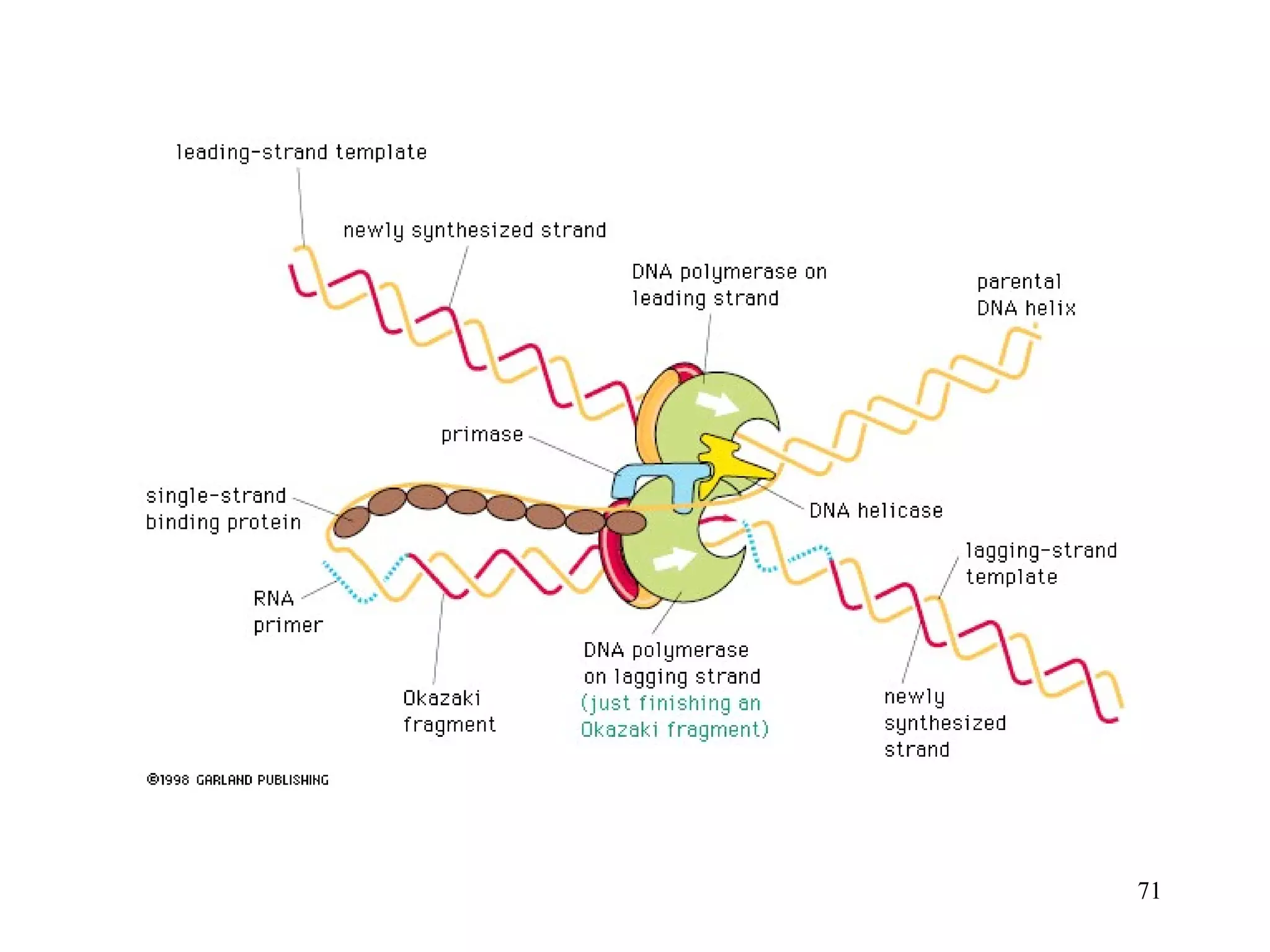
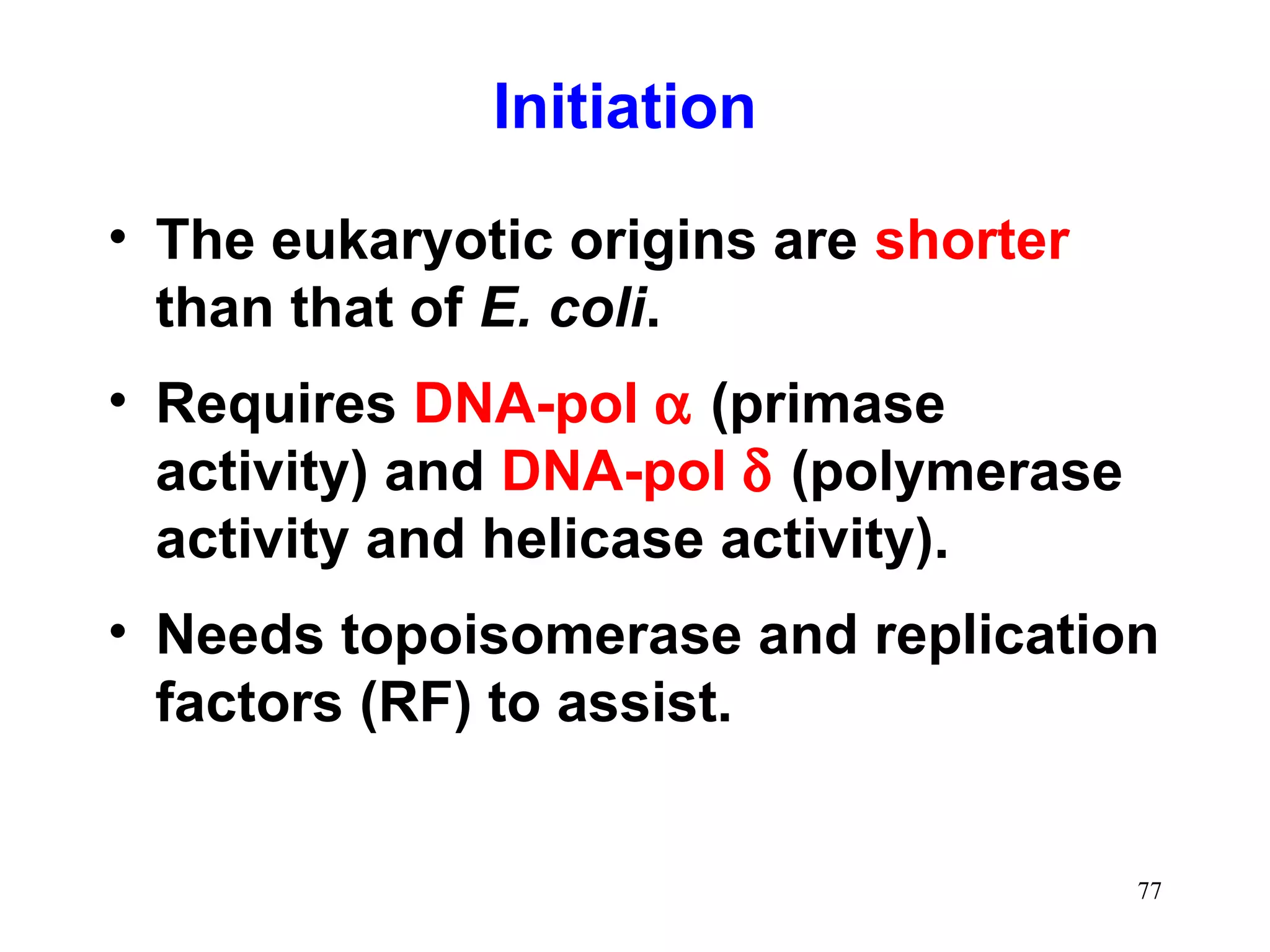
1) Initiation involves enzymes unwinding and separating the parental DNA strands at an origin of replication. RNA primers are synthesized by primase to provide a starting point for DNA polymerase.
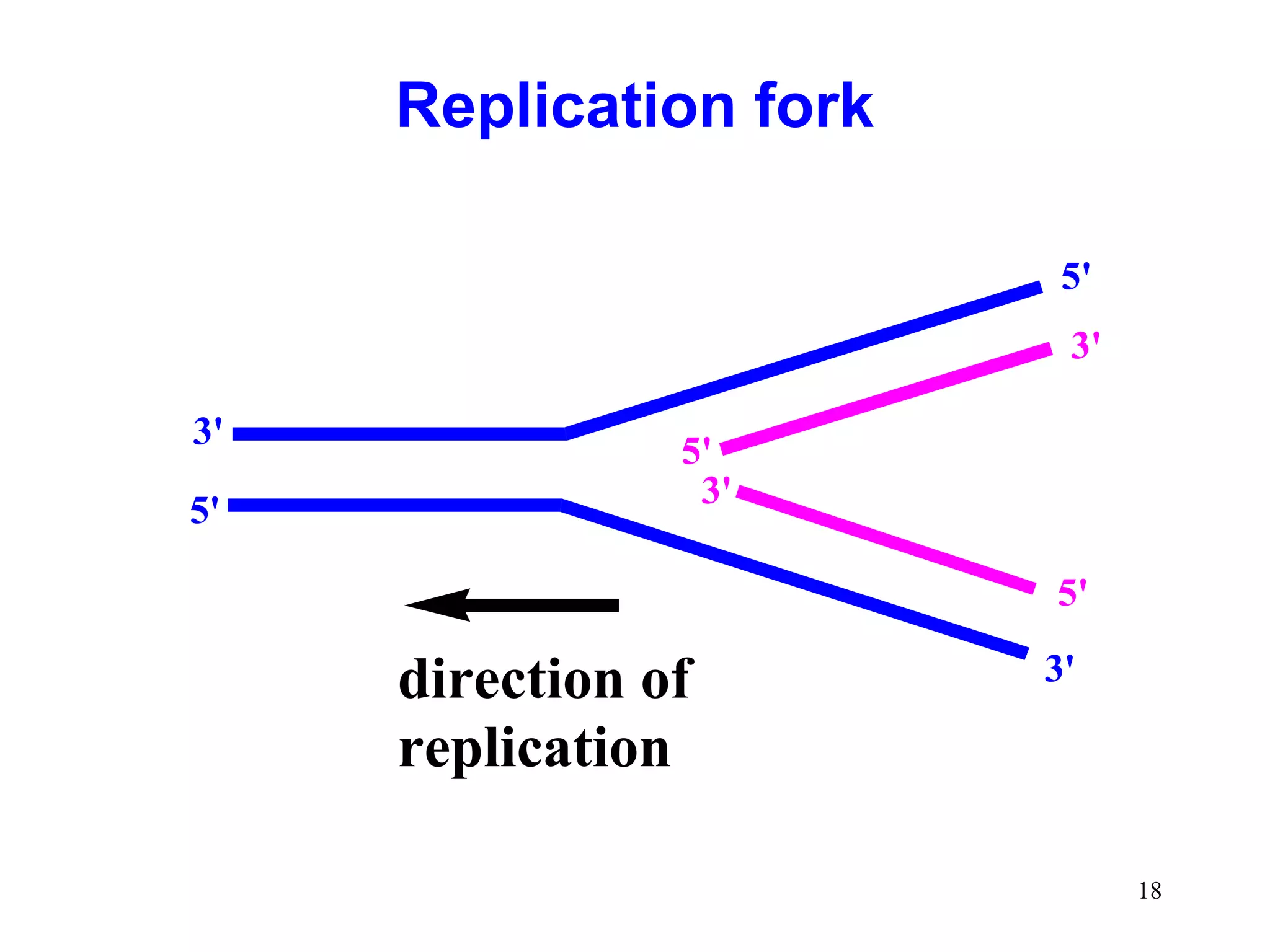
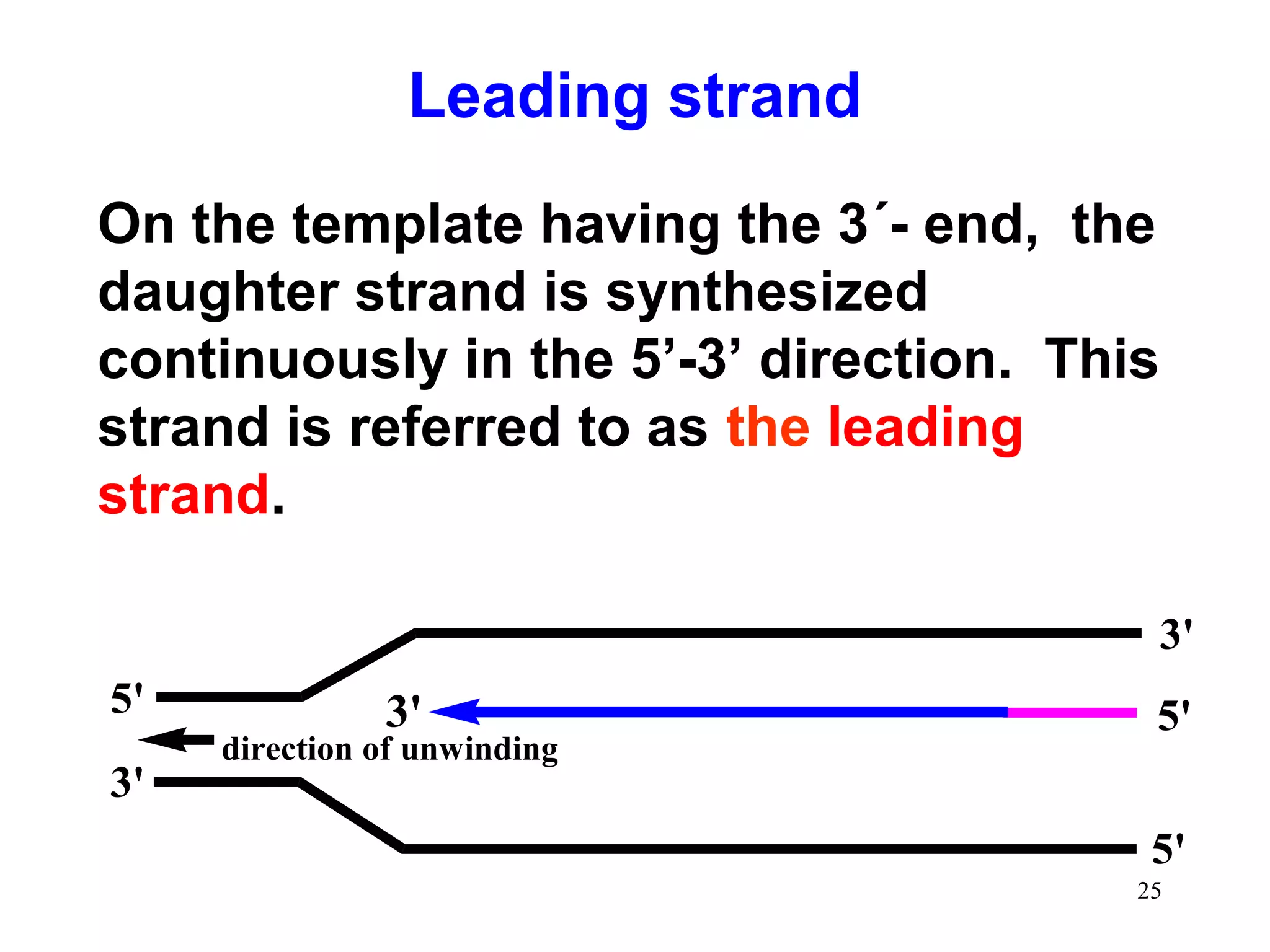
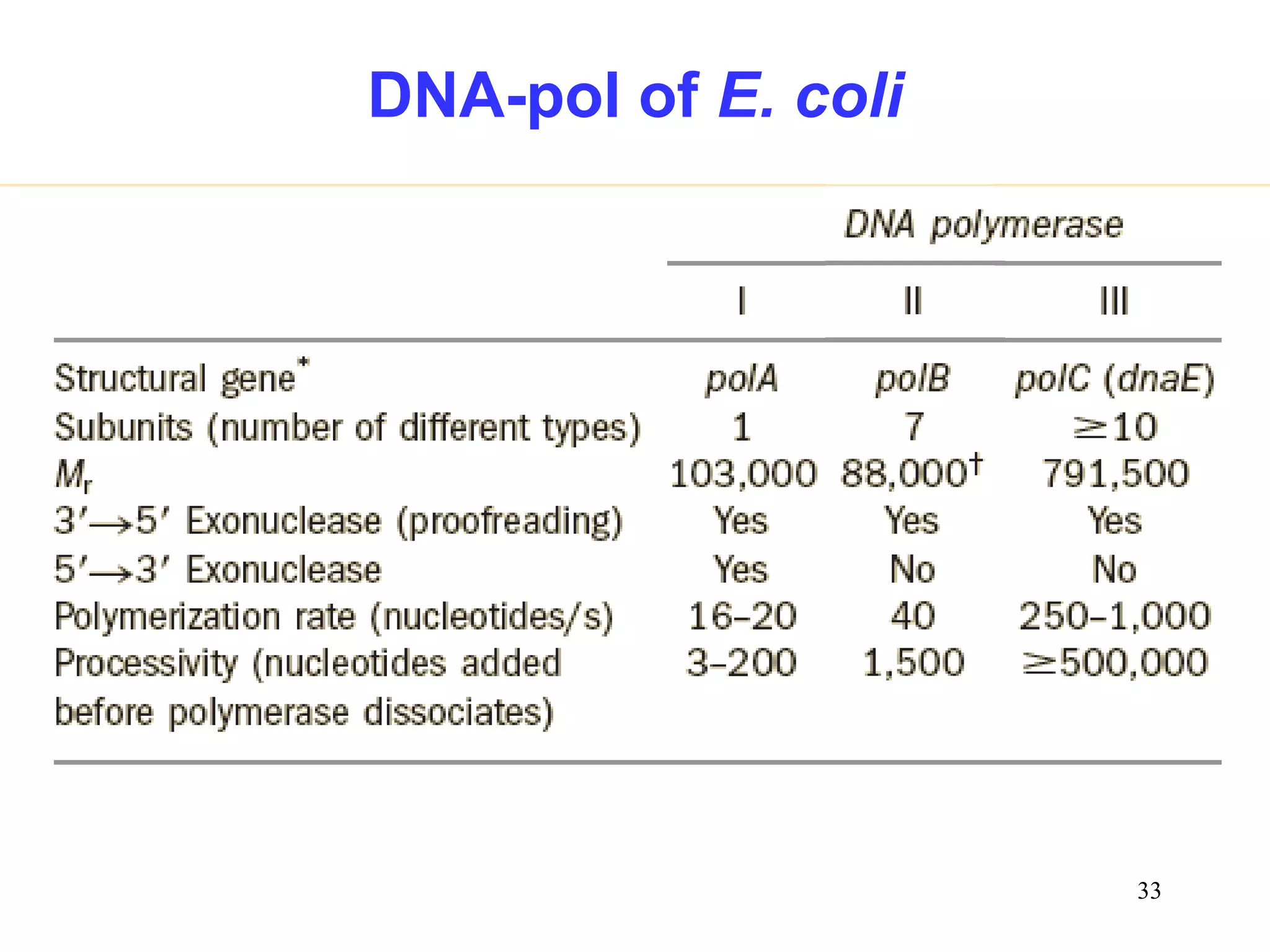
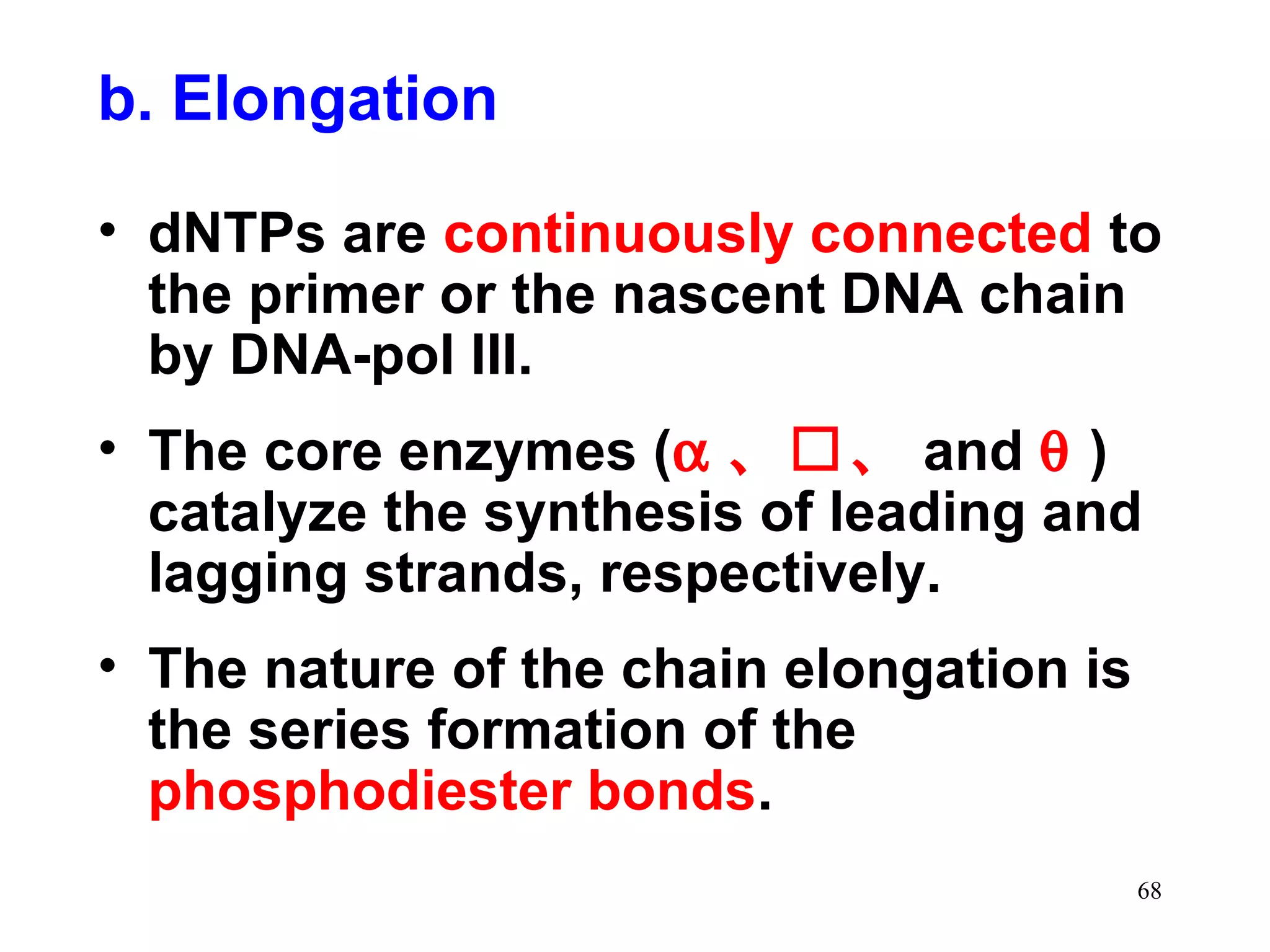
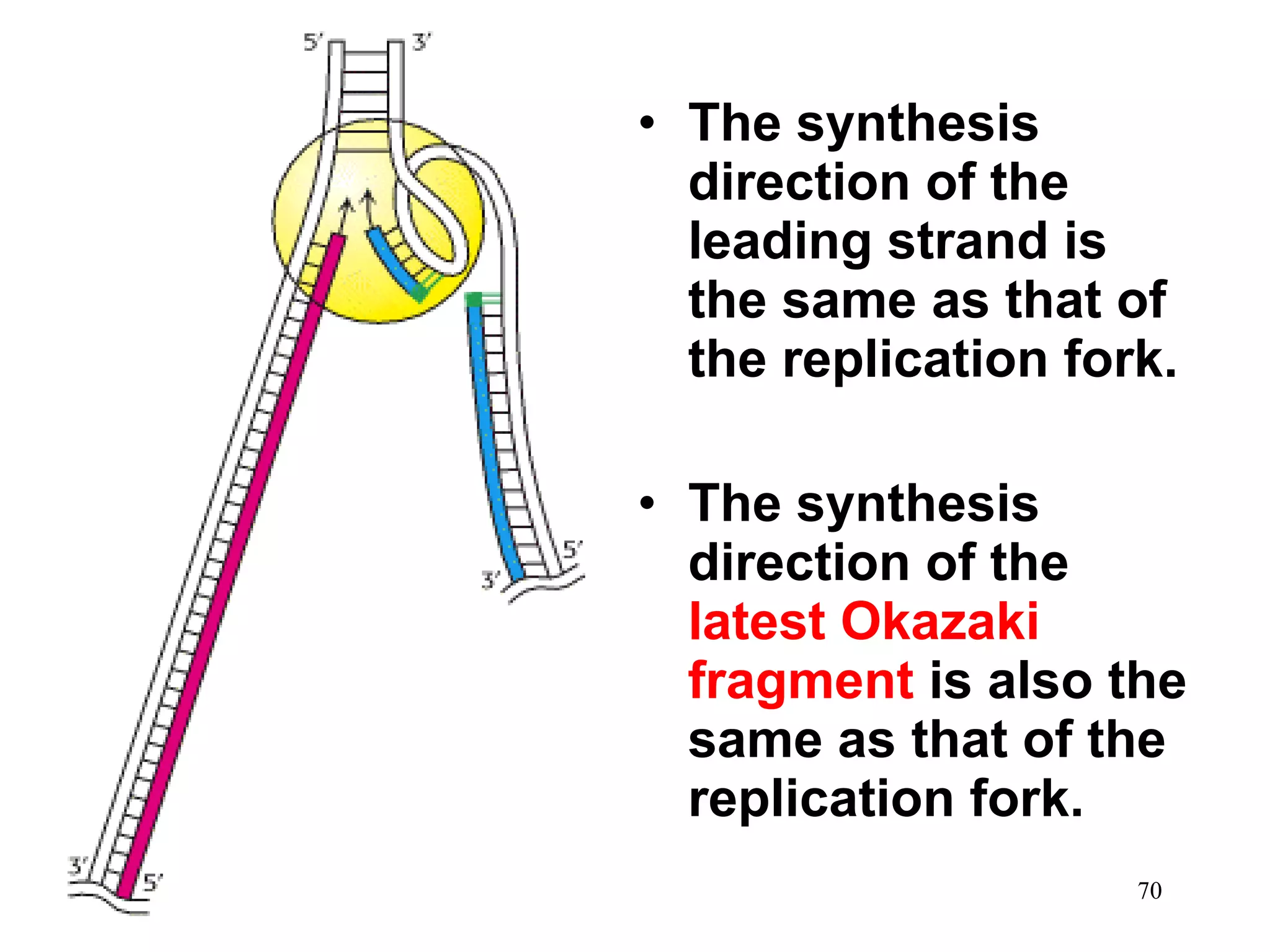
2) Elongation occurs as DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the 3' end of each primer, extending the DNA strands. On the leading strand synthesis is continuous while the lagging strand involves discontinuous Okazaki fragments.
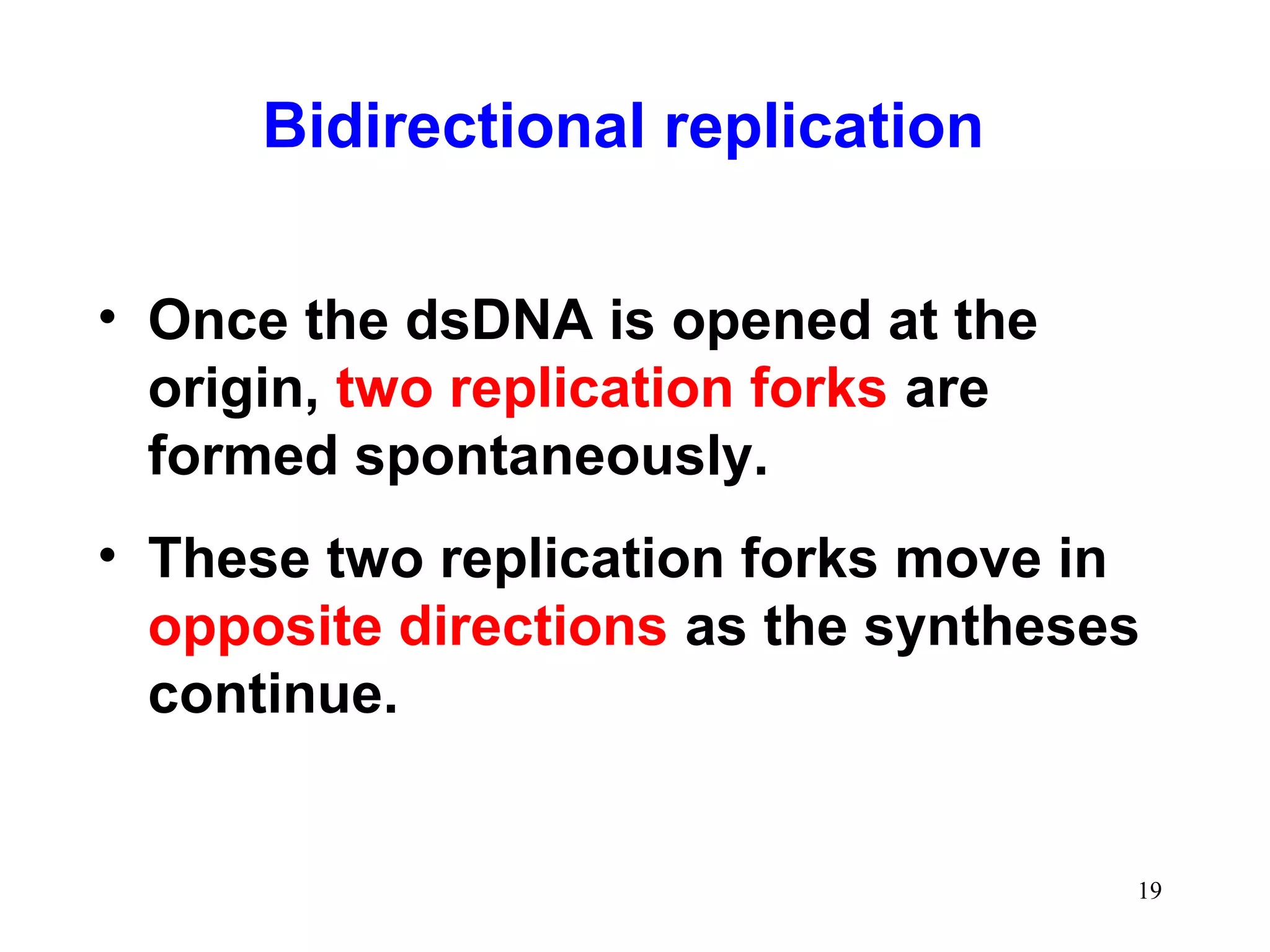
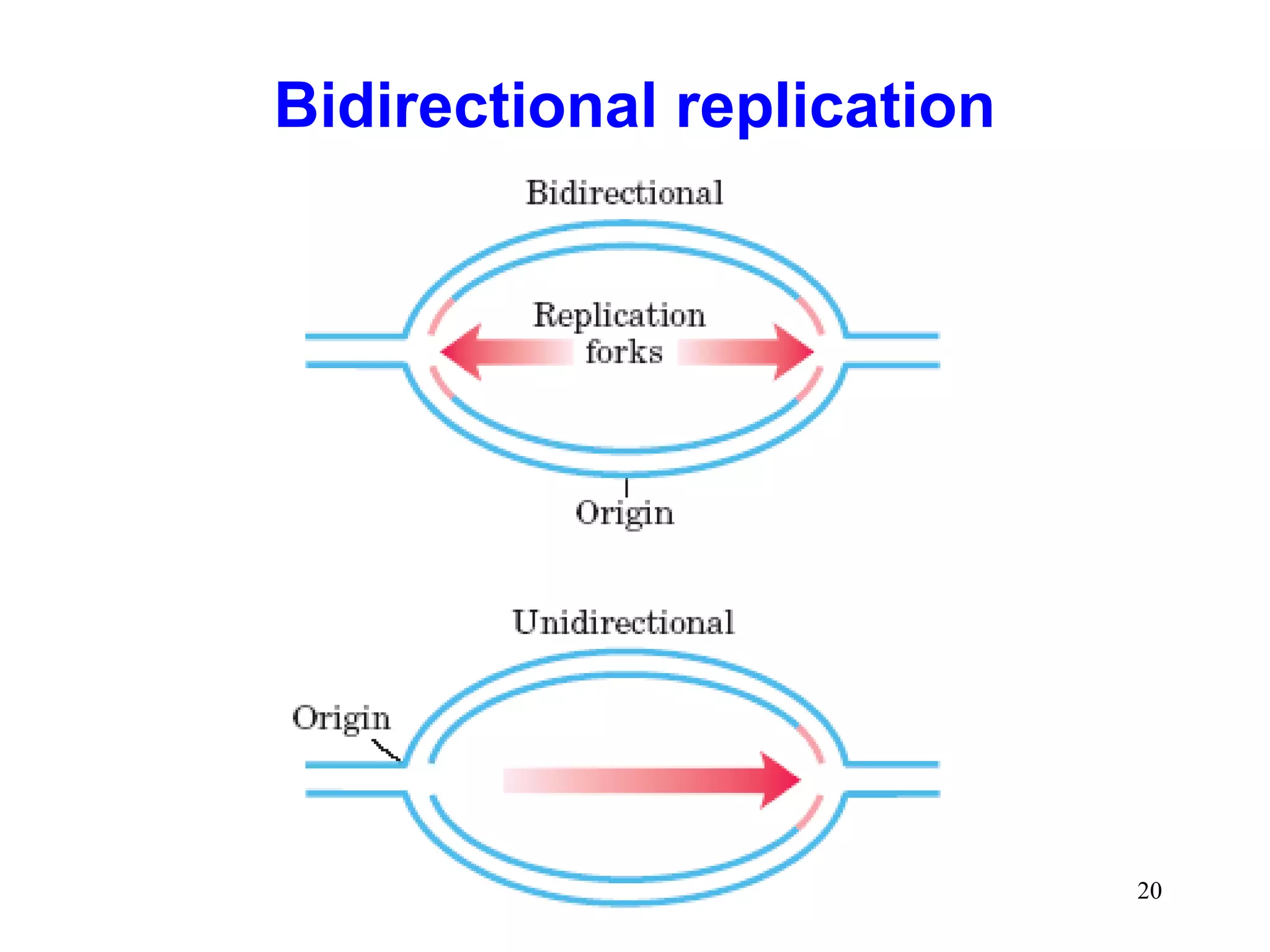
3) Termination occurs when the replication forks from bidirectional replication converge, all