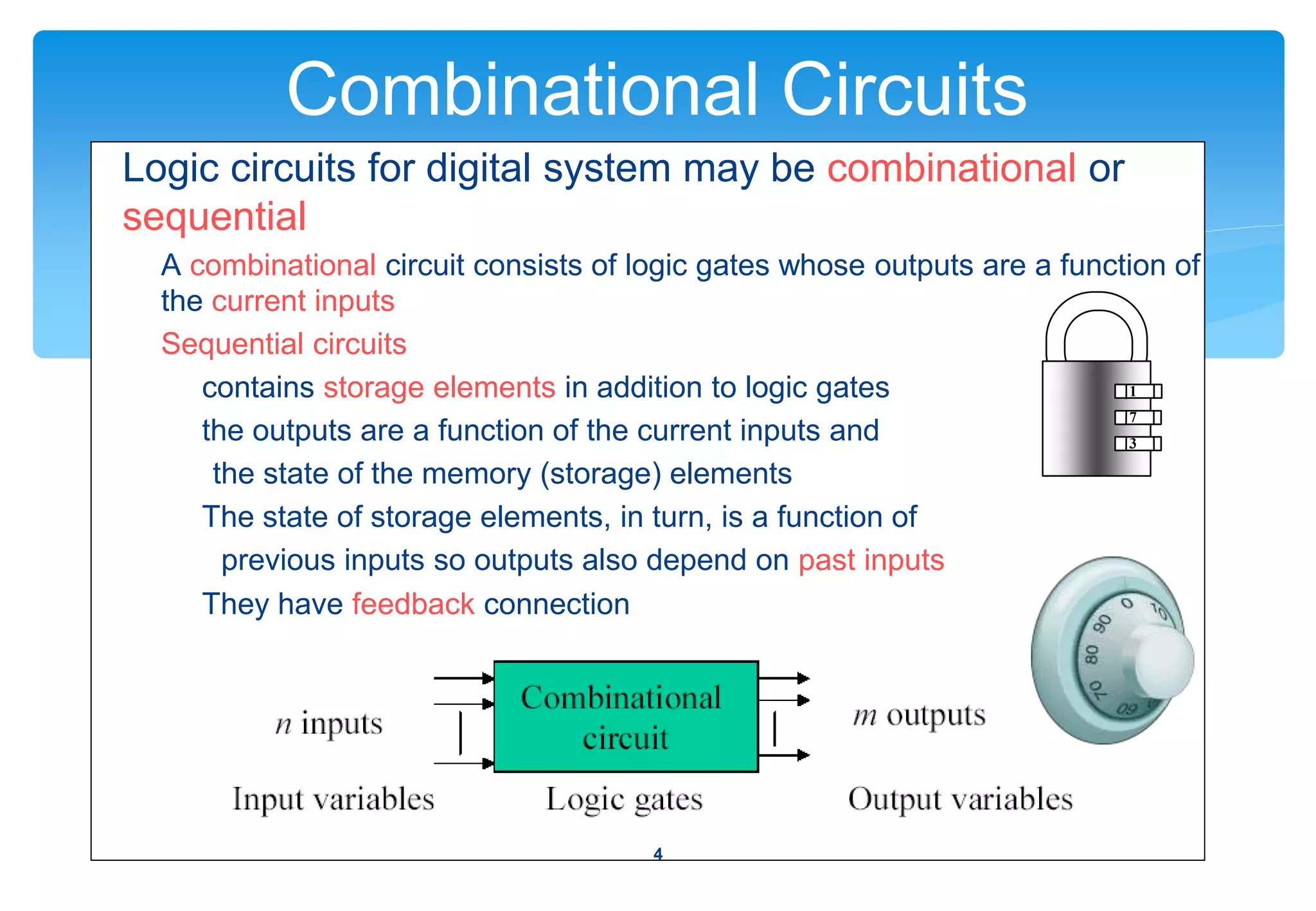
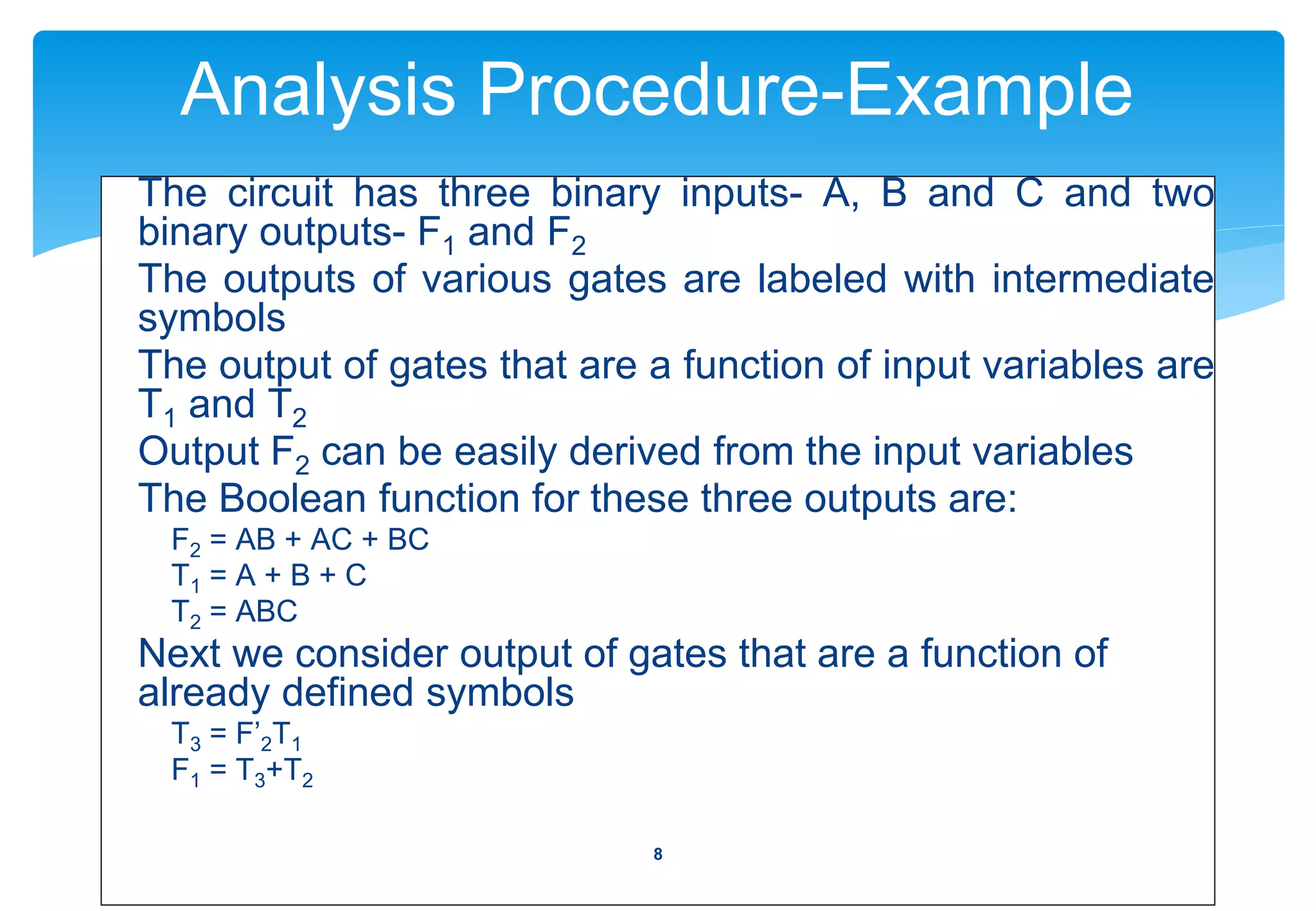
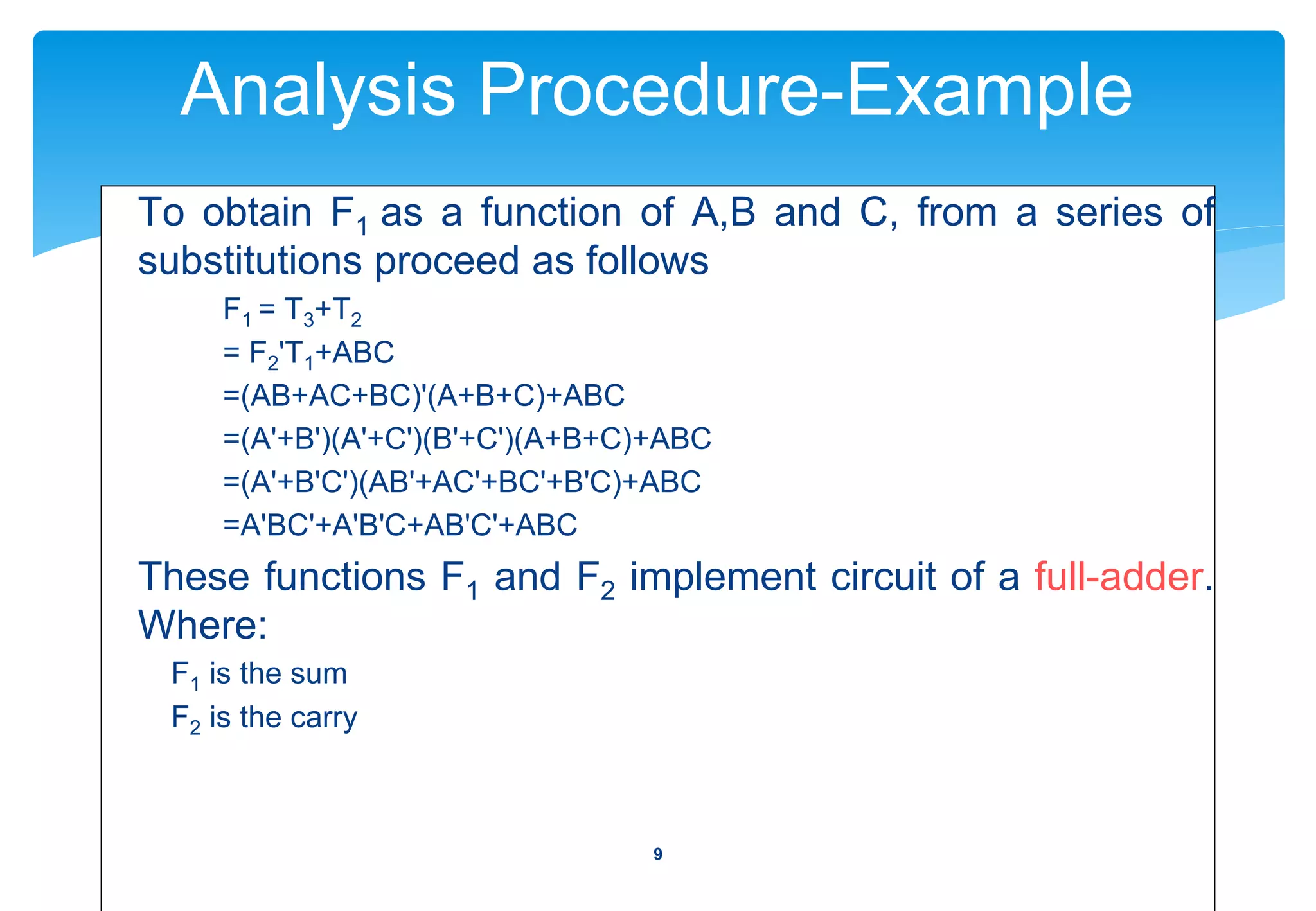
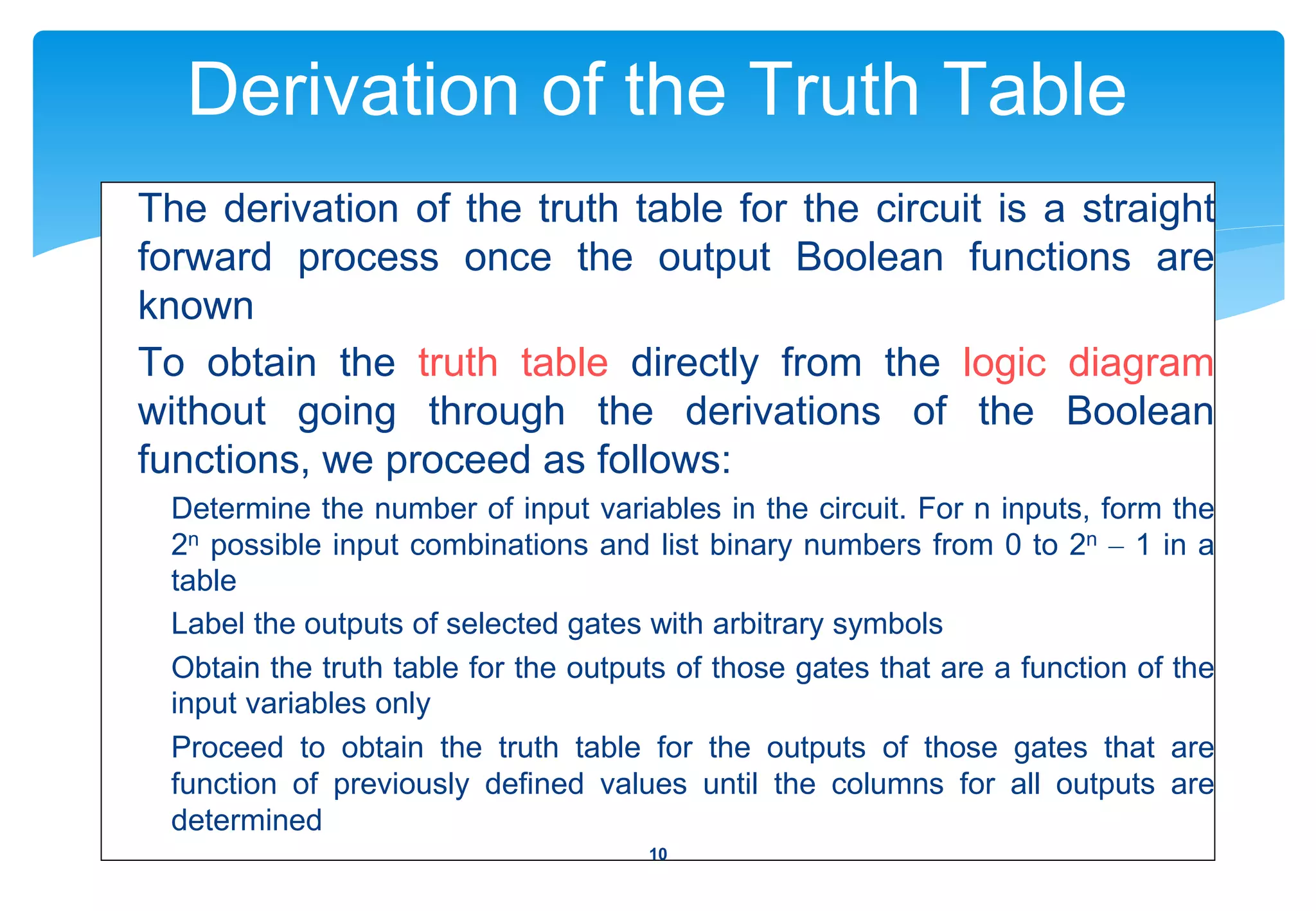
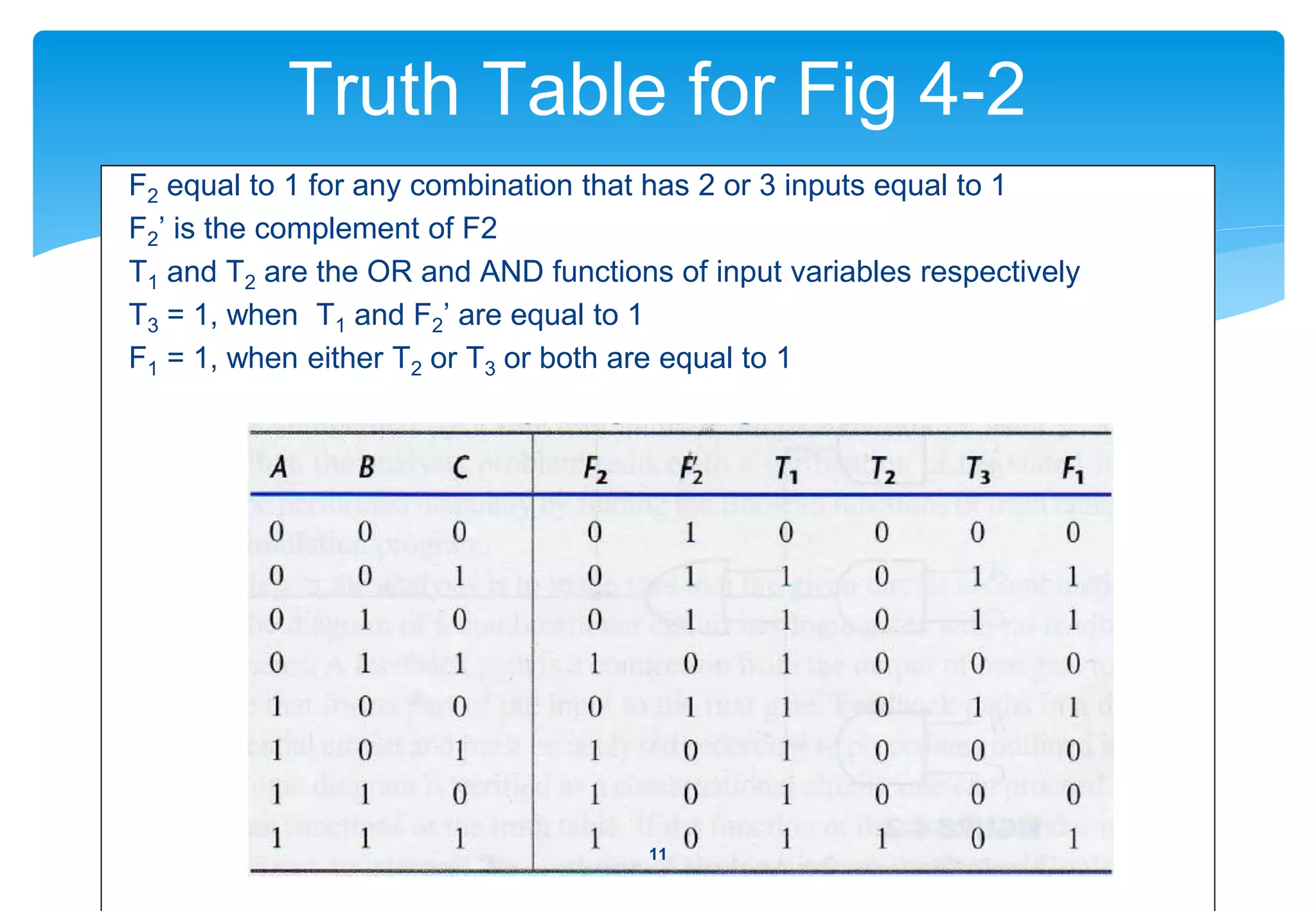
This document discusses the analysis and design of combinational circuits. It begins by defining combinational circuits as logic circuits whose outputs depend only on current inputs, as opposed to sequential circuits whose outputs depend on both current inputs and past states. The summary discusses:
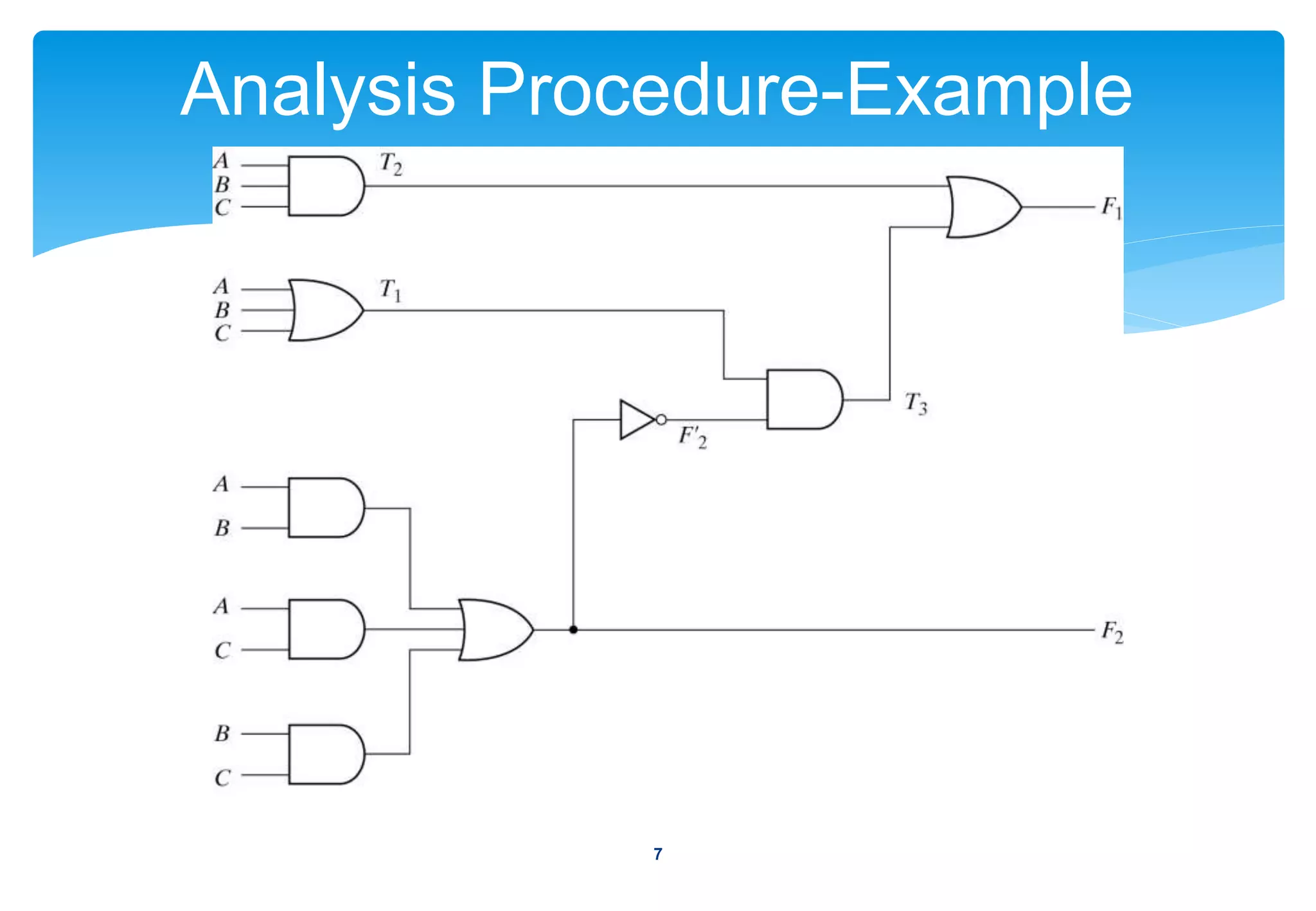
1) The analysis procedure for combinational circuits, which involves determining the Boolean functions that define the circuit's behavior.
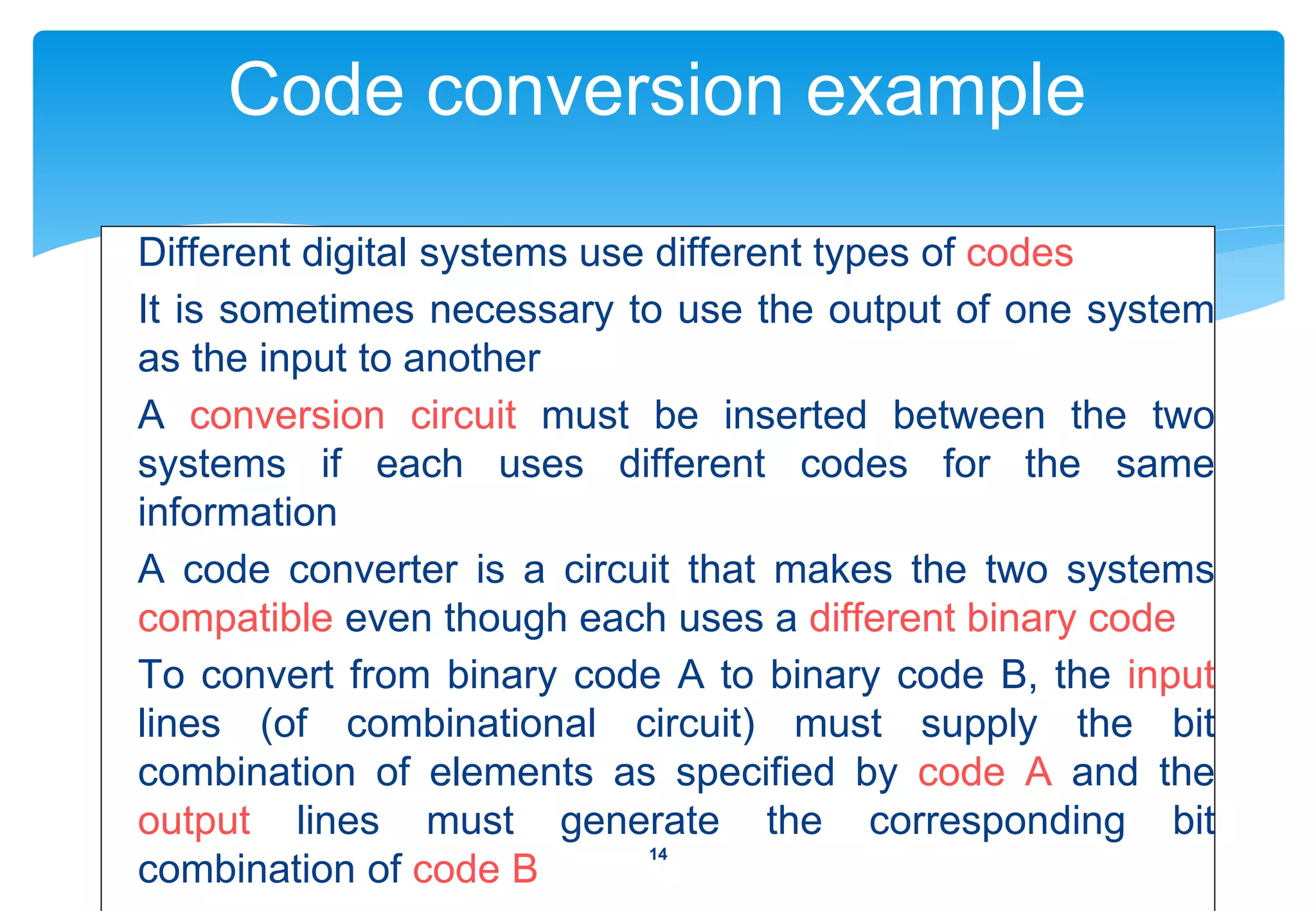
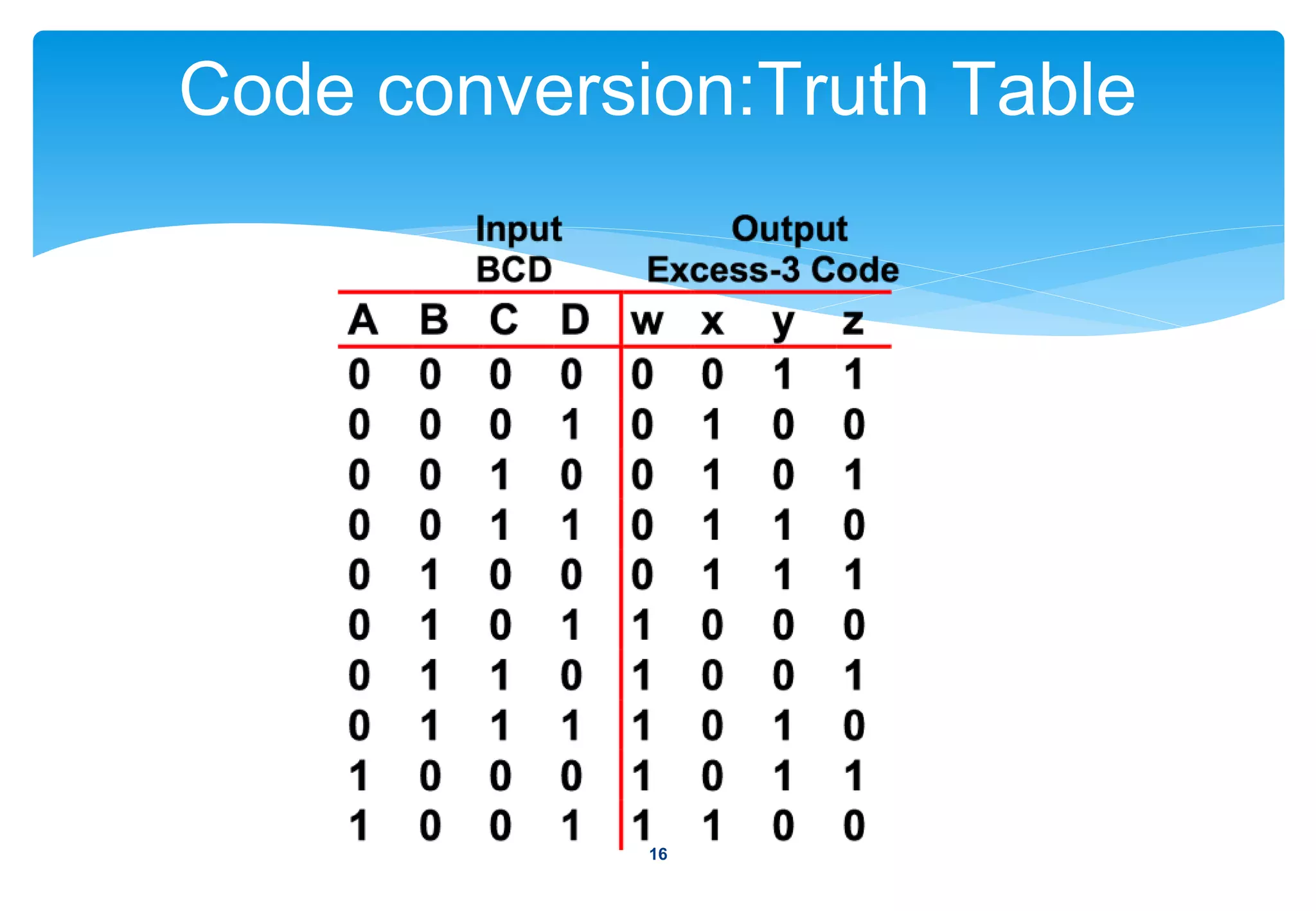
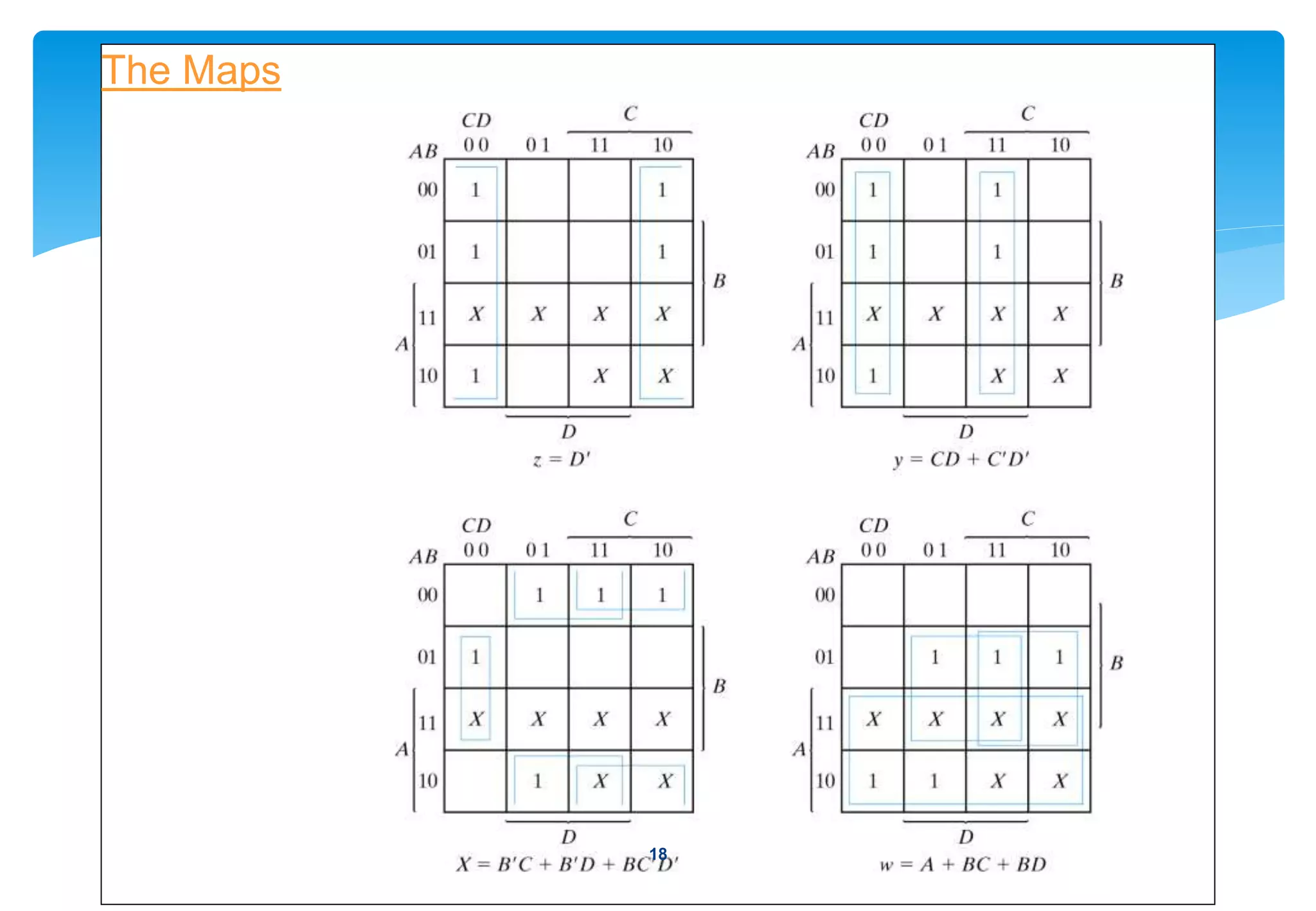
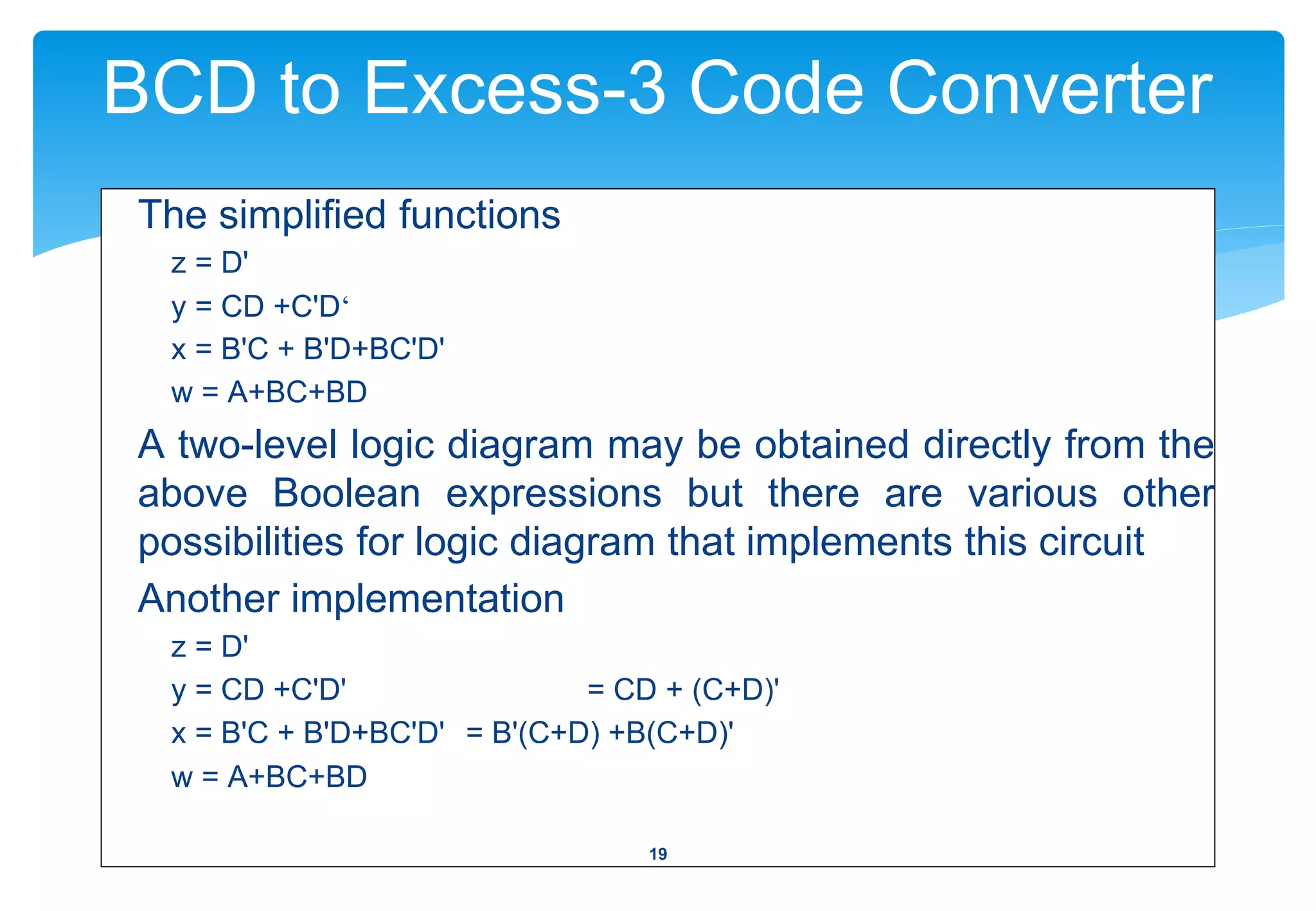
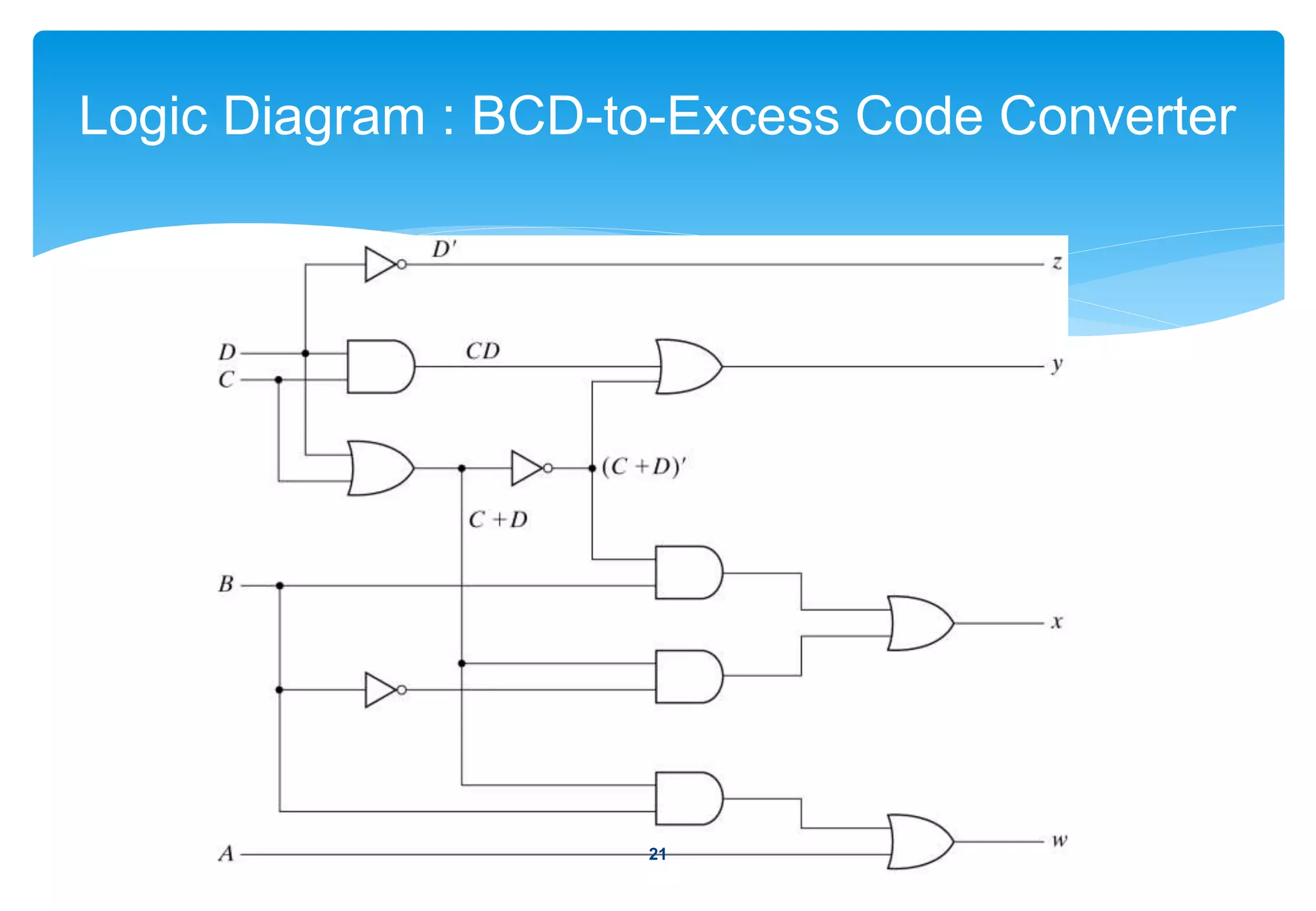
2) Examples of common combinational circuits like code converters, which change one binary code to another.
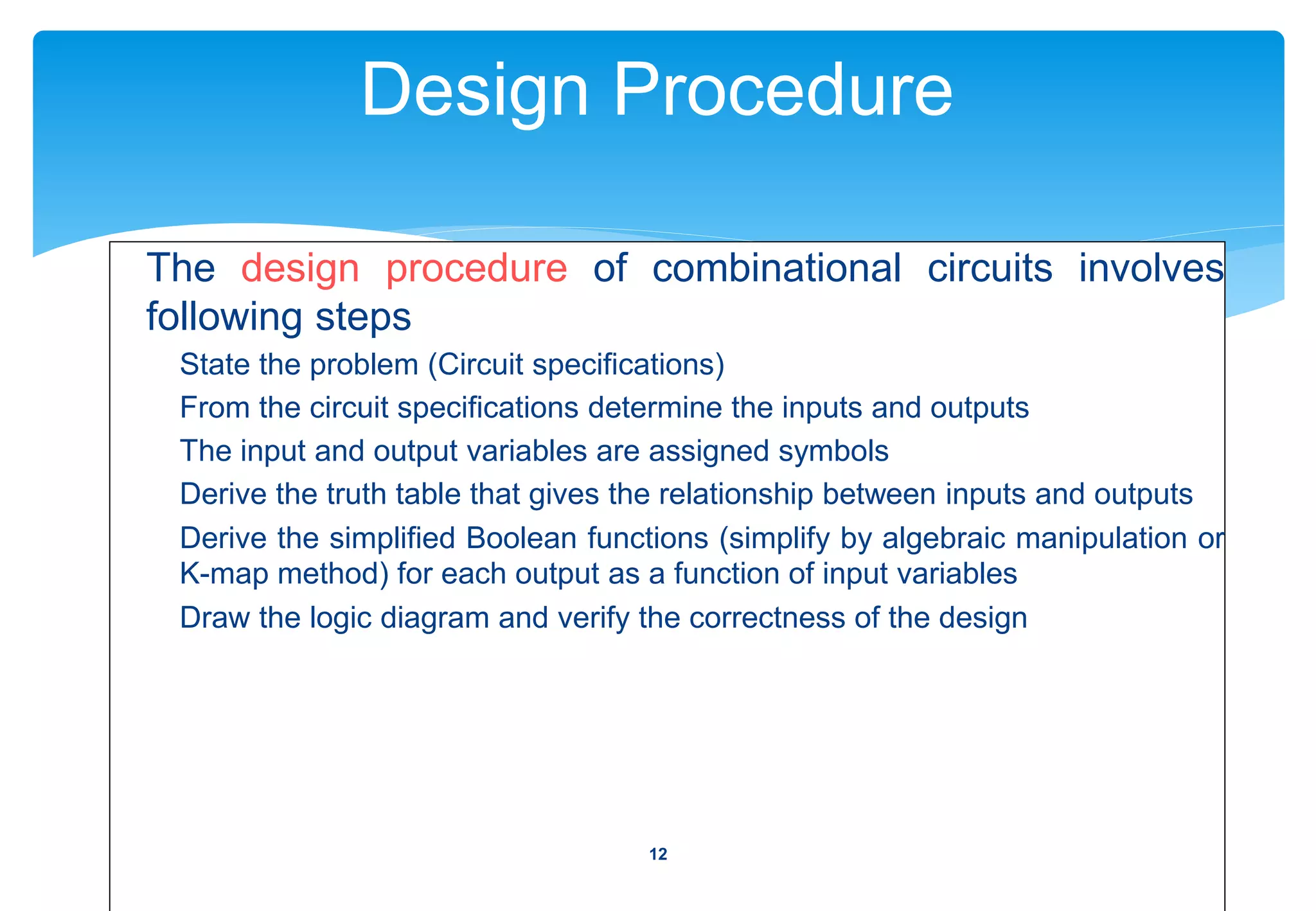
3) The design procedure, which involves specifying inputs/outputs, deriving truth tables, simplifying Boolean functions, and drawing logic diagrams.