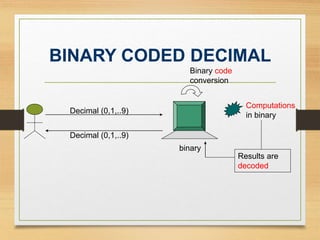
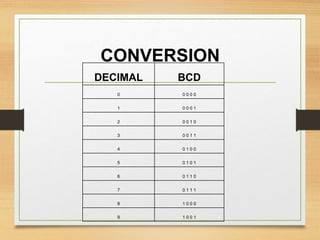
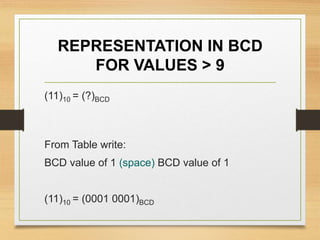
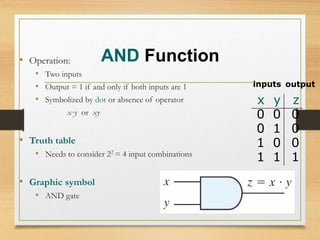
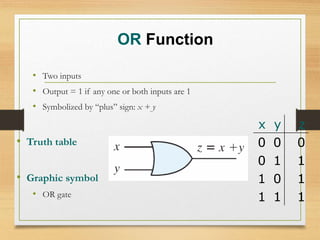
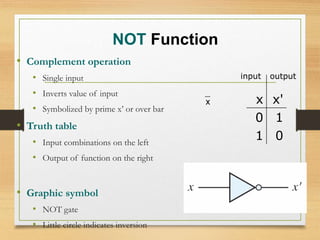
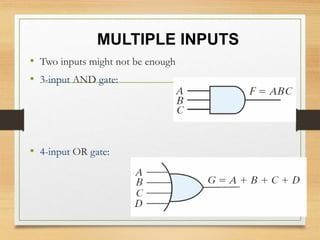
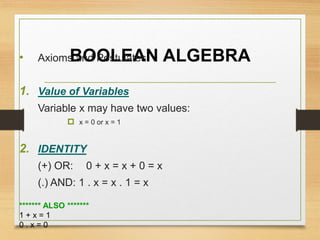
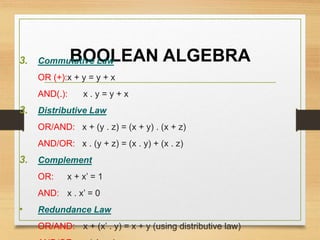
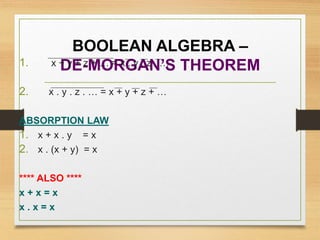
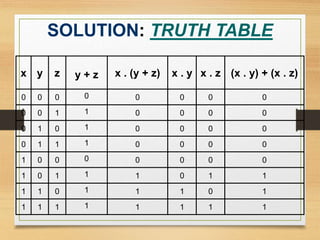
This document provides an overview of binary codes and Boolean algebra concepts. It discusses various binary codes like BCD, excess-3, and Gray codes. It also covers logical operations in Boolean algebra like AND, OR, and NOT. Properties of Boolean algebra like duality, De Morgan's laws, and absorption laws are explained. Digital logic gates are introduced as implementations of Boolean functions.