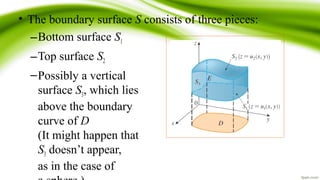
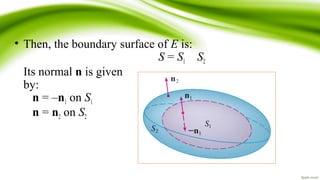
The document summarizes the Divergence Theorem. It states that the theorem relates the integral of the divergence of a vector field F over a region E to the surface integral of F over the boundary S of E. Specifically, the theorem states that the flux of F across S is equal to the triple integral of the divergence of F over E, for a region E that is a simple solid region or a finite union of such regions, and when F has continuous partial derivatives on a region containing E. An example application to computing the flux of a vector field over a unit sphere is also provided.