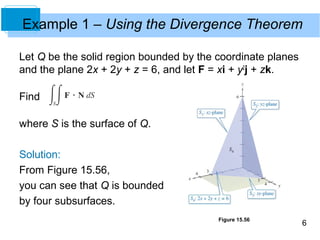
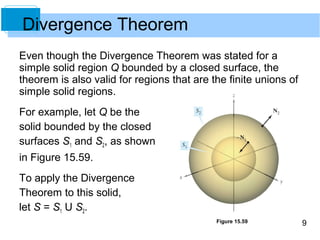
The document discusses the Divergence Theorem, which relates a triple integral over a solid region to a surface integral over the boundary of the region. It states that for a solid region Q bounded by a closed surface S, the theorem equates the triple integral of the divergence of a vector field F over Q to the surface integral of F dotted with the outward normal vector over S. An example application of the theorem is shown to evaluate a triple integral using a single surface integral instead of multiple ones.