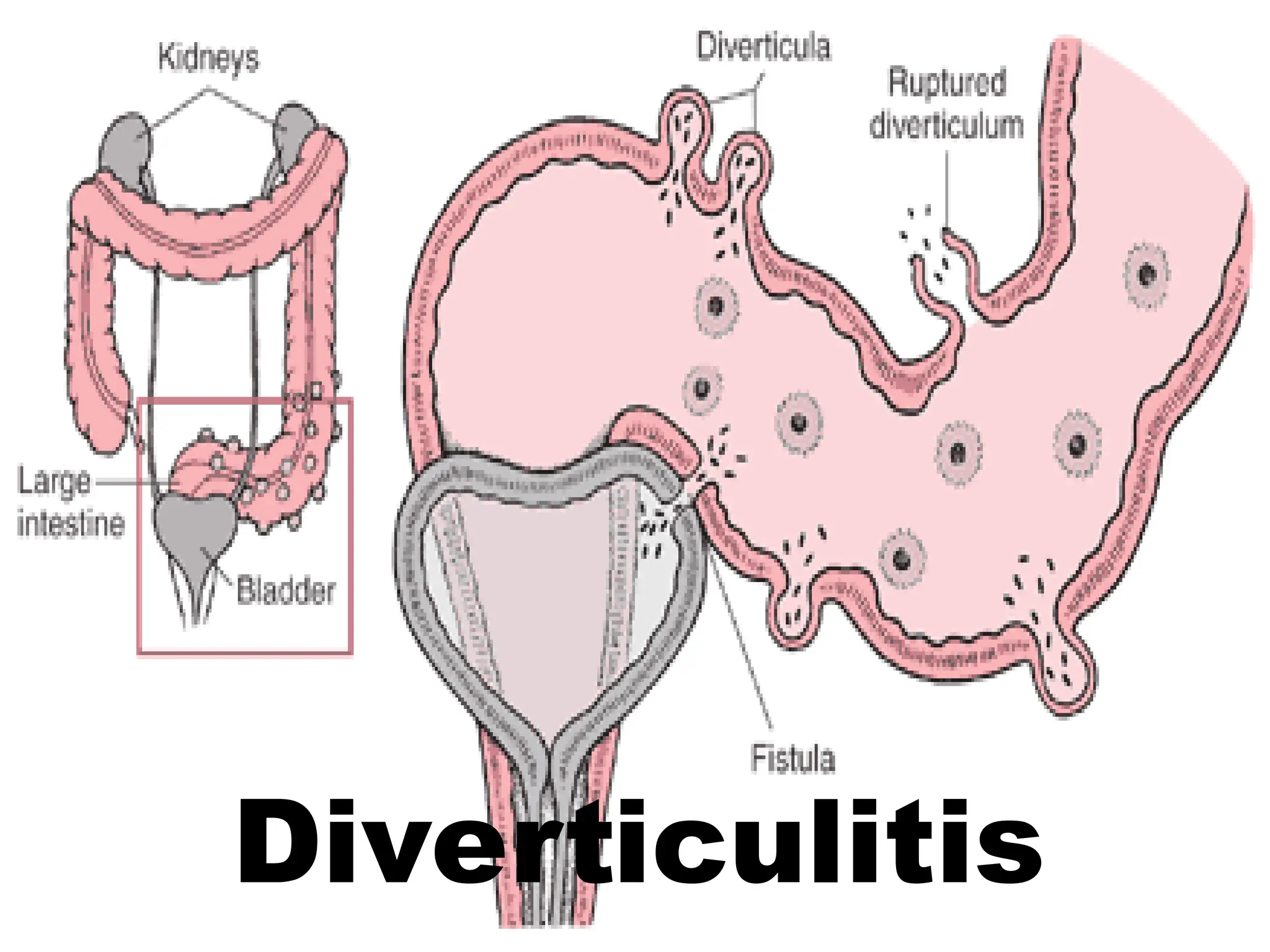
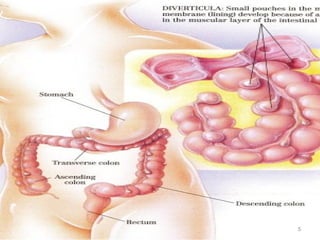
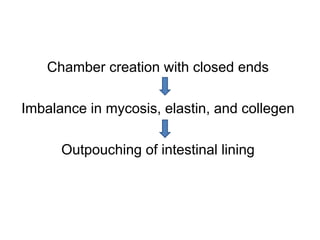
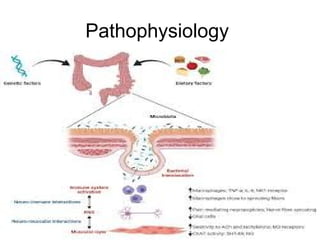
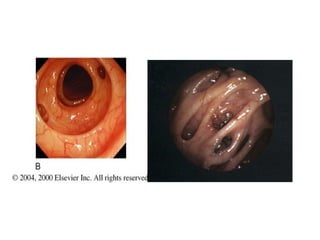
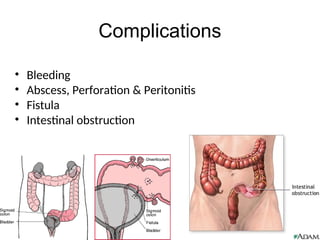
Diverticulitis is an inflammation and infection of outpouchings in the colon, commonly caused by trapped fecal material and bacteria, with contributing risk factors including a low fiber diet, obesity, and age over 50. Symptoms include abdominal pain, fever, and changes in bowel habits, while diagnostic evaluations involve imaging and lab tests. Treatment involves dietary management, antibiotics, pain relief, and, in severe cases, surgical intervention.