Cirrhosis of liver
- 2. Introduction • The liver is a large organ that sits in the right upper abdomen, just under the right lung. It is one of the body's most "intelligent" organs, in that it performs so many different functions at the same time. The liver makes proteins, eliminates waste material from the body, produces cholesterol, stores and releases glucose energy and metabolizes many drugs used in medicine. It also produces bile that flows through bile ducts into the intestine where it helps to digest food. • The liver receives blood from two different sources, the heart and the intestine.
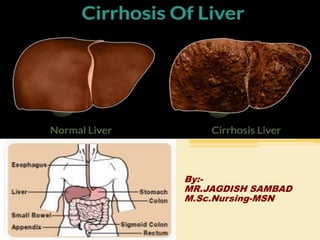
- 4. Definition • “ Cirrhosis is a chronic progressive disease of the liver characterized by extensive degeneration and destruction of the liver paranchymal cells”. • Cirrhosis is a chronic degenerative disease in which normal liver cells are damaged and are then replaced by scar tissue.
- 5. Incidence • The highest incidence occurs between the ages of 40 and 60, and it is twice as common in men as in women.
- 6. Causes
- 7. Causes • Alcohol-related liver disease. Most people who consume alcohol do not suffer damage to the liver. But heavy alcohol use over several years can cause chronic injury to the liver. • Chronic Viral Hepatitis -- Type B and Type C hepatitis, and perhaps other viruses, can infect and damage the liver over a prolonged time and eventually cause cirrhosis. • Chronic Bile Duct Blockage -- This condition can occur at birth (biliary atresia) or develop later in life (primary biliary cirrhosis). The cause of the latter remains unknown. When the bile ducts outside the liver become narrowed and blocked, the condition is called primary sclerosing cholangitis. This condition is often associated with chronic ulceration of the colon (colitis).
- 8. Causes • Abnormal Storage of Copper (Wilson's Disease) or Iron (Hemochromatosis) -- These metals are present in all body cells. When abnormal amounts of them accumulate in the liver, scarring and cirrhosis may develop. • Drugs and Toxins -- Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals or drugs can scar the liver. • Autoimmune Hepatitis -- This chronic inflammation occurs when the body's protective antibodies fail to recognize the liver as its own tissue. The antibodies injure the liver cells as though they were a foreign protein or bacteria.
- 9. causes • Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In NAFLD, fat builds up in the liver and eventually causes cirrhosis. This increasingly common liver disease is associated with obesity, diabetes, protein malnutrition, coronary artery disease, and corticosteroid medications.
- 10. Pathophysiology • Alcohol, drug and Infection • Synthesis of fatty acid & triglycerides increase • Formation & release of lipoproteins decreases • Fat appear in the liver • Liver cells enlarge of accumulation of lipids • Enlarge liver cells rupture
- 11. Pathophysiology • Fatty contents from ruptured liver cells form fatty cysts. • Cell between adjoining veins in the liver are linked by developing fibrosis. • Continued scarring & necrosis lead to the liver shrinking. • Liver function decrease or ceases.
- 12. Pathophysiology • Obstructed flow of blood leads to increased pressure in the portal vein (Portal Hypertension) • Blood backs up in the liver & spleen. • Veins in the abdomen, rectum & esophagus dilate. • The congestion of blood in the liver leads to decrease production of albumin. • Decrease serum albumin levels allow more water to move in to other body compartments.
- 13. Pathophysiology • Renin & aldosterone production level increase, leading to water and sodium retention. • Ascites
- 16. Symptoms • Yellowing of the skin (jaundice) due to the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood. • Fatigue • Weakness • Loss of appetite • Itching • Easy bruising from decreased production of blood clotting factors by the diseased liver. • nausea • vomiting • weight loss • abdominal pain and bloating when fluid accumulates in the abdomen
- 18. Diagnostic findings • History Taking • Physical Examination • Blood tests - To check whether the liver is functioning normally. • Ultrasound, CT scan, or radioisotope scan - To look for signs of cirrhosis within or on the surface of the liver. • Laparoscope - A very tiny camera inserted through a small slit in the abdomen to view the liver directly. • Liver biopsy - Removing tissue from the liver and studying it under a microscope to identify fibrosis and scarring. Biopsy is the only way diagnosis can be 100% certain.
- 19. Treatment • Aim of the treatment :- 1. preventing further damage to the liver, 2. treating the complications of cirrhosis, and 3. liver transplantation.
- 20. Preventing further damage to the liver • Consume a balanced diet and one multivitamin daily. • Avoid drugs (including alcohol) that cause liver damage. • Avoid nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, e.g., ibuprofen). Patients with cirrhosis can experience worsening of liver and kidney function with NSAIDs. • Eradicate hepatitis B and hepatitis C virus by using anti-viral medications. Not all patients with cirrhosis due to chronic viral hepatitis are candidates for drug treatment.
- 21. • Remove blood from patients with hemochromatosis to reduce the levels of iron and prevent further damage to the liver. • Suppress the immune system with drugs such as prednisone and azathioprine (Imuran) to decrease inflammation of the liver in autoimmune hepatitis. • Immunize patients with cirrhosis against infection with hepatitis A and B to prevent a serious deterioration in liver function.
- 23. Treating the complications of cirrhosis 1) Edema and ascites:- • Retention of salt and water can lead to swelling of the ankles and legs (edema) or abdomen (ascites) in patients with cirrhosis. • To restrict dietary salt (sodium) and fluid to decrease edema and ascites. • Diuretics are medications that work in the kidneys to promote the elimination of salt and water into the urine. A combination of the diuretics spironolactone (Aldactone) and furosemide can reduce or eliminate the edema and ascites in most patients.
- 25. 2) Bleeding from varices:- • If large varices develop in the esophagus or upper stomach, patients with cirrhosis are at risk for serious bleeding due to rupture of these varices. Once varices have bled, they tend to rebleed and the probability that a patient will die from each bleeding episode is high (30%-35%). • Propranolol (Inderal), a beta blocker, is effective in lowering pressure in the portal vein and is used to prevent initial bleeding and rebleeding from varices in patients with cirrhosis • Octreotide (Sandostatin) also decreases portal vein pressure and has been used to treat variceal bleeding.
- 27. • Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is a non-surgical procedure to decrease the pressure in the portal vein. TIPS is performed by a radiologist who inserts a stent (tube) through a neck vein, down the inferior vena cava and into the hepatic vein within the liver. The stent then is placed so that one end is in the high pressure portal vein and the other end is in the low pressure hepatic vein.
- 28. 3)Hepatic encephalopathy:- • Patients with an abnormal sleep cycle, impaired thinking, odd behavior, or other signs of hepatic encephalopathy usually should be treated with a low protein diet and oral lactulose. • Dietary protein is restricted because it is a source of the toxic compounds that cause hepatic encephalopathy. • To be sure that adequate lactulose is present in the colon at all times, the patient should adjust the dose to produce 2-3 semiformed bowel movements a day. (Lactulose is a laxative, and the adequacy of treatment can be judged by loosening or increasing frequency of stools.) • If symptoms of encephalopathy persist, oral antibiotics such as neomycin or metronidazole (Flagyl), can be added to the treatment regimen.
- 30. 4) Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP):- • Patients suspected of having spontaneous bacterial peritonitis usually will undergo paracentesis. Fluid that is removed is examined for white blood cells and cultured for bacteria. • Most patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis are hospitalized and treated with intravenous antibiotics such as ampicillin, gentamycin, and one of the newer generation cephalosporin.
- 31. Liver transplantation • Cirrhosis is irreversible. Many patients' liver function will gradually worsen despite treatment and complications of cirrhosis will increase and become difficult to treat. • Therefore, when cirrhosis is far advanced, liver transplantation often is the only option for treatment.
- 32. Nursing Management • Assessment • Subjective Data • Objective Data
- 33. Nursing Diagnosis 1. Activity intolerance related to fatigue and malaise. 2. Imbalance nutrition less than body requirement related to increase metabolic demand. 3. Impaired skin integrity related to pruritus from jaundice and edema. 4. Chronic pain and discomfort related to enlarge tender liver and Ascites. 5. Fluid volume excess related to ascites and edema formation. 6. G.I Bleeding and hemorrhage related to portal hypertension. 7. Knowledge deficit related to disease process and treatment plan.
- 34. Study of Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis in Hospital Based Patients, Bijapur, Northern Karnataka, India. A . M . Patil et.all • This study related to the prevalence of alcoholic liver cirrhosis in relation to age, sex, rural and urban area patients and also prevalence of ALC in literate and illiterate Patients. Prevalence of morphological types of cirrhosis of liver and complications of alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Material and Methods: The material for this study is obtained from in-patient and out-patients attending the Al-Ameen Medical College and Hospital, Bijapur, Karnataka. A total of 100 cases of Alcoholic liver cirrhosis patients studied over a period of three year of study from January 2010 to January 2014. Results: The study includes 100 cases of Alcoholic liver c cirrhosis (ALC). The sex wise distribution of prevalence of ALC cases was highest in males i.e. 74 cases (74%), as compare to females, prevalence rate is 26 cases (26%). According to age wise, prevalence of ALC it is highest in age group of 31-40 years i.e. 30 cases (30%) and next highest in the age group 41-50 years i.e. 28 cases (28%). The prevalence of Morphological types of cirrhosis in out of 100 cases. 42 cases (42.0%) are micro nodular cirrhosis and 30 cases (30.0%) macro nodular and 28 cases (28.0%) mixed cirrhosis. The Prevalence rate is high in the illiterate patients as compare to literate patients. In rural and urban area wise, highest cases seen in rural area patients i.e., 62 cases (62%) as compared to urban area patients i.e. 38 cases (38%) were observed in present study.
