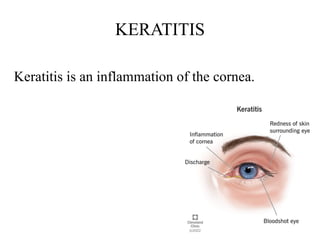
Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea, the clear front part of the eye. It can be caused by infections (microbial keratitis) or other factors like injury or dry eye. Symptoms include eye pain, redness, blurry vision, and light sensitivity. Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent vision loss.
Infectious Keratitis (Microbial Keratitis):
Bacterial Keratitis: Often caused by bacteria like Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Staphylococcus aureus, especially in contact lens wearers.
Viral Keratitis: Commonly caused by herpes simplex virus (cold sores) or other viruses.
Fungal Keratitis: Less common, but can occur after eye injuries or with contact lens wear.
Parasitic Keratitis (Acanthamoeba Keratitis): Can be caused by the parasite Acanthamoeba, often linked to poor contact lens hygiene.
Non-Infectious Keratitis:
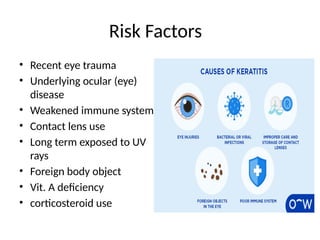
Contact Lens-Related Keratitis: Prolonged wear, improper care, or wearing lenses while sleeping can irritate the cornea.
Dry Eye: Insufficient tears can lead to corneal inflammation and keratitis.
Injury: Trauma, scratches, or burns to the cornea can cause keratitis.
Systemic Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can sometimes cause keratitis.
Symptoms:
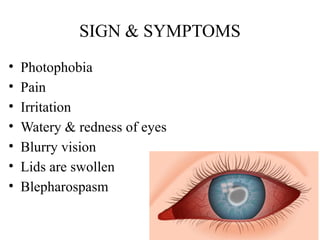
Eye pain.
Redness and swelling of the eye.
Blurred or reduced vision.
Sensitivity to light (photophobia).
Gritty feeling in the eye.
Excessive tearing or discharge.
Difficulty opening the eyelids.
Treatment:
Infectious Keratitis: Treatment typically involves antibiotic, antiviral, or antifungal eye drops or medications, depending on the cause.
Non-Infectious Keratitis: Treatment may include artificial tears, lubricating drops, or other measures to relieve symptoms.
Severe Cases: In some cases, corneal transplantation may be necessary.