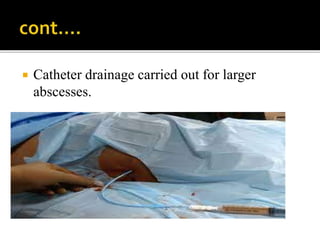
A liver abscess is a collection of pus in the liver that can be caused by bacteria, fungi, or parasites. It develops when infectious organisms destroy hepatic tissue, creating a cavity filled with pus, dead and infected cells, and leukocytes. Common causes include bacterial infections from the biliary tract or GI tract, as well as amoebic parasites. Symptoms include right upper abdominal pain, fever, nausea and jaundice. Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging like ultrasound or CT scan, and biopsy. Treatment depends on the identified cause but generally involves antibiotics, drainage procedures, or surgery.