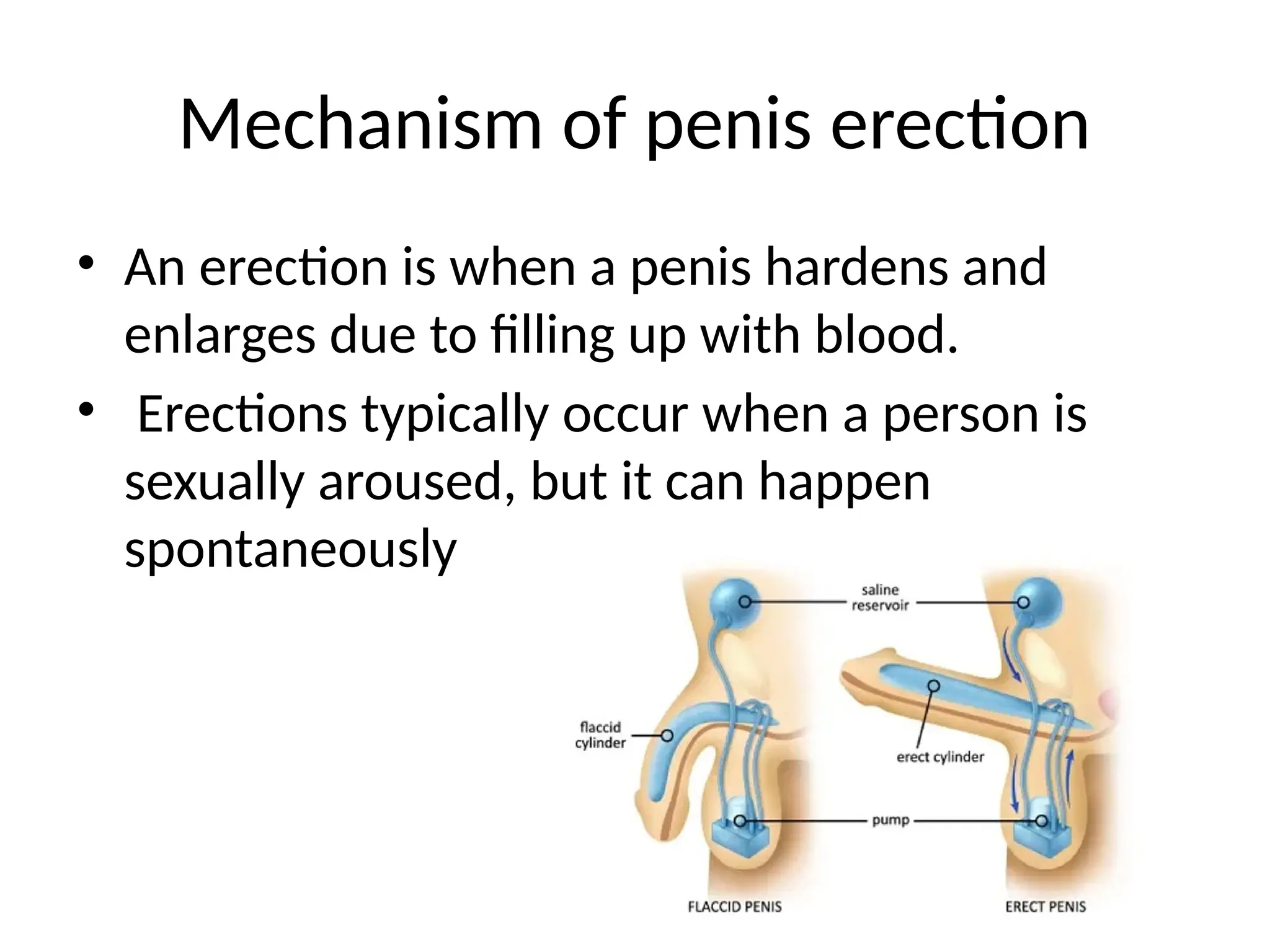
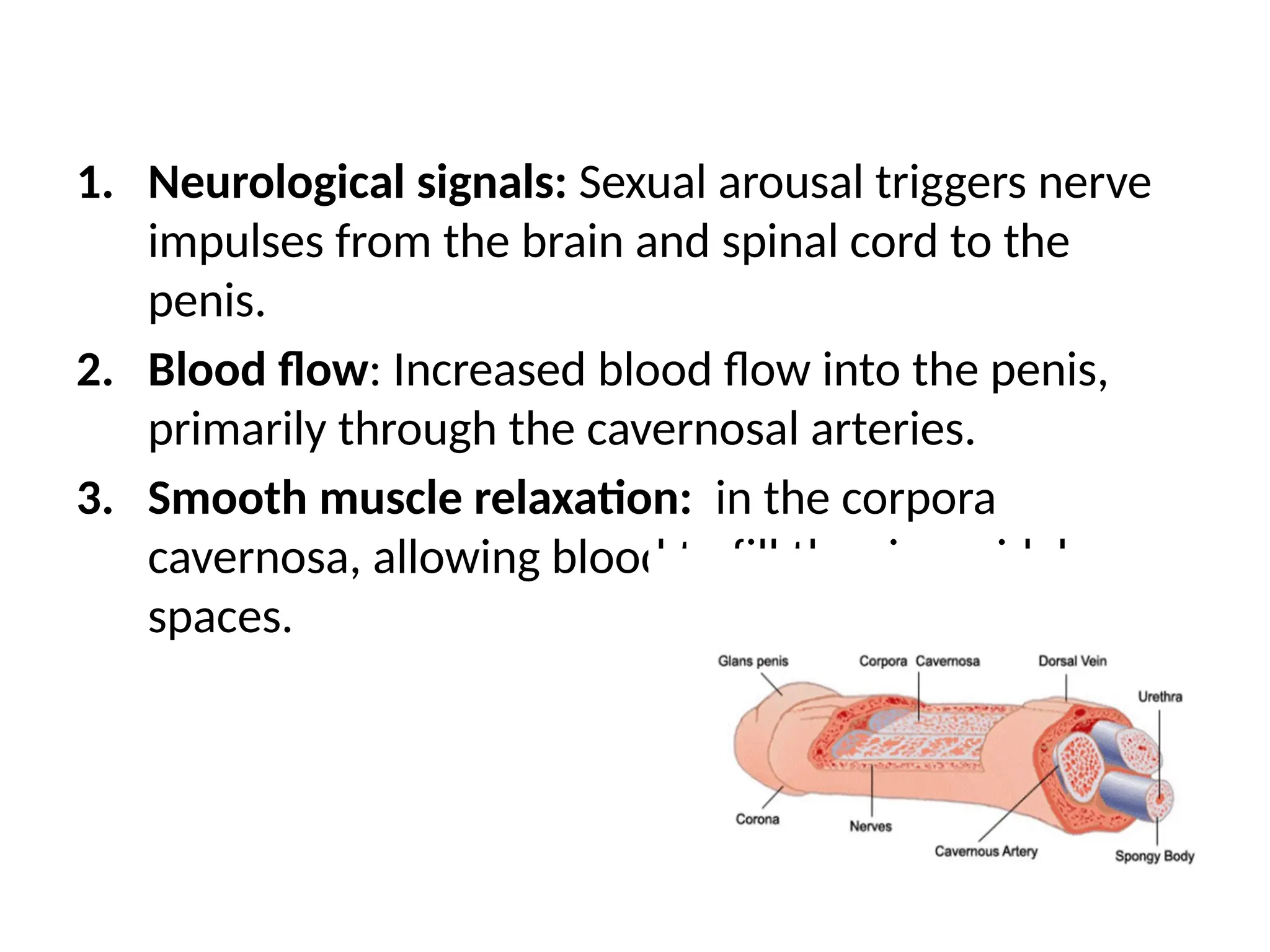
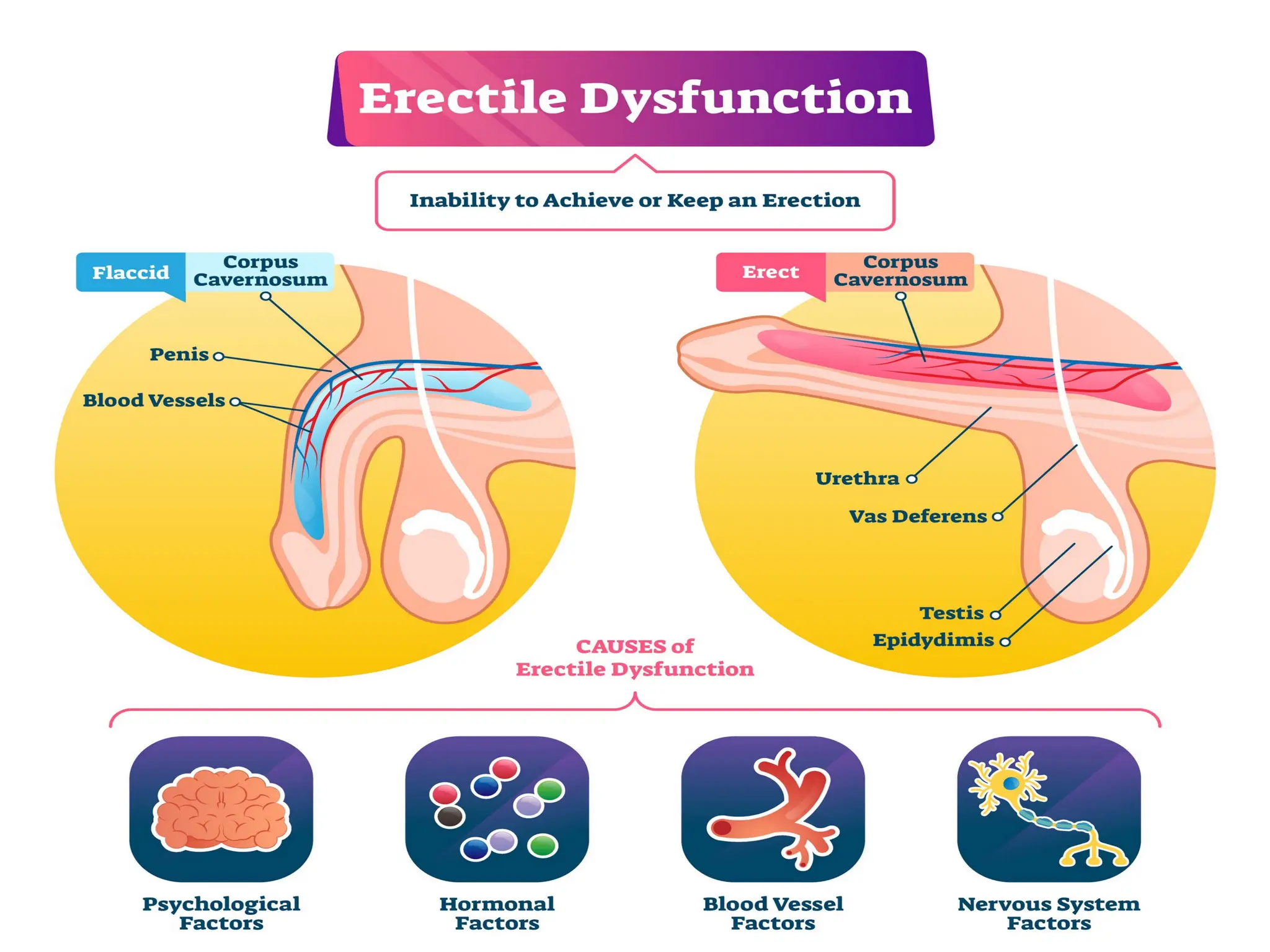
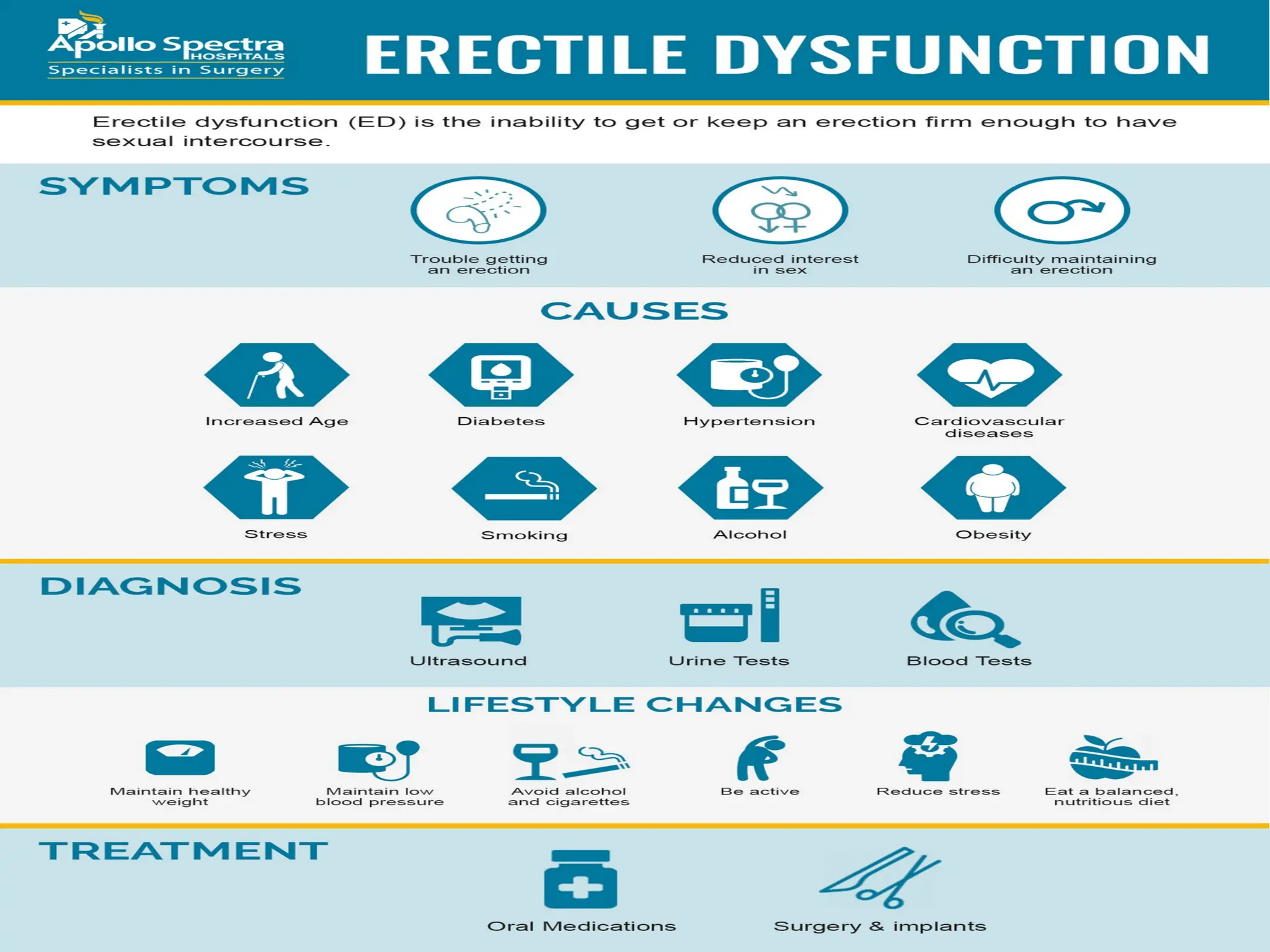
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also known as impotence, is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection suitable for sexual intercourse. It can be caused by various factors, including physical health problems, psychological issues, or a combination of both. Treatment options range from lifestyle changes to medication and other medical interventions.
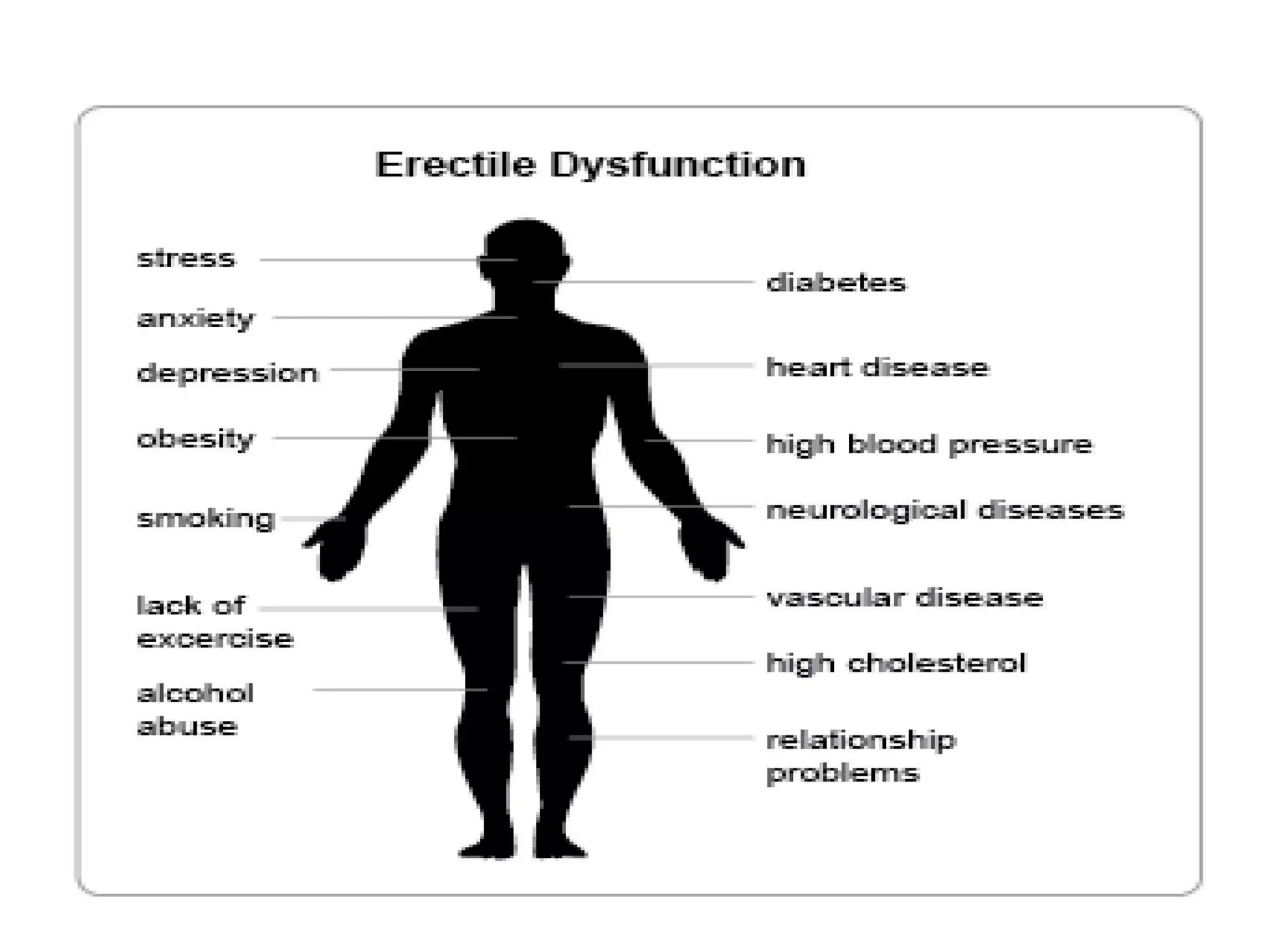
Causes of Erectile Dysfunction:
Physical Health Problems: Conditions like heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and obesity can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to ED.
Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship problems can also contribute to ED.
Hormonal Imbalances: Low testosterone levels can affect sexual function and libido.
Medications: Certain medications can have ED as a side effect.
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use can negatively impact erectile function.
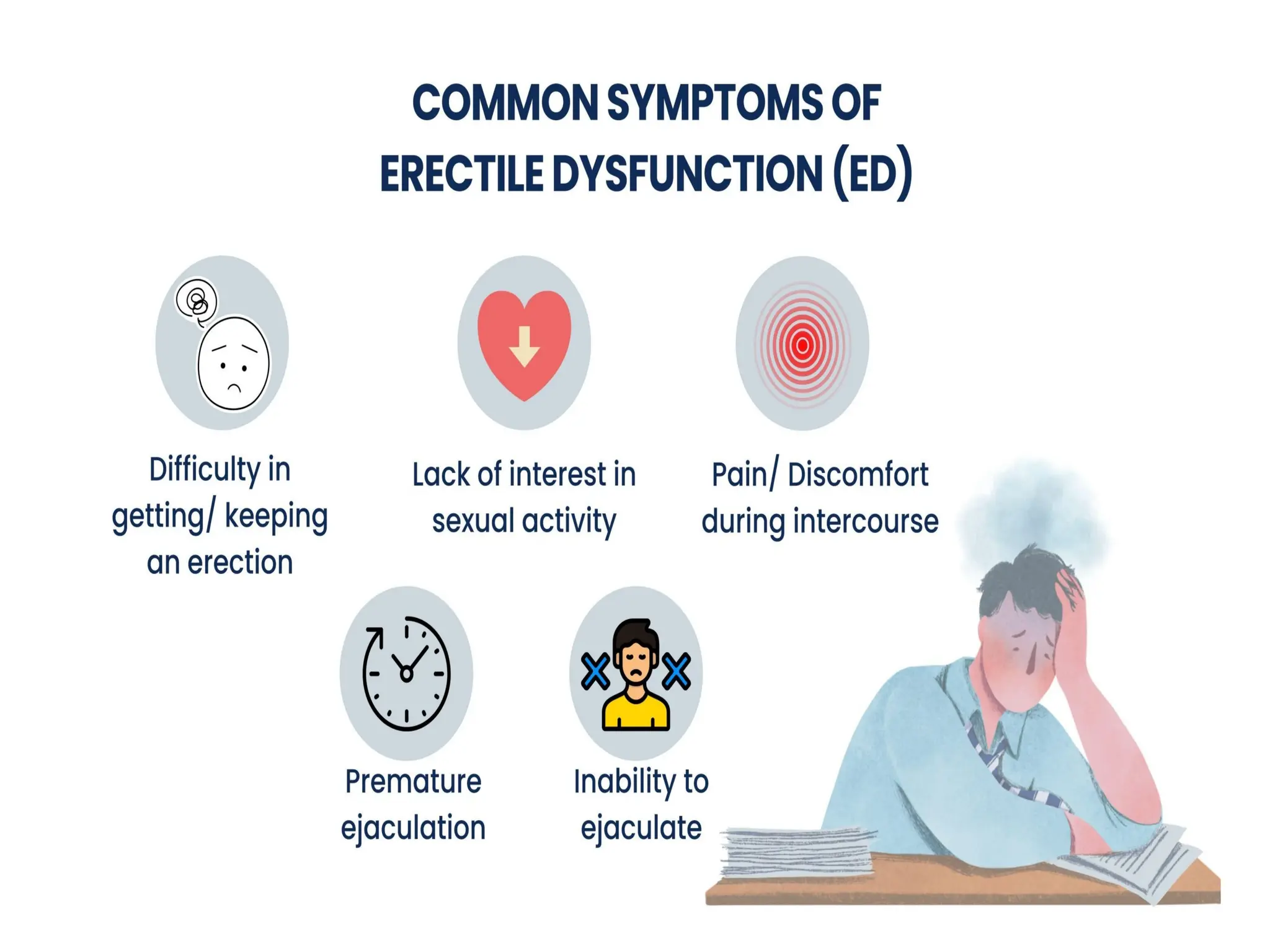
Symptoms of Erectile Dysfunction:
Inability to get an erection.
Inability to maintain an erection long enough for satisfactory sexual intercourse.
Sometimes being able to get an erection, but not every time.
Low libido.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
A doctor will assess your medical history, perform a physical exam, and may recommend blood tests or other tests to identify any underlying medical conditions.
Treatment options may include:
Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet, exercise, and smoking cessation.
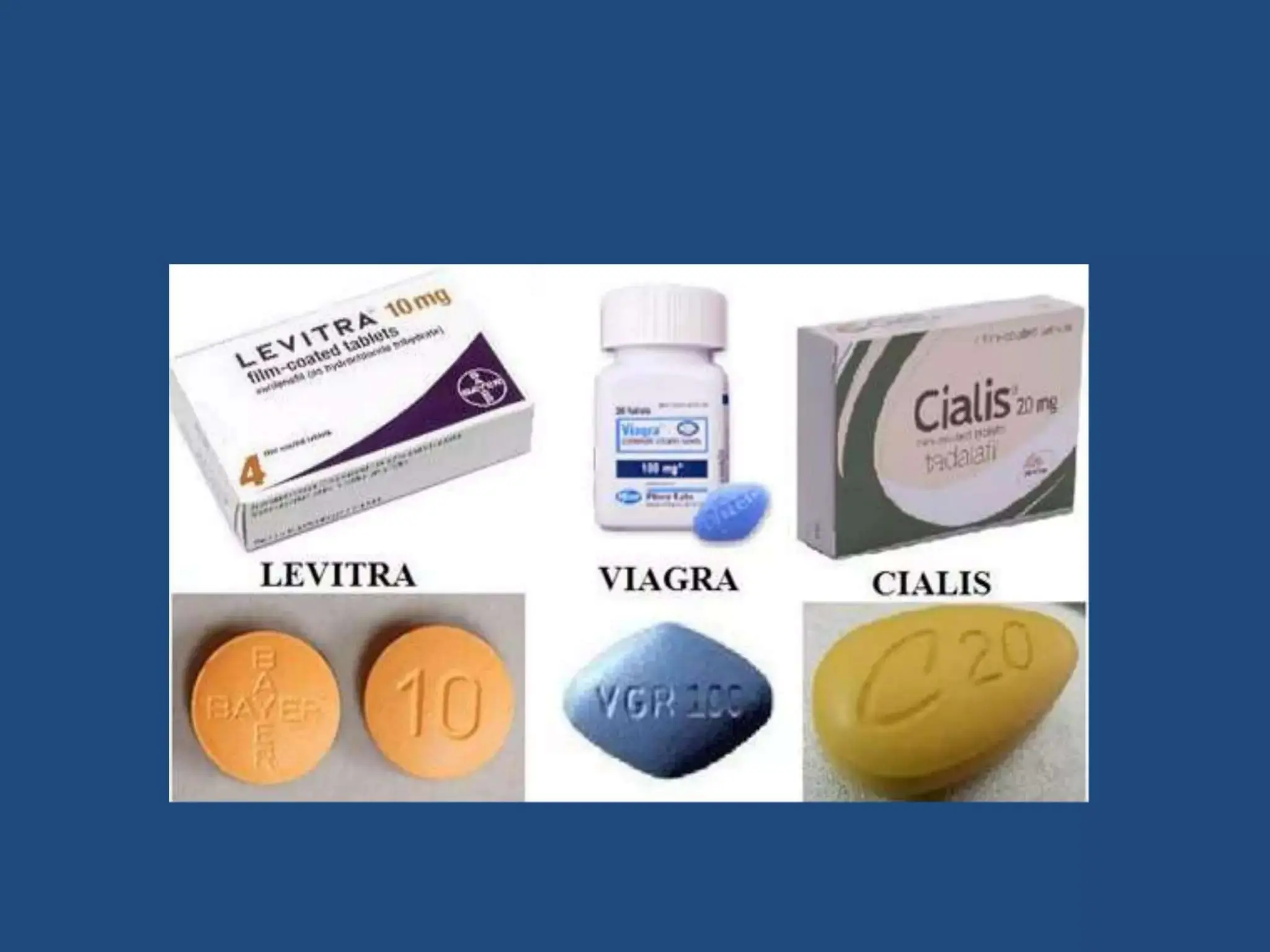
Medications, such as PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil).
Counseling or therapy for psychological factors.
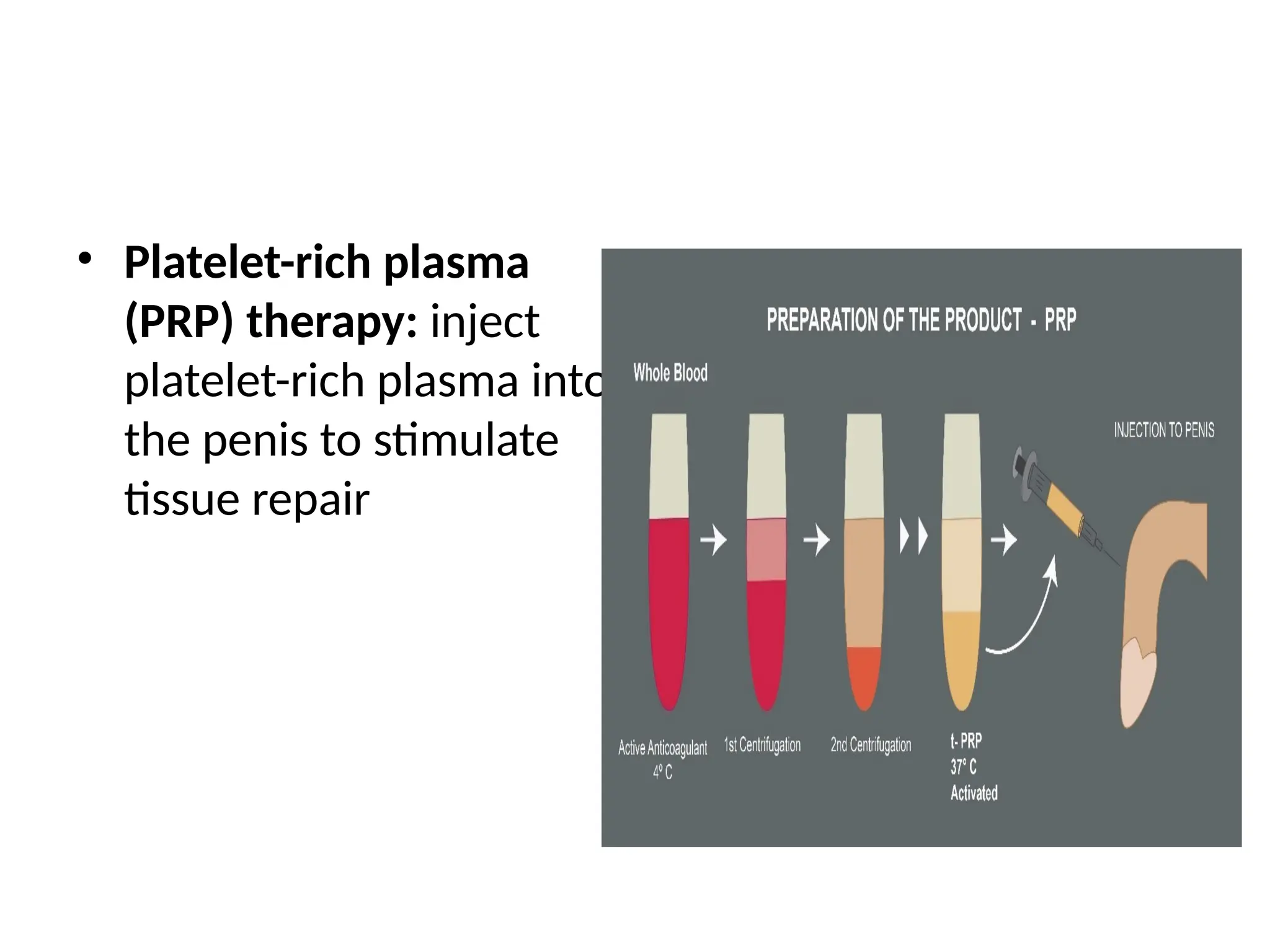
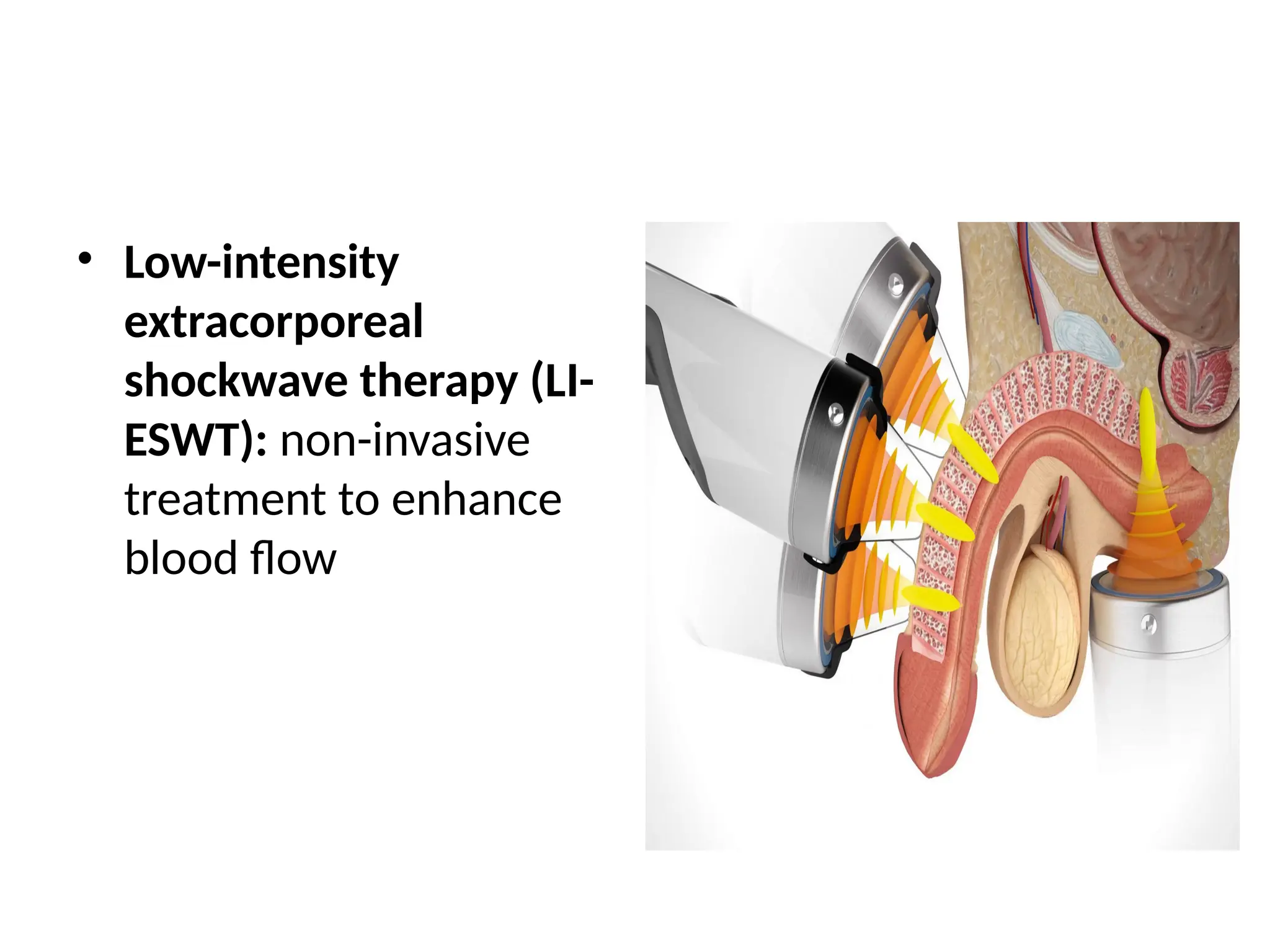
Penile injections or vacuum devices.
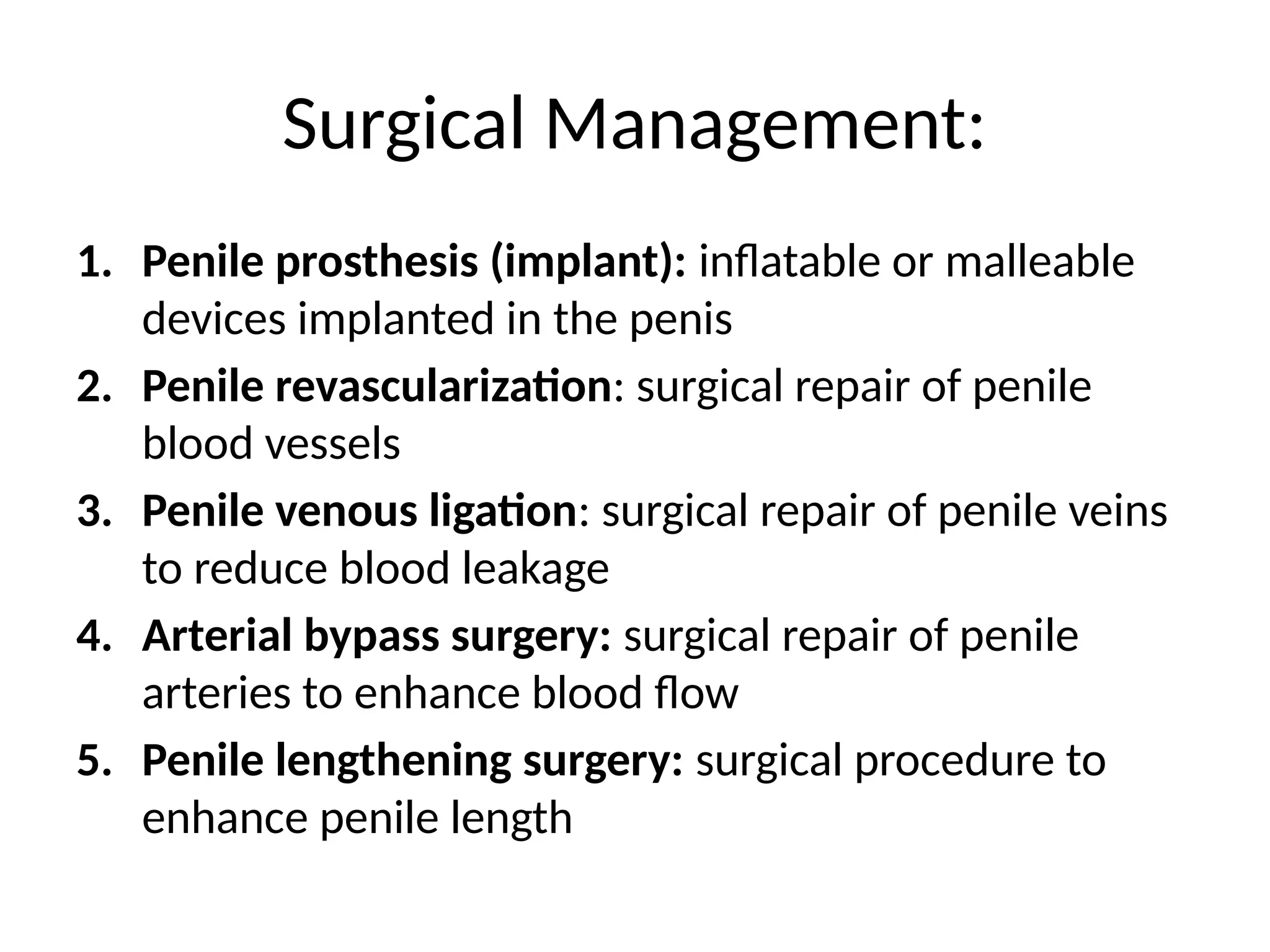
Surgery in rare cases.
Important Considerations:
ED can be a symptom of other underlying health problems, so it's important to seek medical advice if you experience persistent issues.
There are many effective treatments available, and a healthy sexual life is an important part of overall health.
Open communication with a doctor about ED concerns is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.