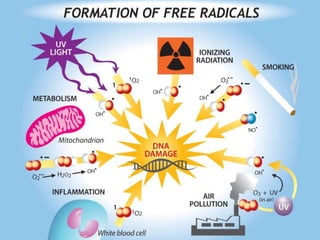
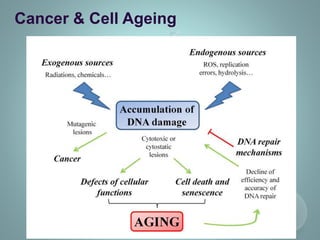
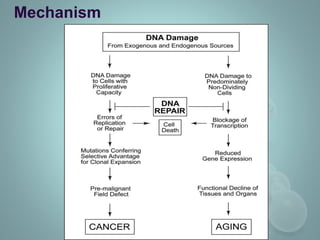
DNA damage can result from metabolic processes, hydrolysis, or exogenous sources and can lead to various human diseases if left unrepaired. Defects in the cellular response to repair DNA damage can cause cancer, inflammation, cell aging, and neurodegeneration. Neurodegeneration involves the death of neurons and is associated with diseases like Huntington's, Parkinson's, and Alzheimer's. Neurons are post-mitotic cells that are susceptible to DNA damage from endogenous and exogenous agents. If the damage is not repaired, unrepaired DNA accumulates in neurons and can cause cell cycle reentry and apoptosis, leading to neurodegeneration. Chronic inflammation from infection or other sources can also cause DNA damage through reactive oxygen species