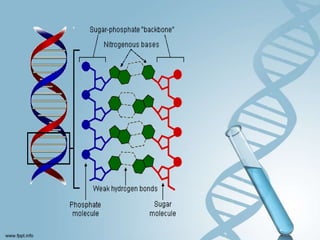
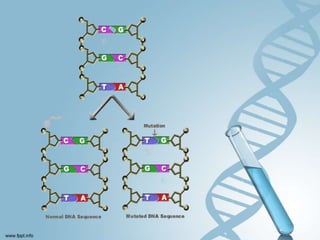
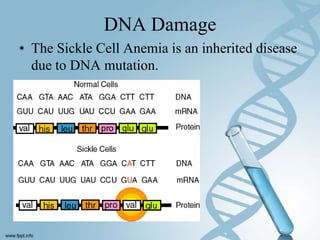
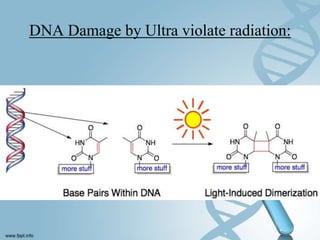
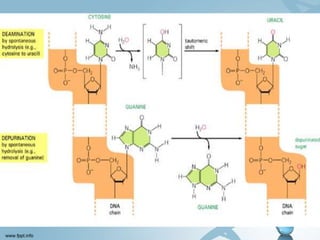
DNA can be damaged through mutations, spontaneous reactions, ultraviolet radiation, and depurination/deamination. The DNA repair mechanism involves recognizing and removing the damaged DNA, filling in the gap using the undamaged strand as a template, and sealing the repaired strand. DNA stores and passes on genetic information from generation to generation in its spiral ladder-like structure.