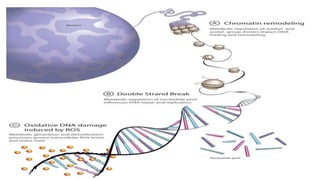
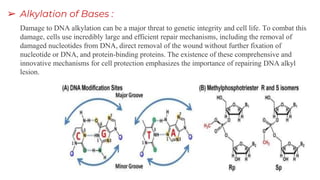
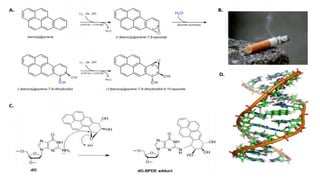
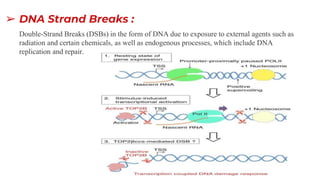
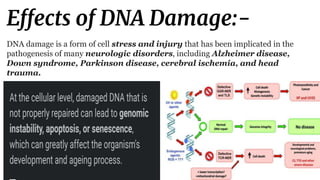
DNA contains our genetic material and can be damaged through various means. DNA damage is an alteration in the structure of DNA, such as breaks in strands or changes to nucleotide bases. Living things are constantly exposed to factors that can damage DNA, both endogenously through natural processes in the body and exogenously through external environmental sources like radiation. While repair systems work to fix most DNA damage, unrepaired damage accumulates and has been linked to various health conditions and diseases.