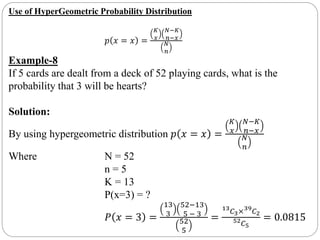
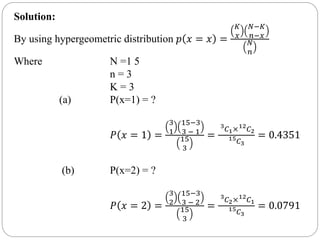
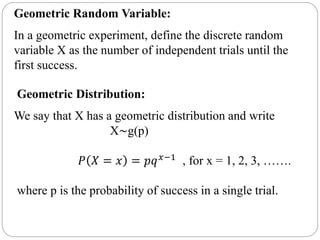
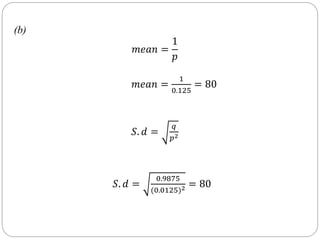
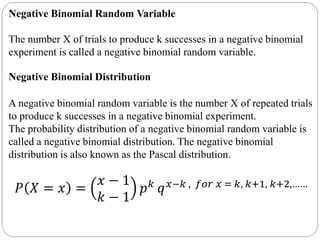
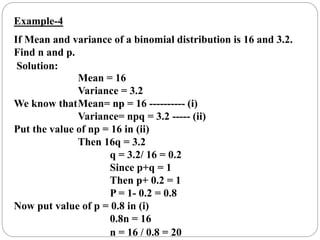
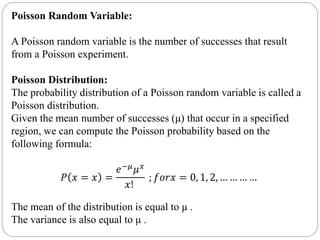
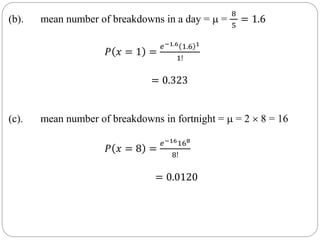
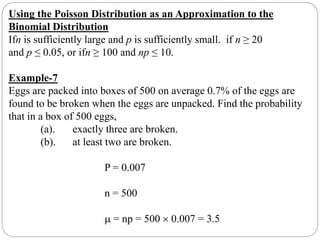
The document discusses binomial, Poisson, and hypergeometric probability distributions. It provides examples of experiments that follow each distribution and how to calculate probabilities using the respective formulas. For binomial experiments, the probability of success must be constant on each trial and trials must be independent. Poisson experiments involve rare, independent events with a known average rate. Hypergeometric probabilities are used when the probability of success changes on each dependent trial, such as sampling without replacement.






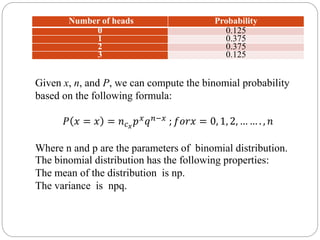

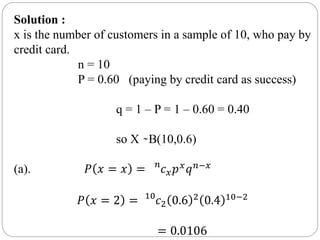
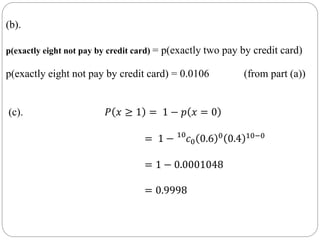












![Hypergeometric Random Variable:
A hypergeometric random variable is the number of successes that
result from a hypergeometric experiment.
Hypergeometric Distribution:
The probability distribution of a hypergeometric random variable is
called a hypergeometric distribution.
Given x, N, n, and k, we can compute the hypergeometric probability
based on the following formula:
𝑃 𝑥 = 𝑥 =
𝐾
𝑥
𝑁 − 𝐾
𝑛 − 𝑥
𝑁
𝑛
; 𝑓𝑜𝑟𝑥 = 0, 1, 2, 3, … … … . , 𝑛
The mean of the distribution is equal to n × k / N .
The variance is n × k × ( N - k ) × ( N - n ) / [ N
2
× ( N - 1 ) ] .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discreteprobabilitydistributions-200508102518/85/Discrete-probability-distributions-28-320.jpg)