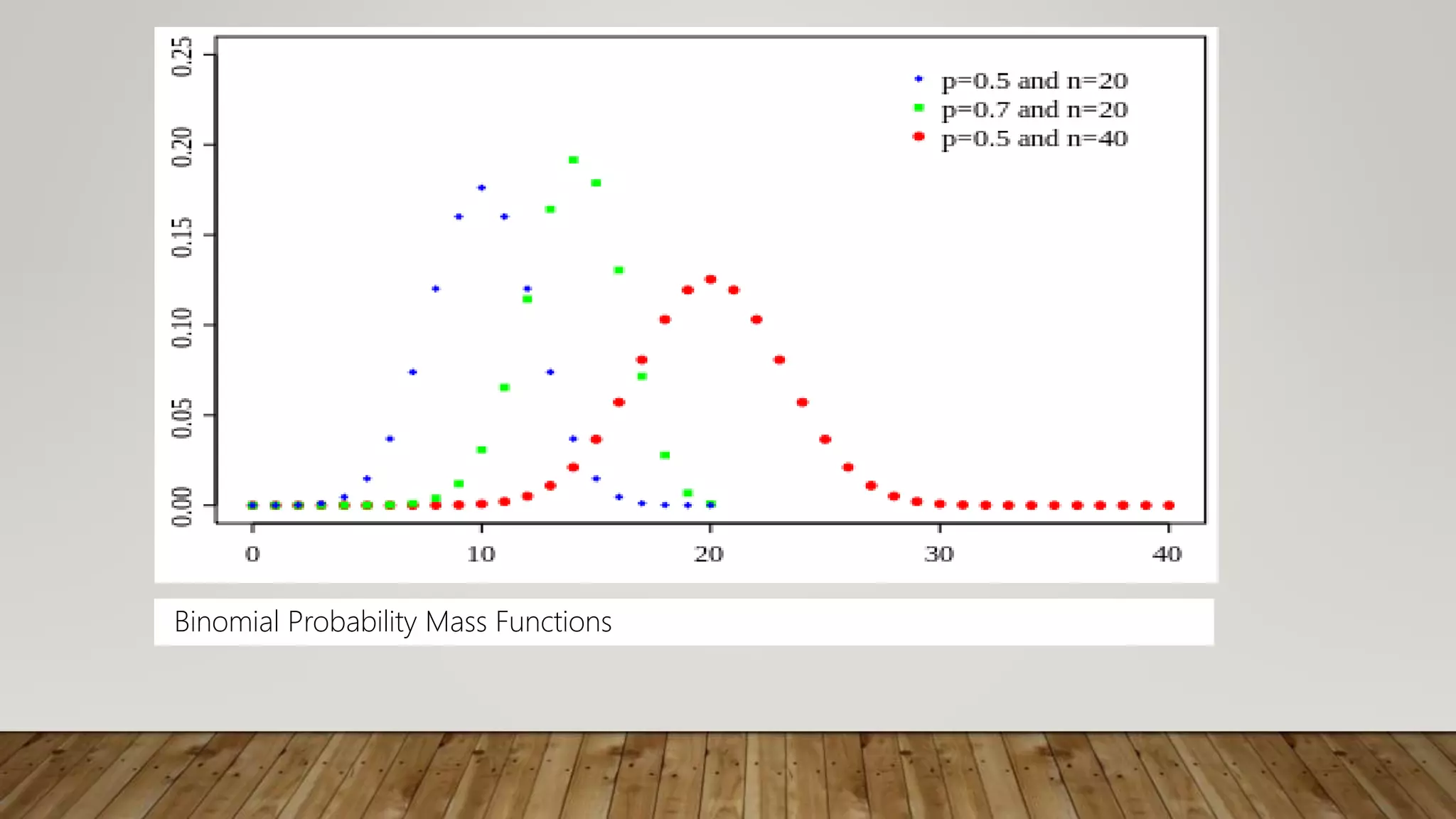
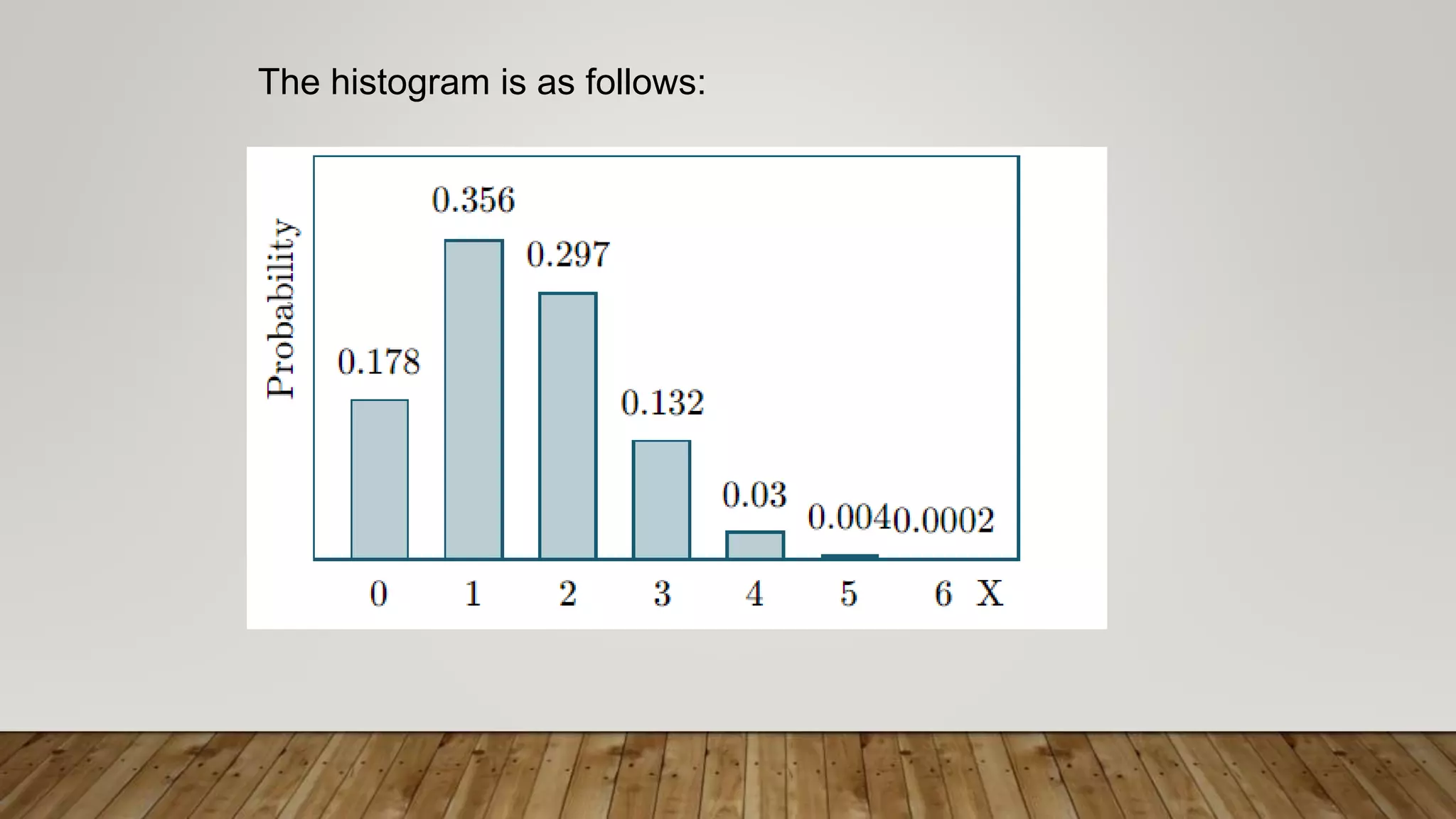
The document discusses binomial distributions, which model outcomes that can be classified as successes or failures, with a constant probability of success for each trial. A binomial distribution is defined by the number of trials (n) and the probability of success (p) for each trial. The mean is np and the standard deviation is npq. Examples are given of calculating binomial probabilities, such as the probability of a certain number of patients recovering from a disease out of a sample size.