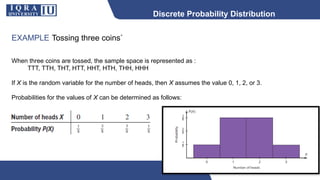
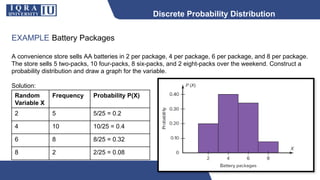
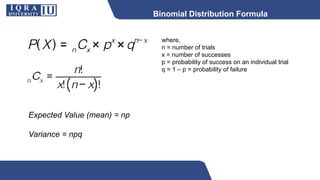
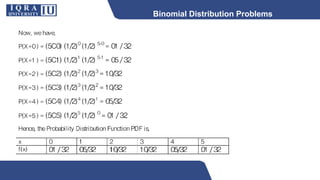
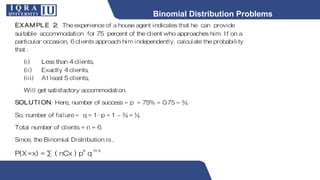
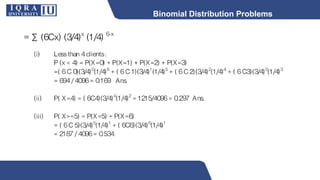
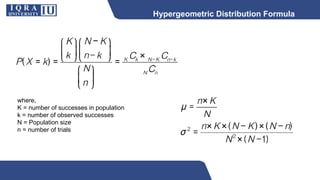
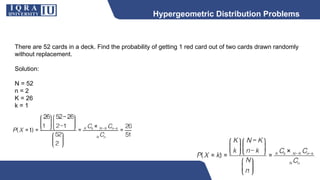
This document discusses different types of discrete probability distributions, including binomial, hypergeometric, and Poisson distributions. It provides examples and formulas for each. The binomial distribution describes probability of success/failure outcomes from repeated independent trials. The hypergeometric deals with sampling without replacement. The Poisson distribution applies when the number of rare events occurs over an interval of time or space and the mean rate is known.