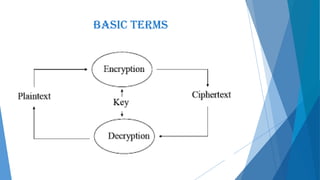
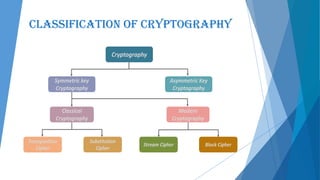
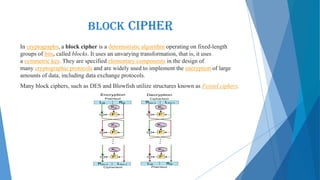
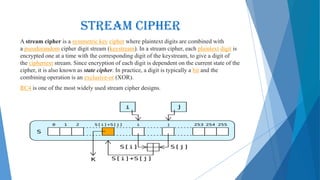
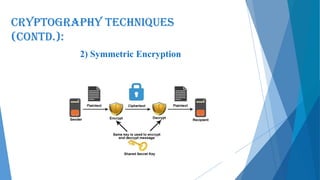
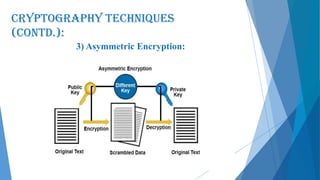
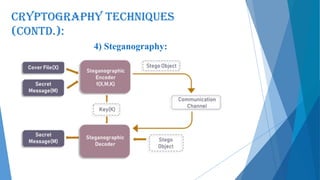
This document presents an overview of cryptography including its definition, history, basic terms, classifications, techniques, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Cryptography is defined as the art and science of achieving security by encoding messages. The earliest evidence of cryptography dates back 4000 years to ancient Egypt. Techniques covered include symmetric and asymmetric encryption, transposition ciphers, substitution ciphers, block ciphers, stream ciphers, hashing, and steganography. Advantages of cryptography include confidentiality, authentication, data integrity, and non-repudiation, while disadvantages include reduced accessibility and inability to ensure high availability. Cryptography has applications in defense, e-commerce, business transactions, internet payments, user identification, and data security.