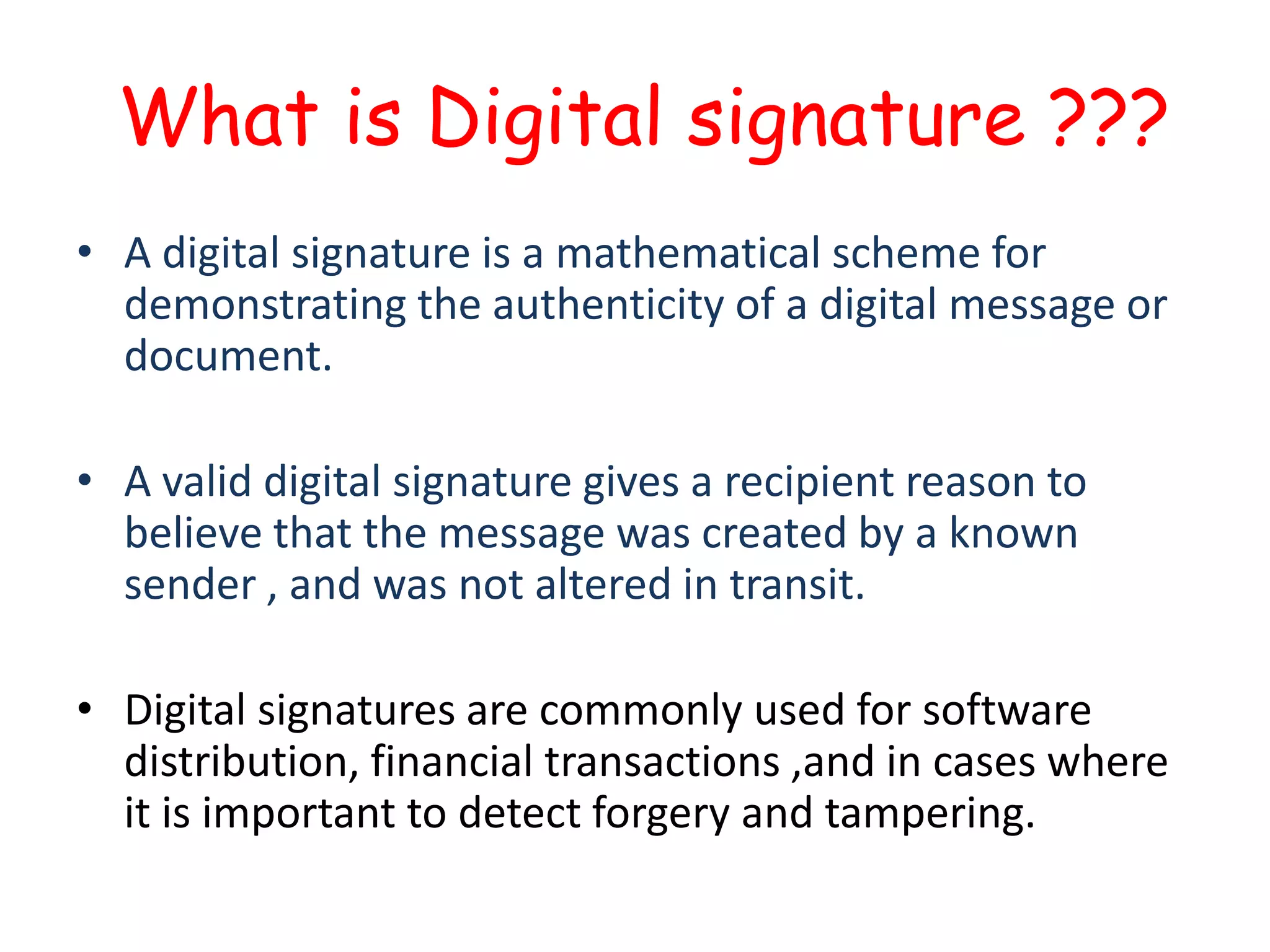
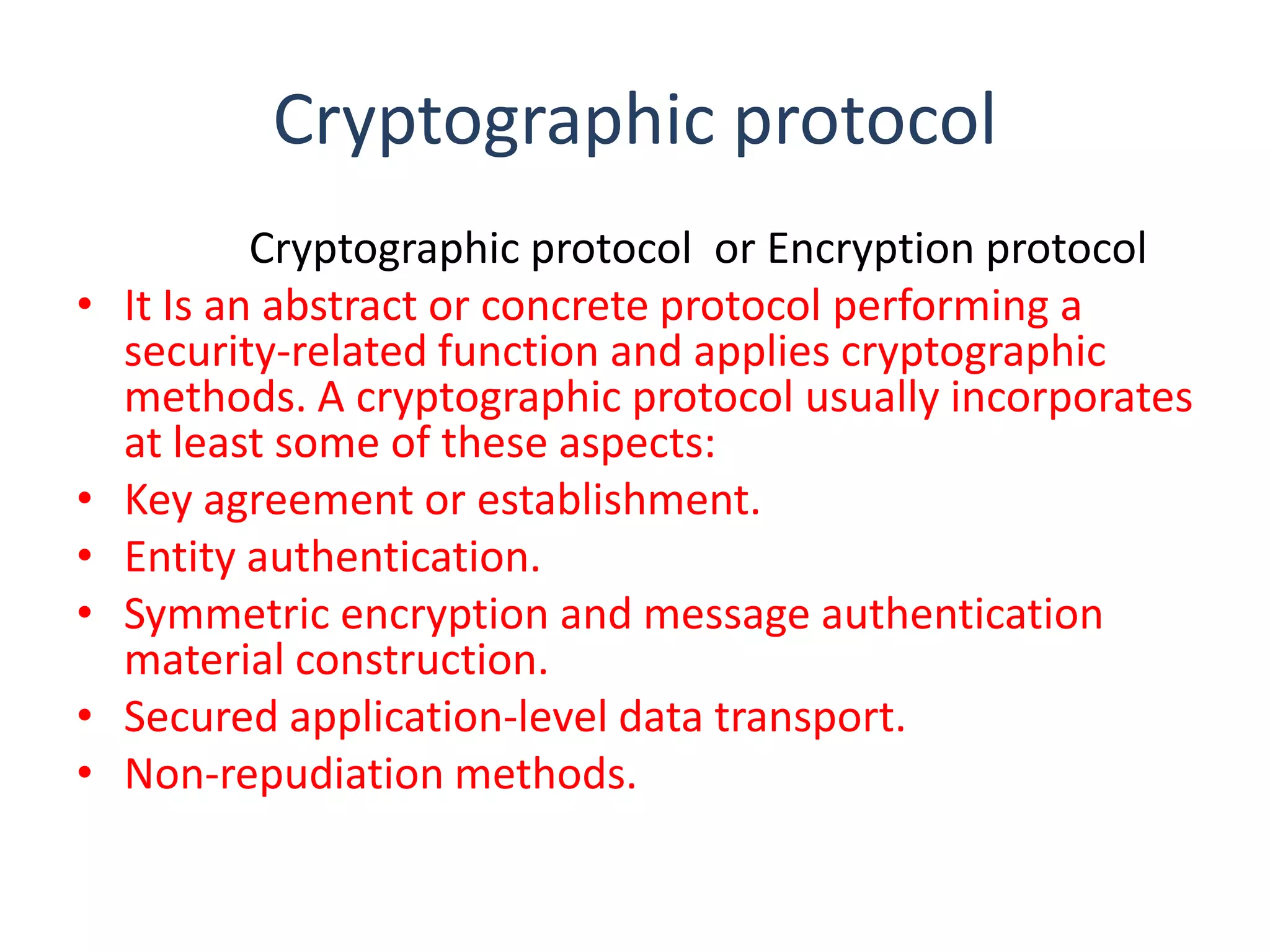
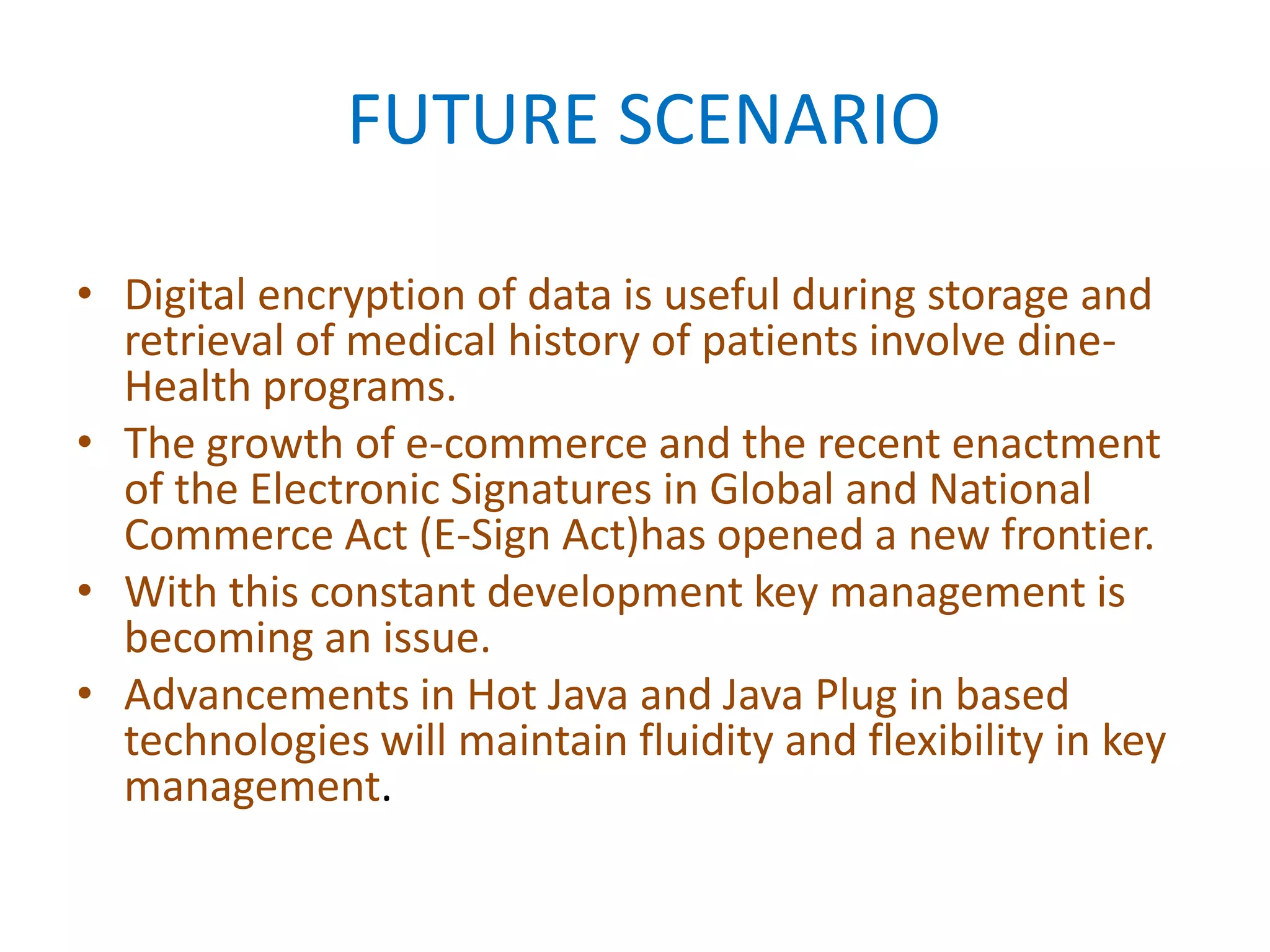
Digital signatures provide authentication of digital messages and documents using asymmetric cryptography. A digital signature is generated using a private key and can be verified by anyone using the corresponding public key. This allows the recipient to confirm the identity of the sender and verify that the message was not altered during transmission. Digital signatures are commonly used for software distribution, financial transactions, and other situations where detecting forgery and tampering is important. The document discusses how digital signatures work using both asymmetric key encryption and keyed hash functions.