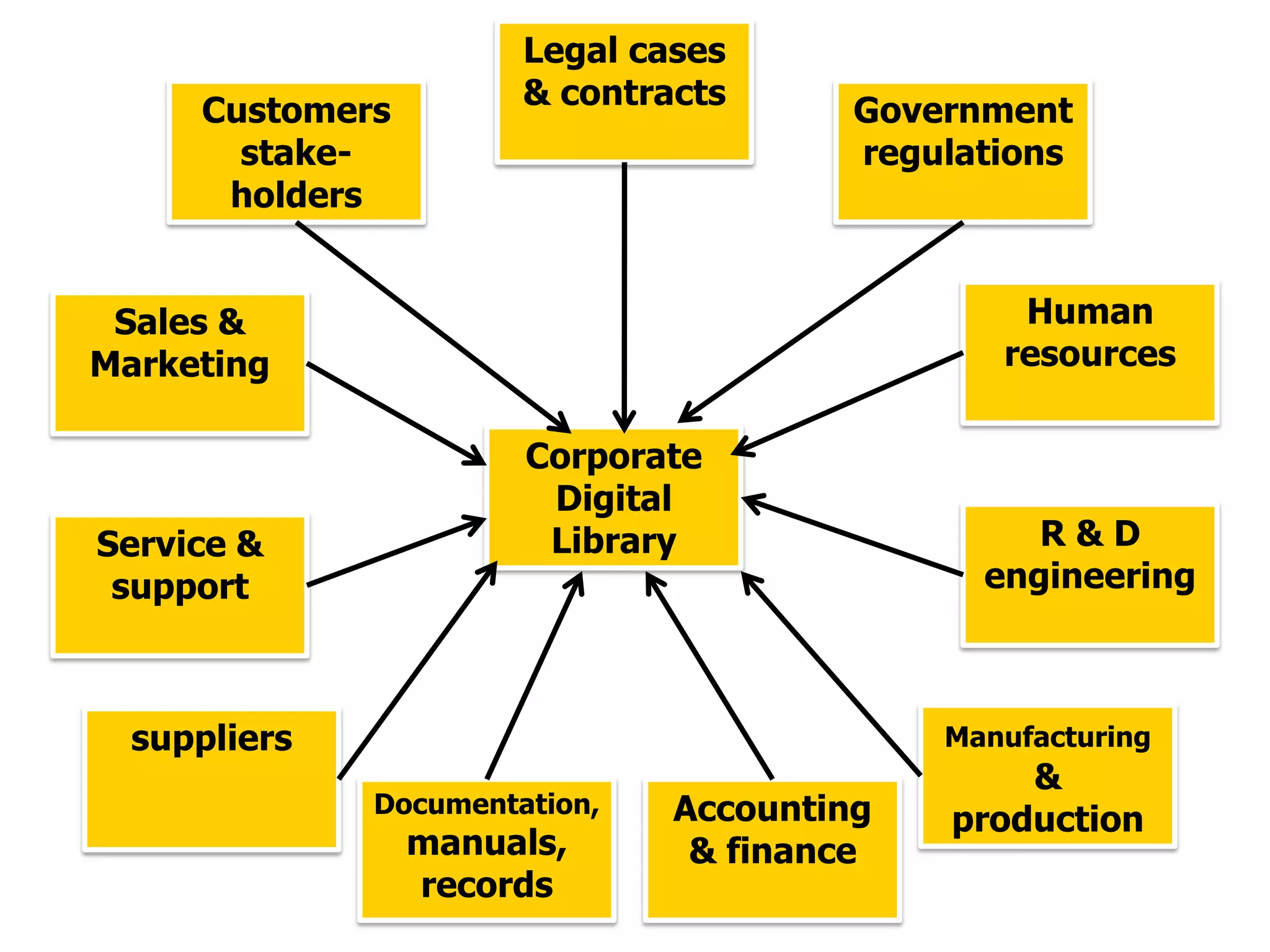
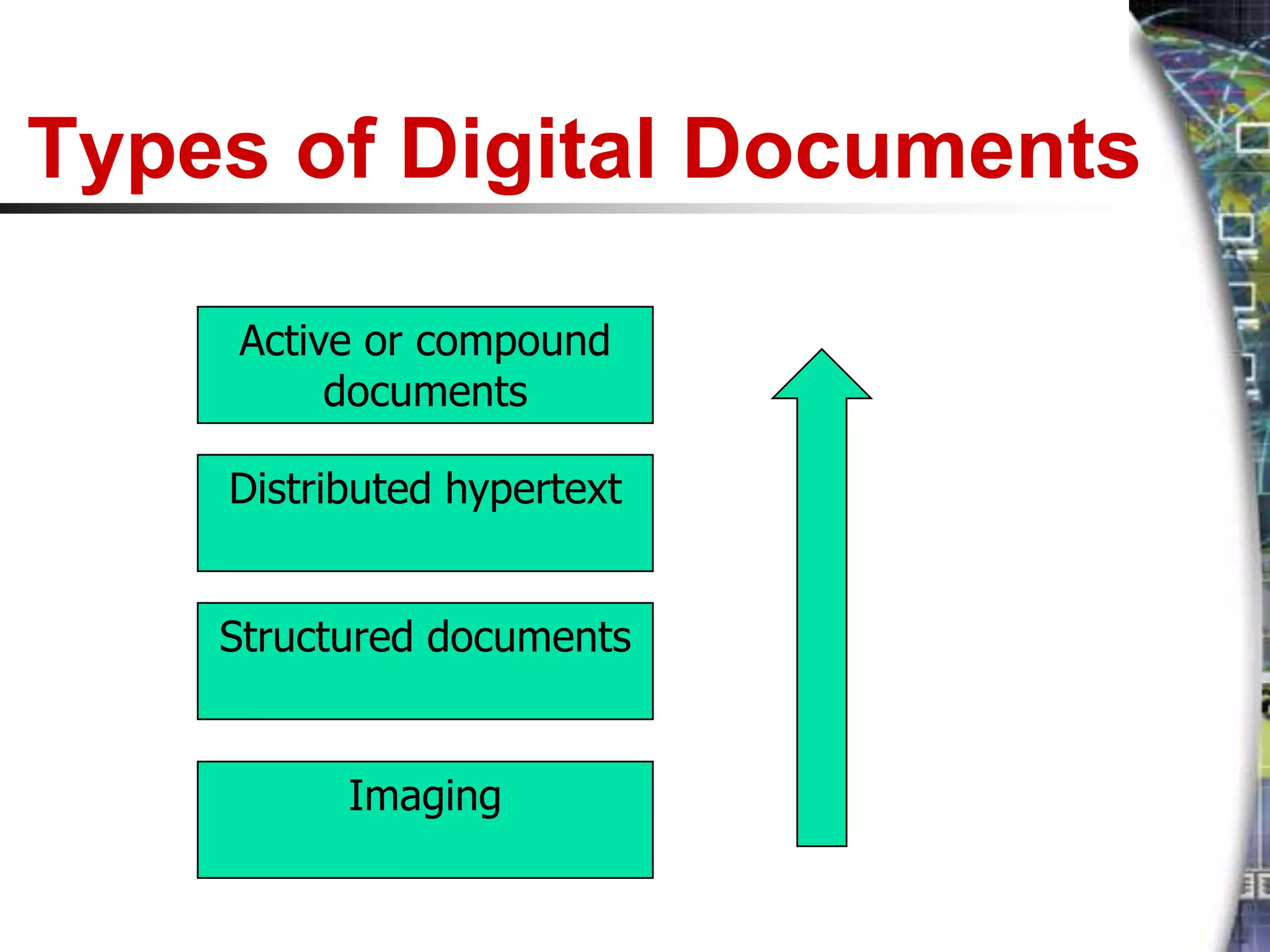
A digital library stores collections of information in digital formats that are accessible via computer networks. It provides an architecture to organize, integrate and transform scattered digital documents. Companies can use a digital library as the foundation for decision support systems to perform more accurate analyses. There are different types of digital libraries including document libraries containing books and reports, and data warehouses which combine and store vast amounts of historical reference data from multiple sources. While digital libraries provide benefits like unlimited access and storage, they also involve significant costs for conversion, maintenance and technical support.