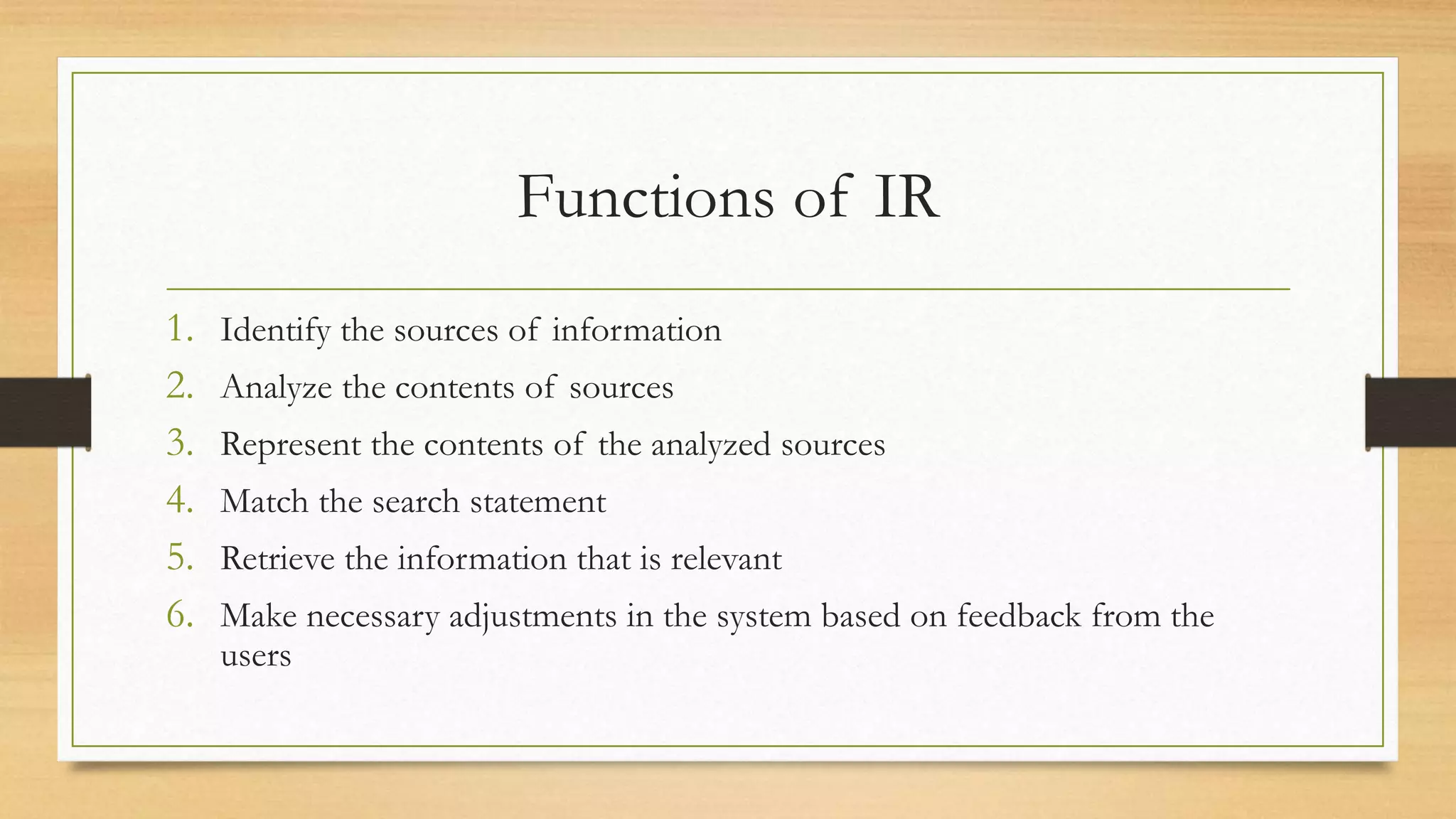
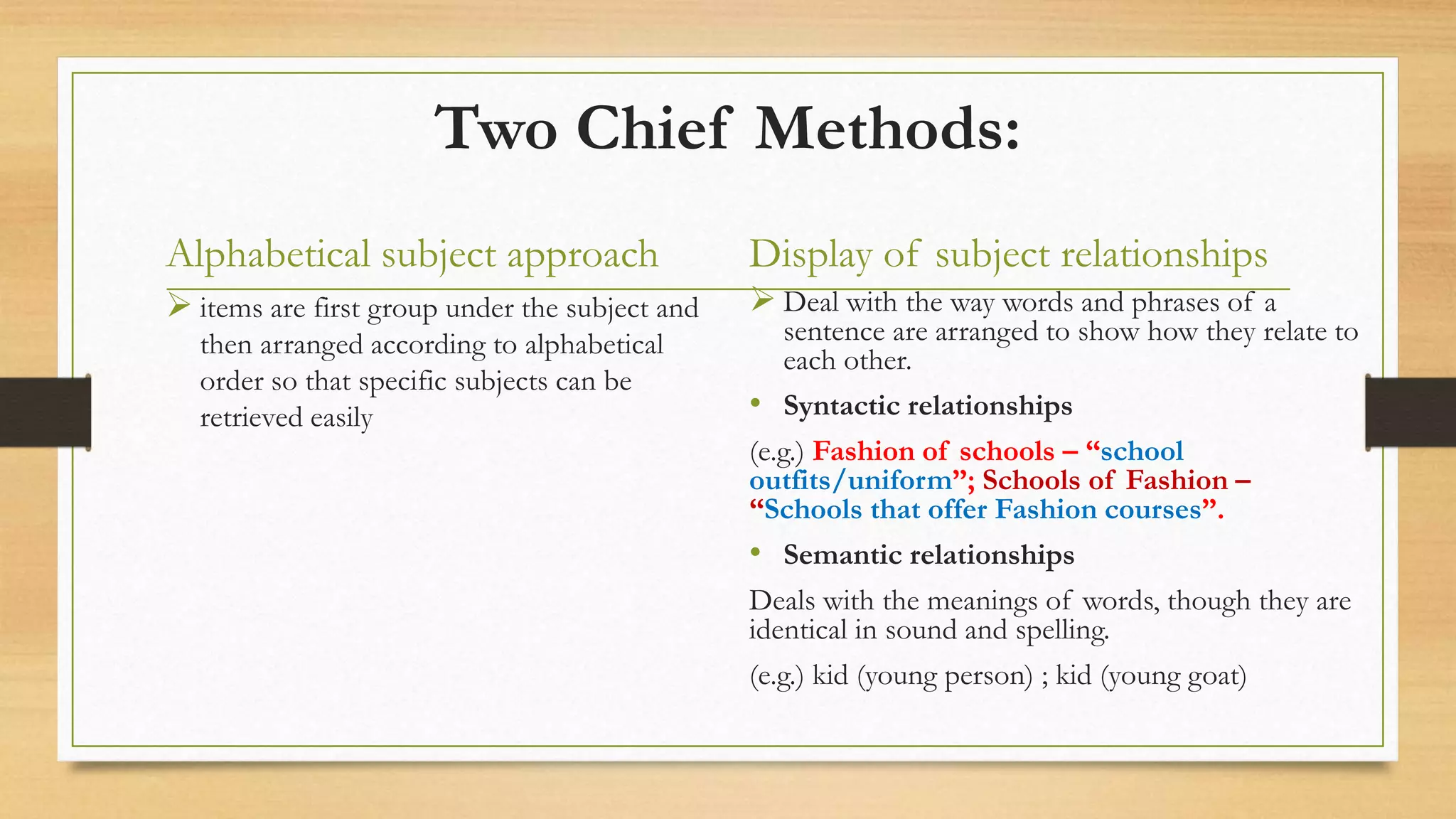
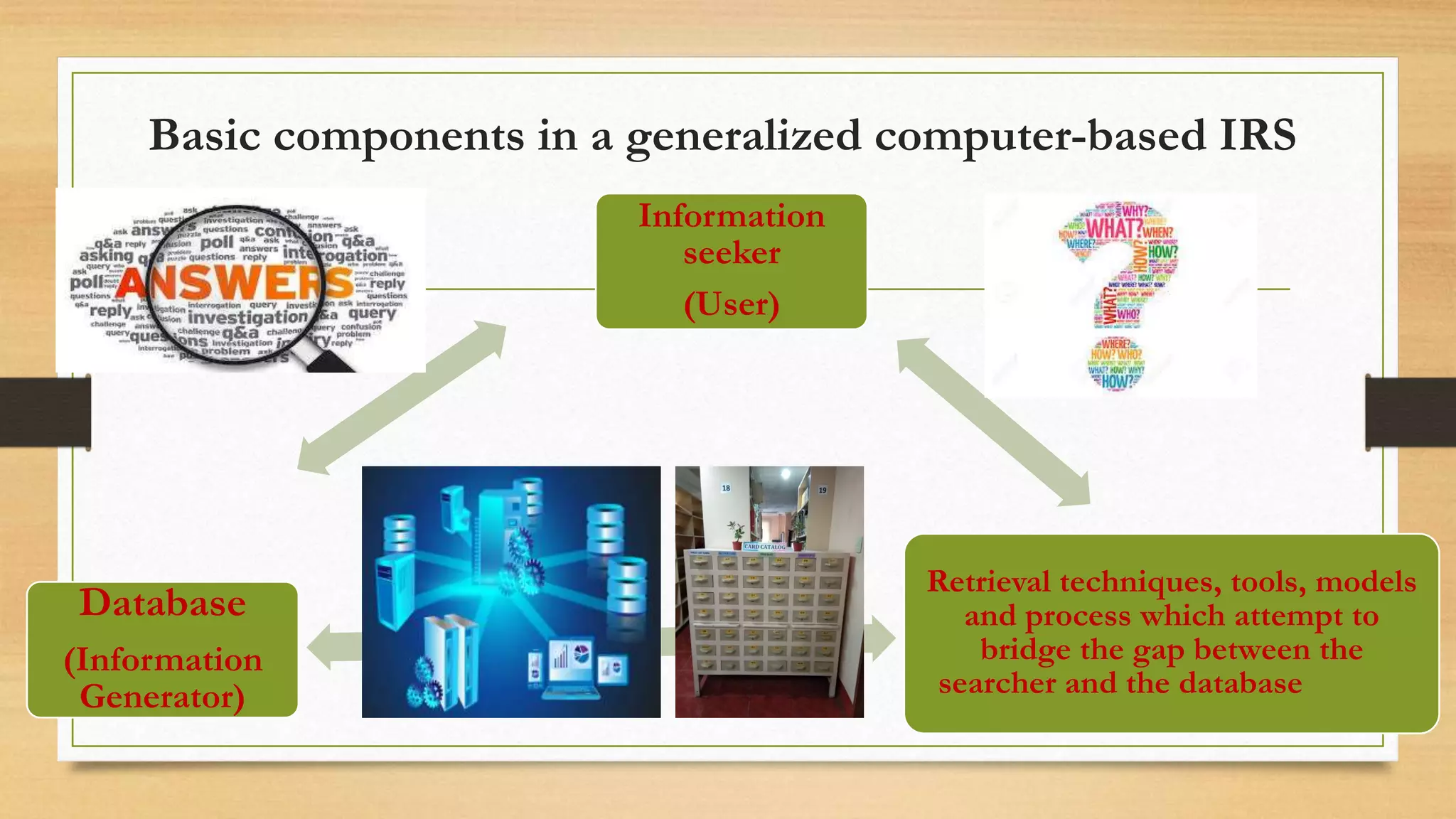
1. The document defines key terms related to information retrieval systems such as information, retrieval, system, and discusses the basic components and functions of IRS.
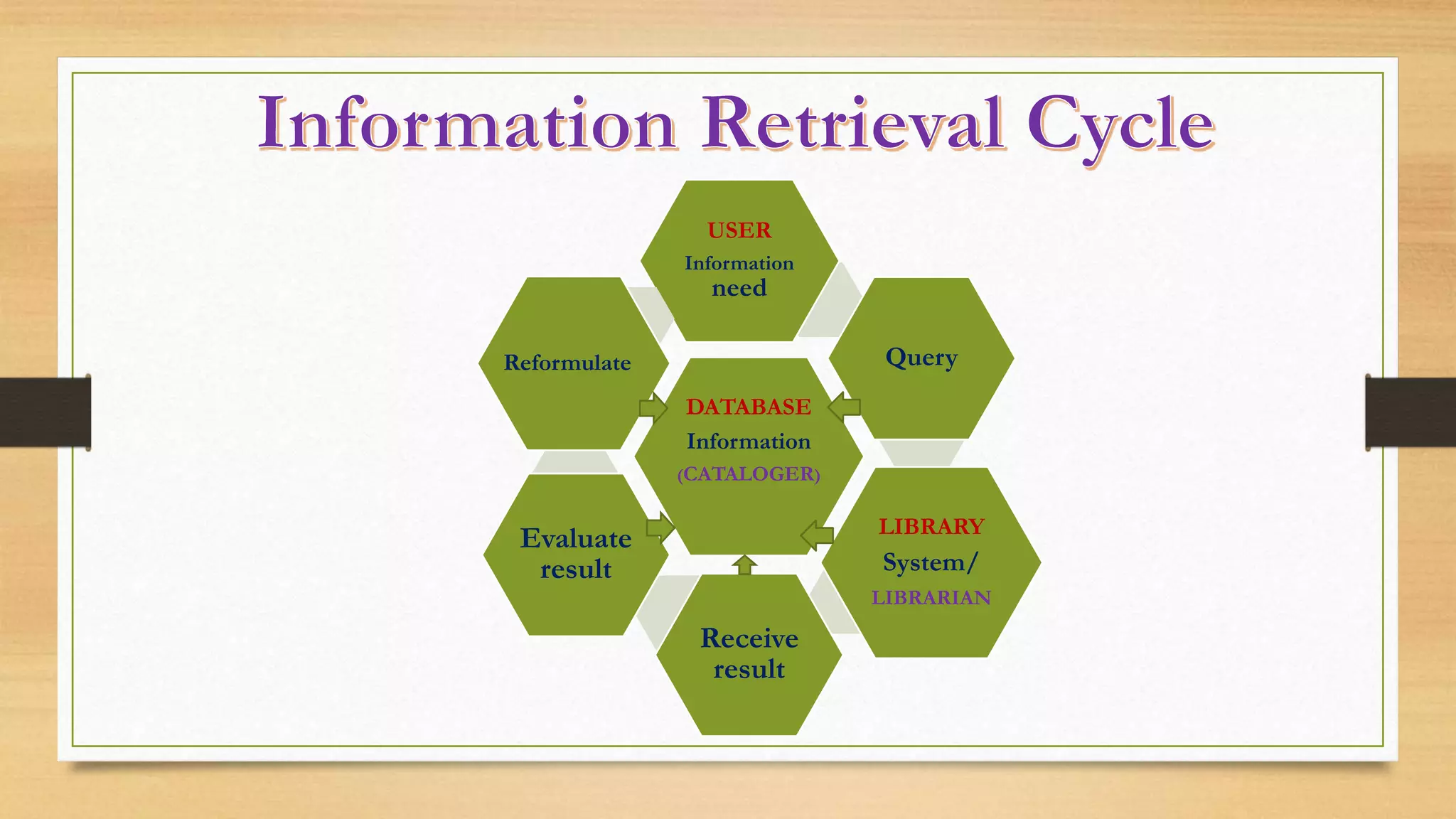
2. It explains that the role of users is to formulate queries, and the role of librarians is to assist users in meeting their information needs.
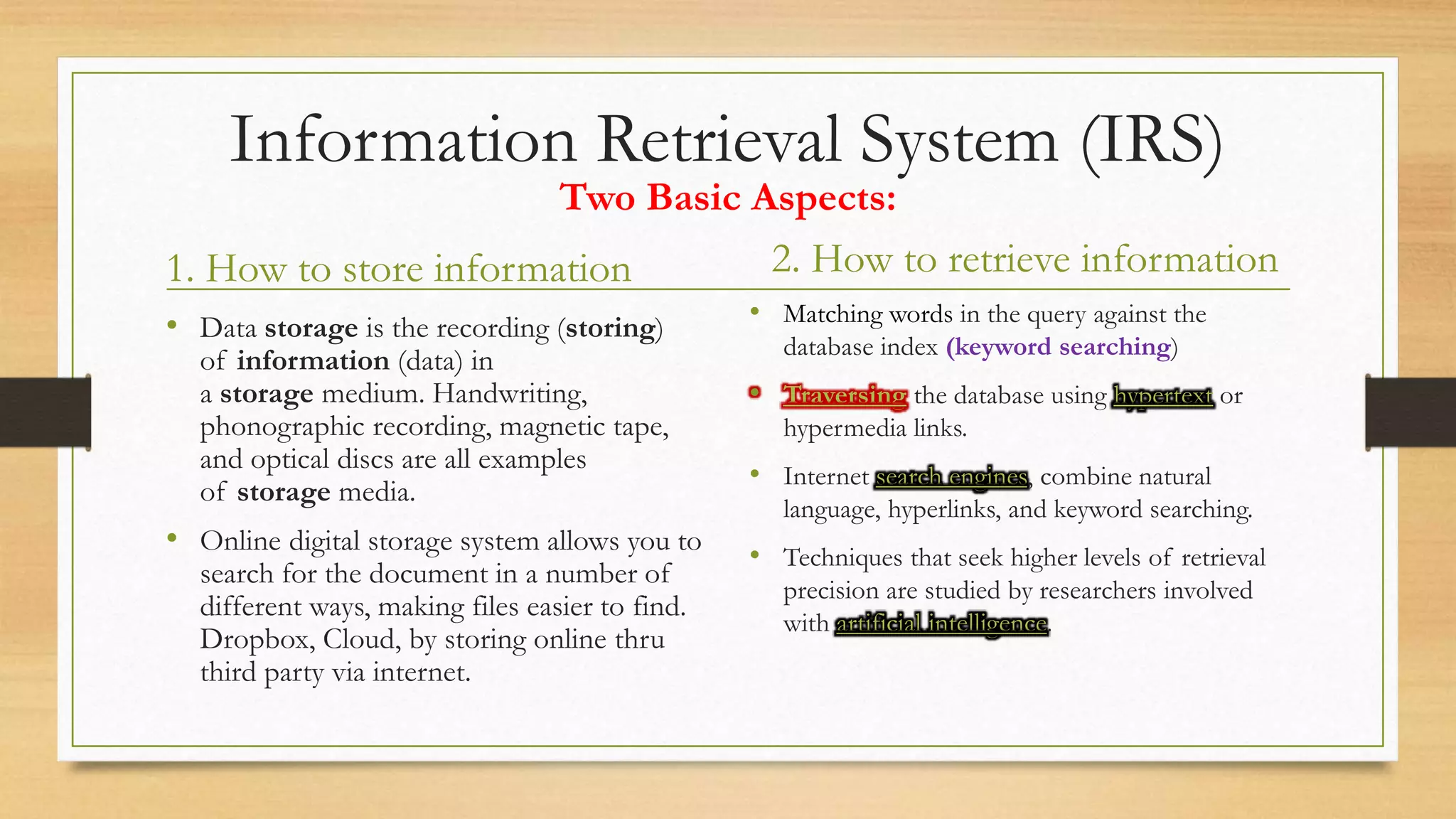
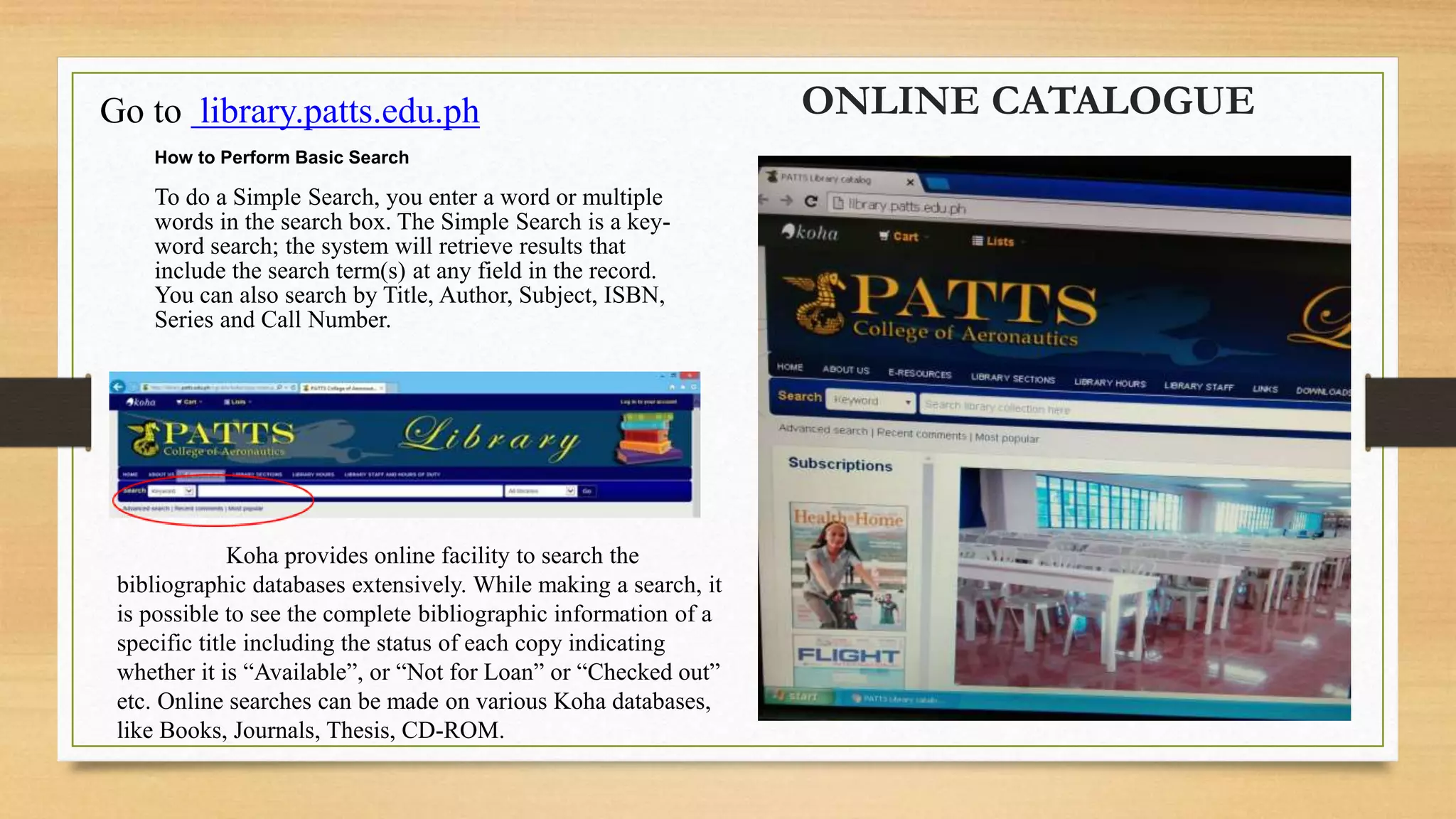
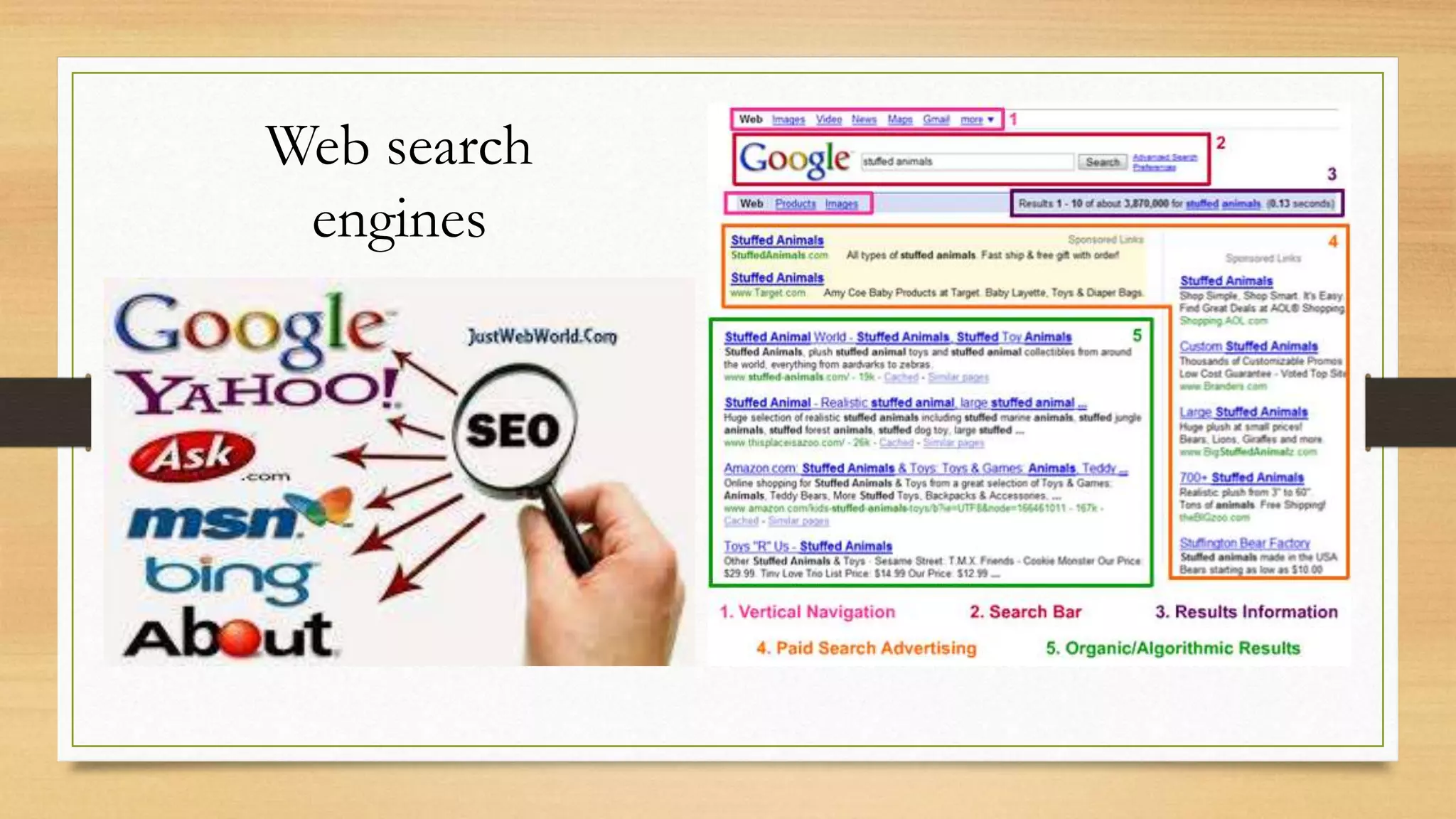
3. The document contrasts older IRS that retrieved entire documents with modern IRS that allow storage, organization, and access to text and multimedia information through techniques like keyword searching and hyperlinks.