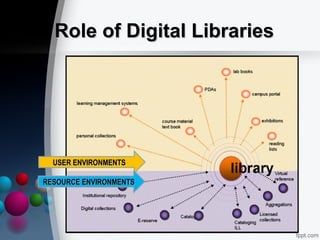
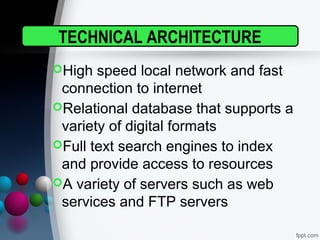
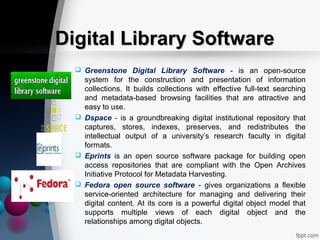
The document provides a comprehensive overview of digital libraries, detailing their definitions, history, roles, and major challenges. It discusses issues such as copyright management, preservation of digital materials, and the technical architecture required for successful digital library operation. Additionally, it highlights the advantages and disadvantages of digital libraries, along with examples of digital library software.