Embed presentation
Downloaded 44 times
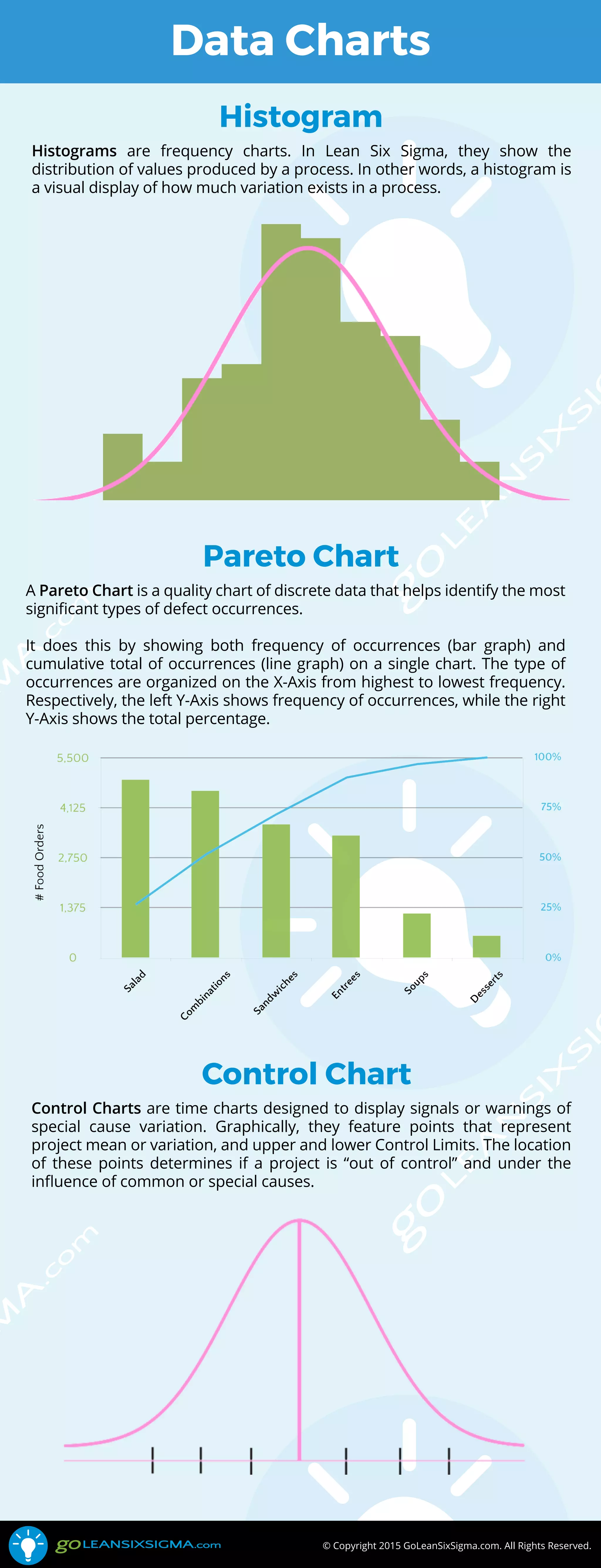

The document discusses three types of quality charts used in Lean Six Sigma: histograms, Pareto charts, and control charts. Histograms visualize the distribution of process values, Pareto charts identify significant defect occurrences by displaying frequency and cumulative percentages, and control charts indicate process stability by showing project means and control limits. Each chart serves a unique purpose for analyzing process variation and quality control.
