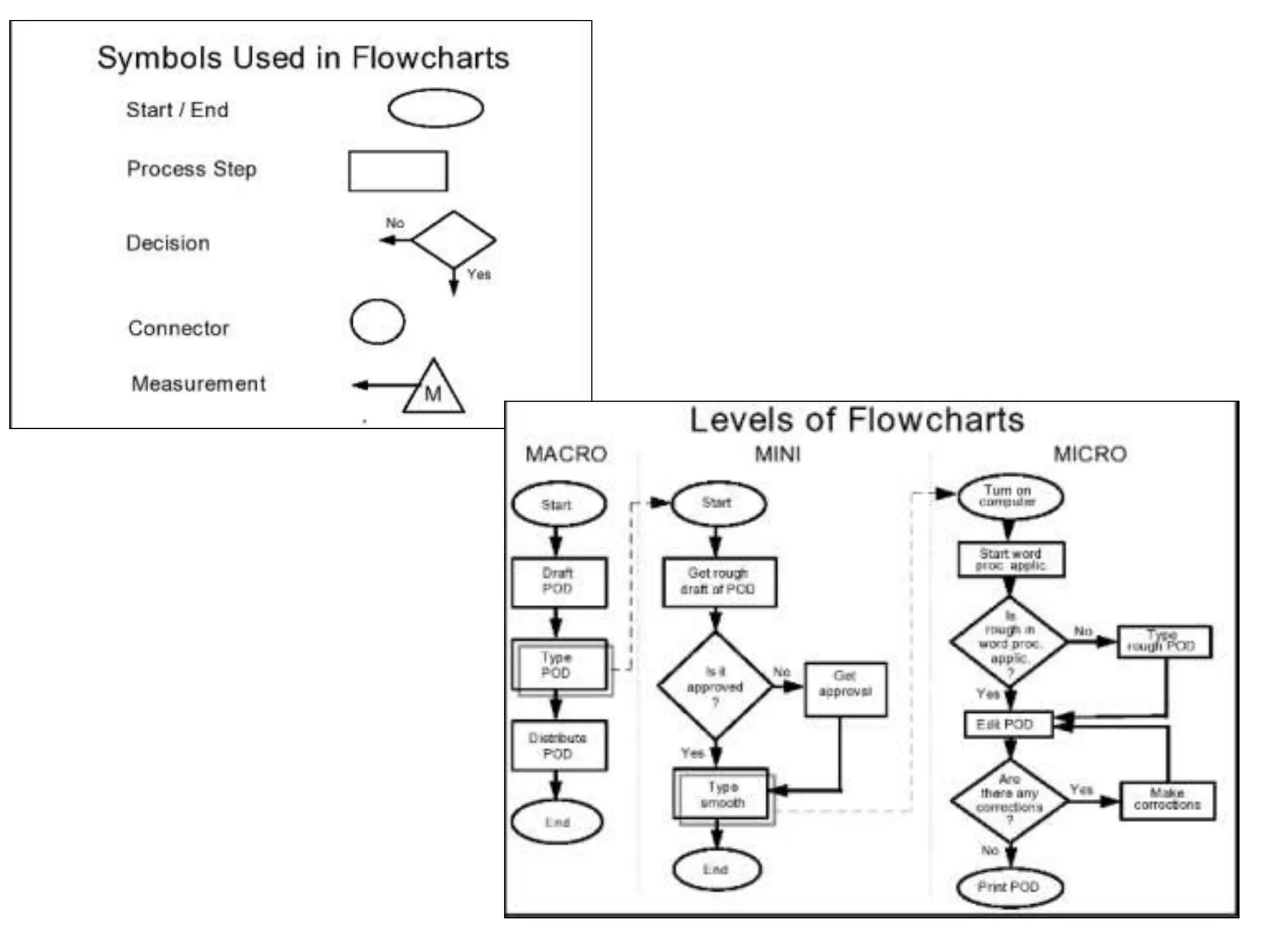
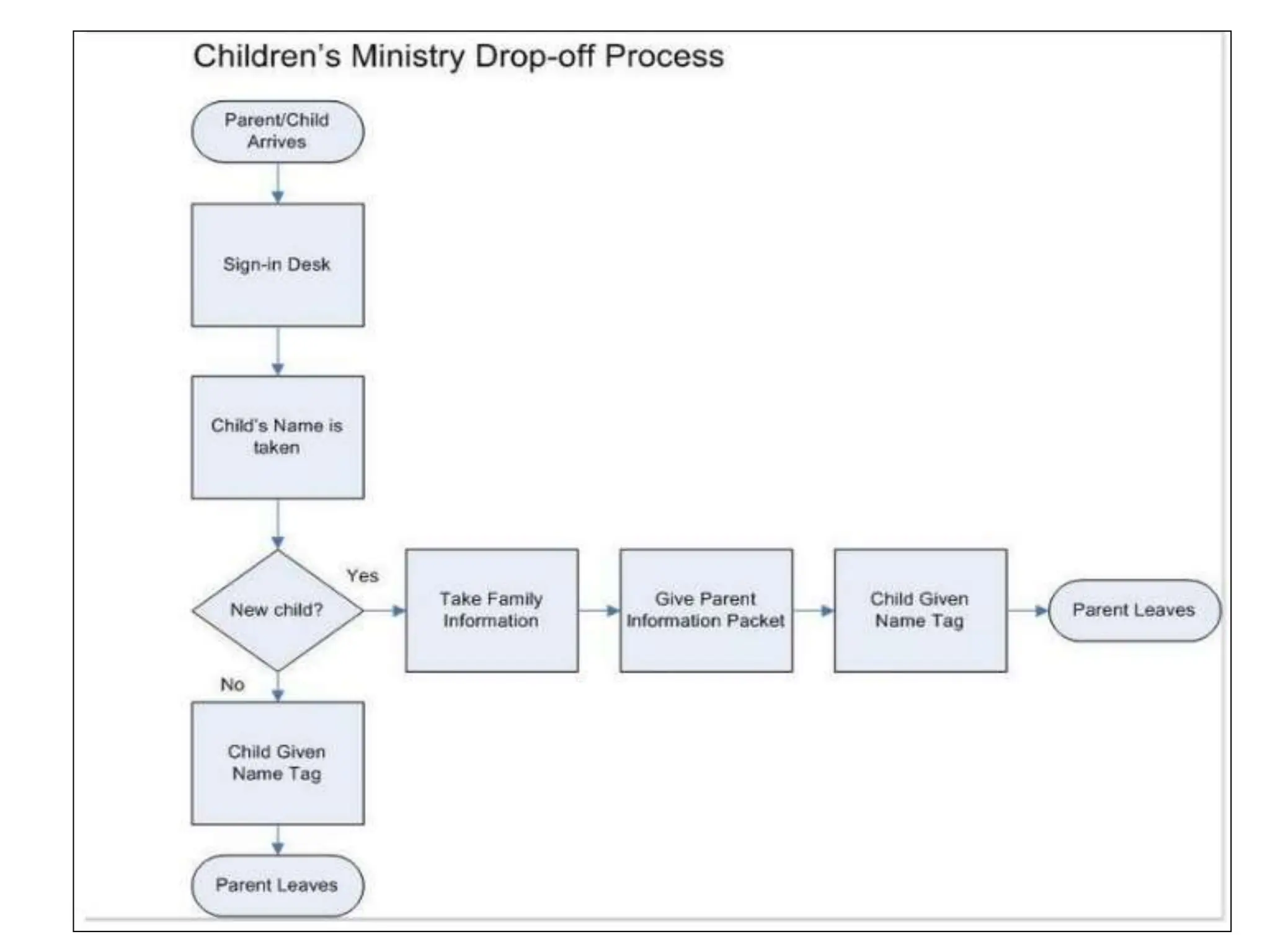
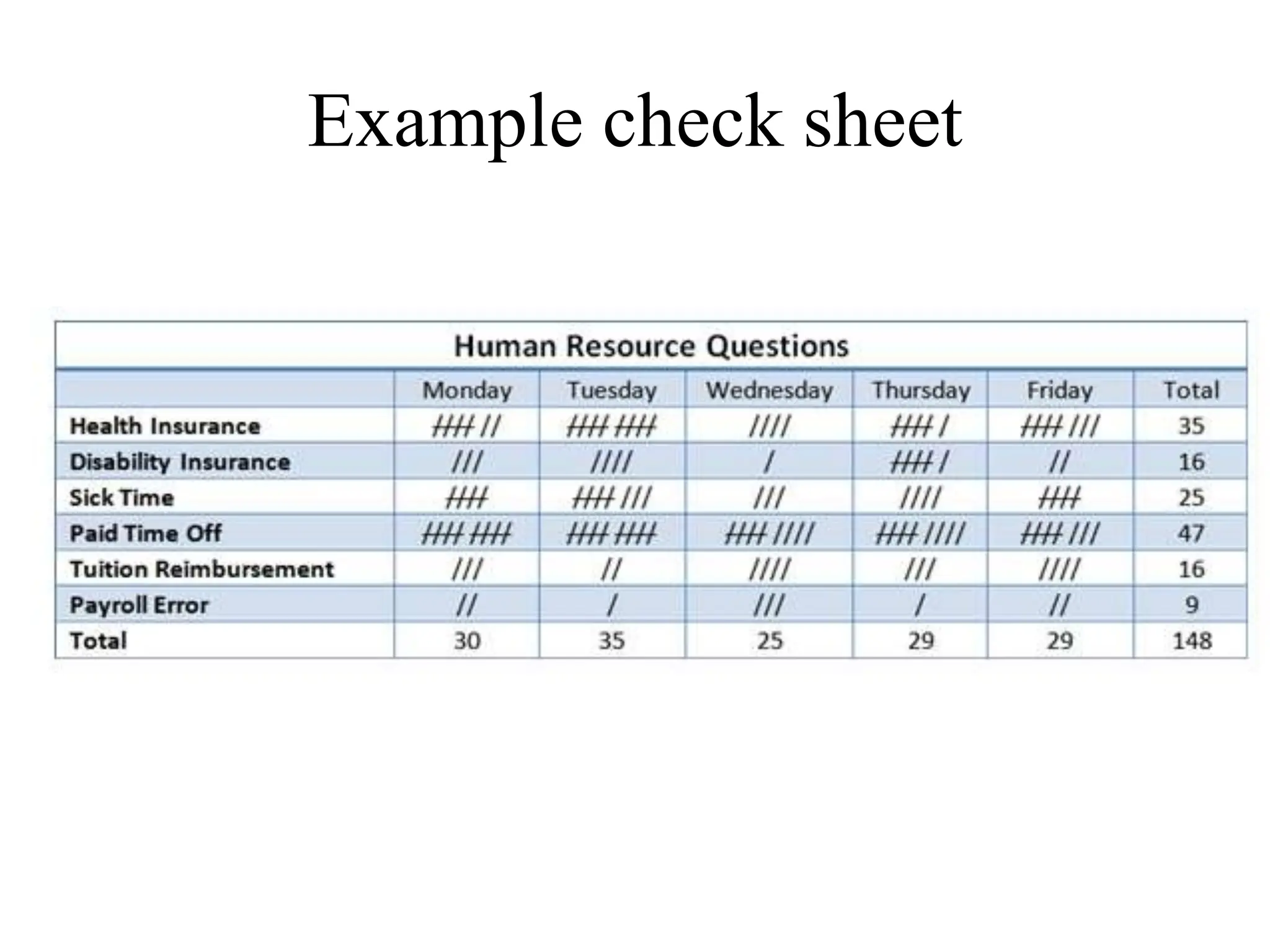
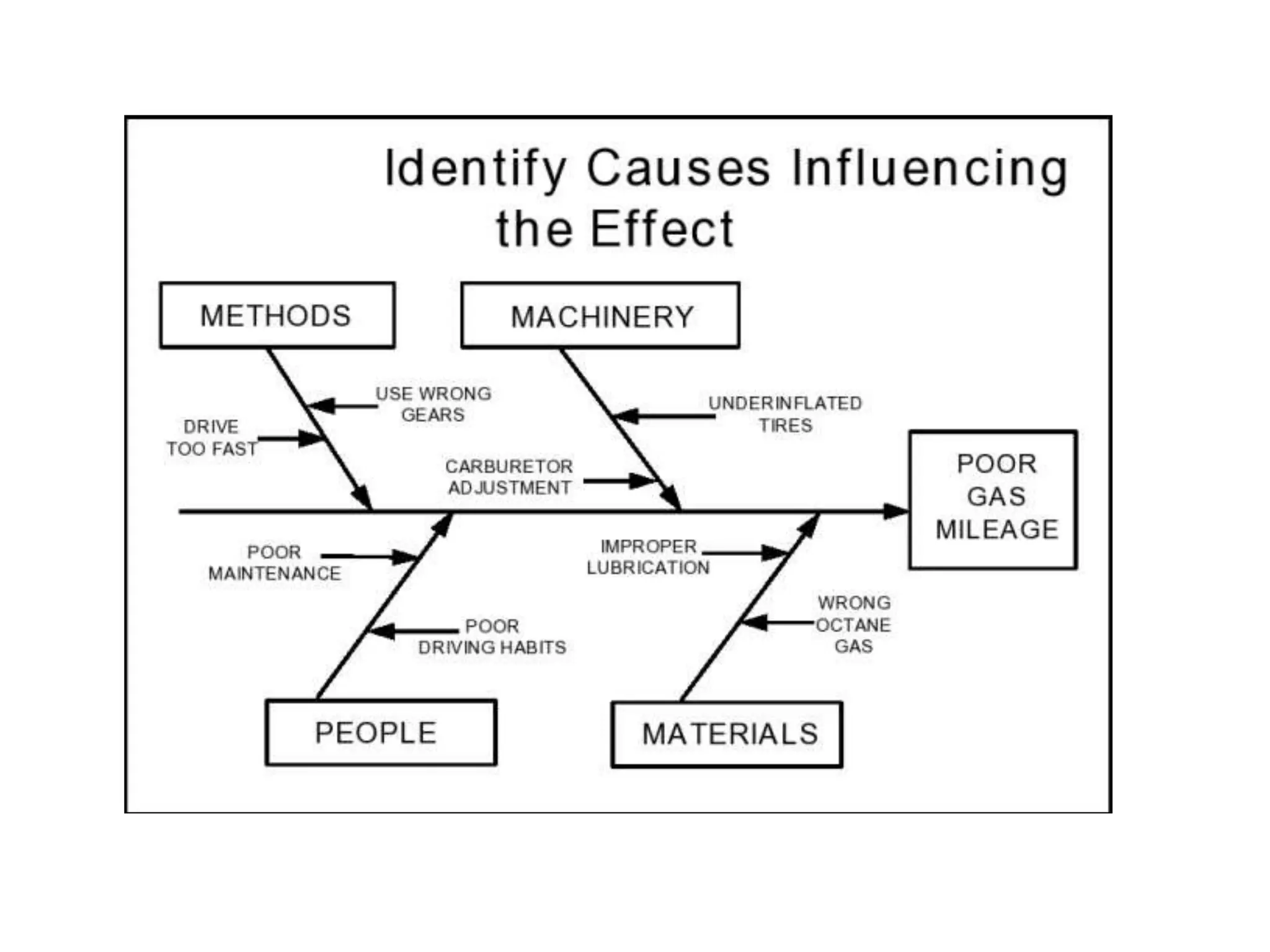
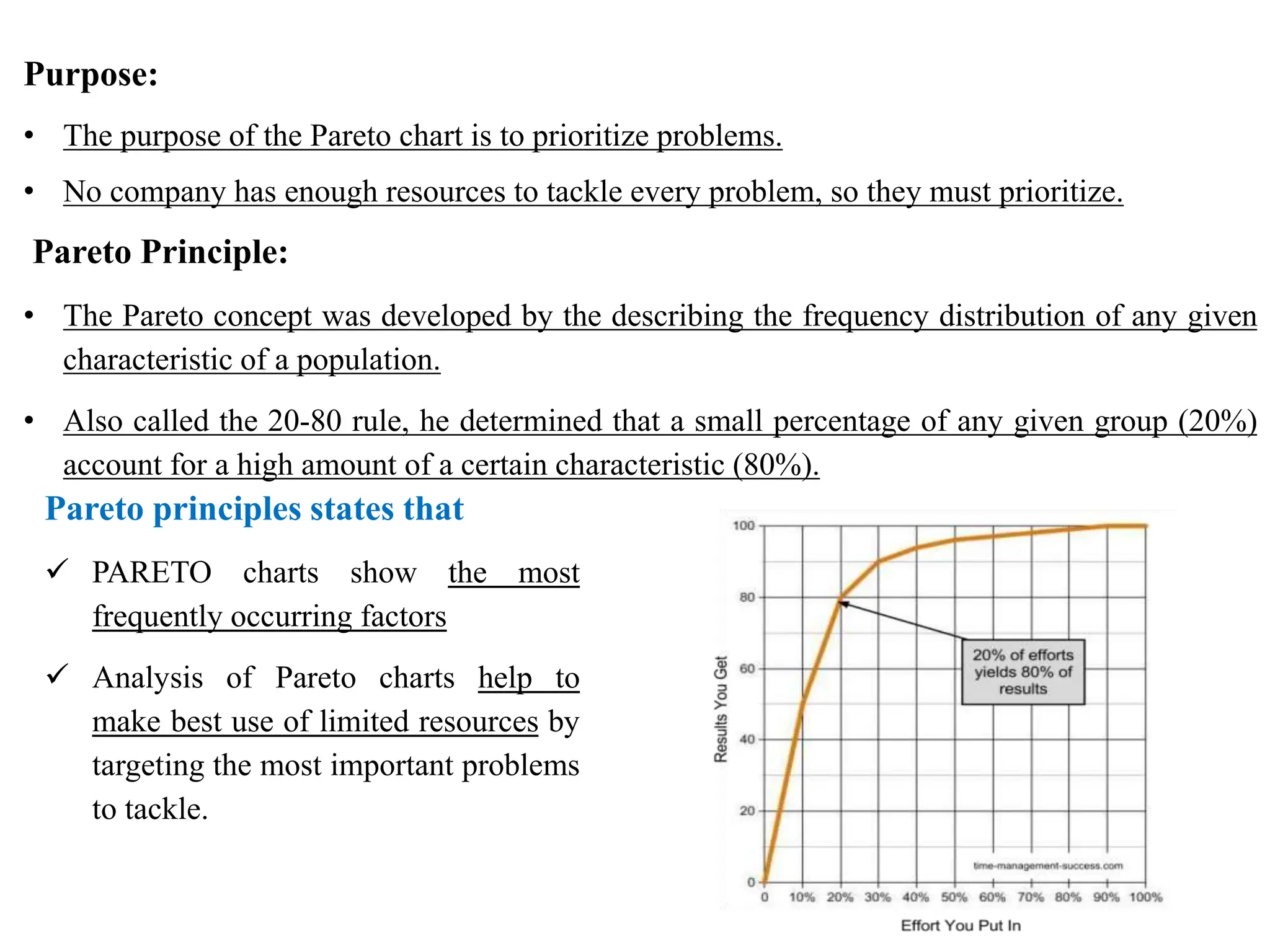
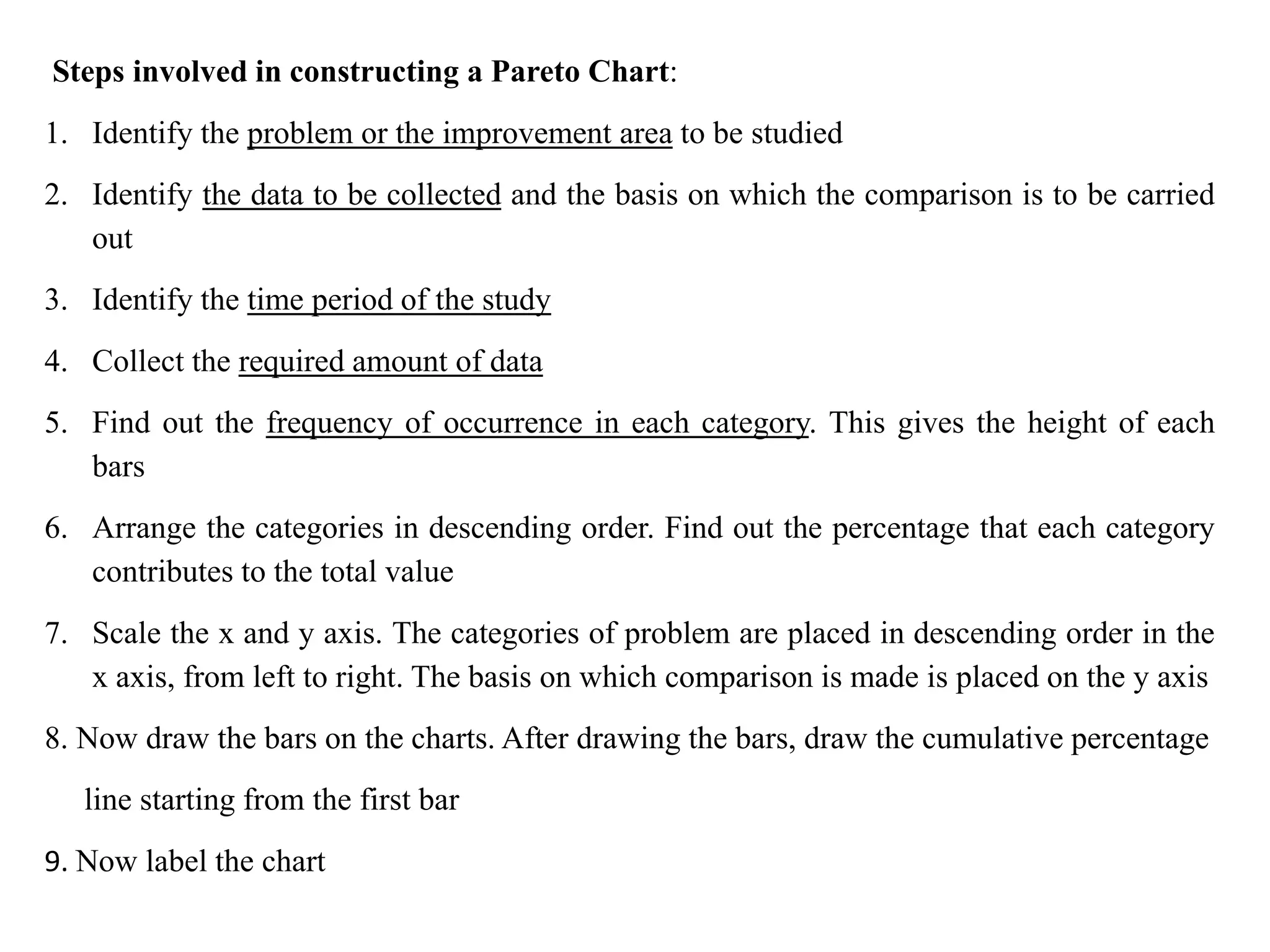
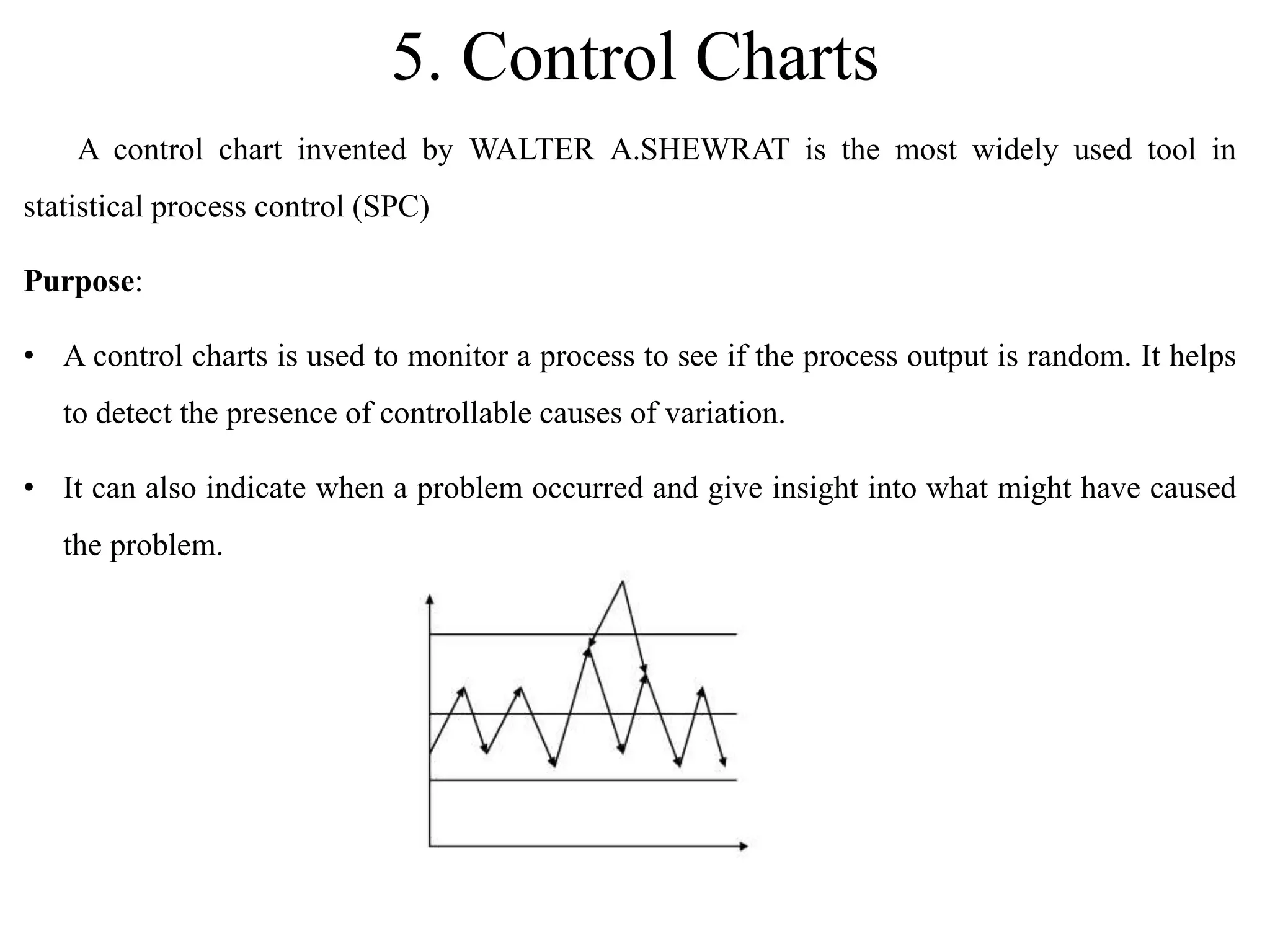
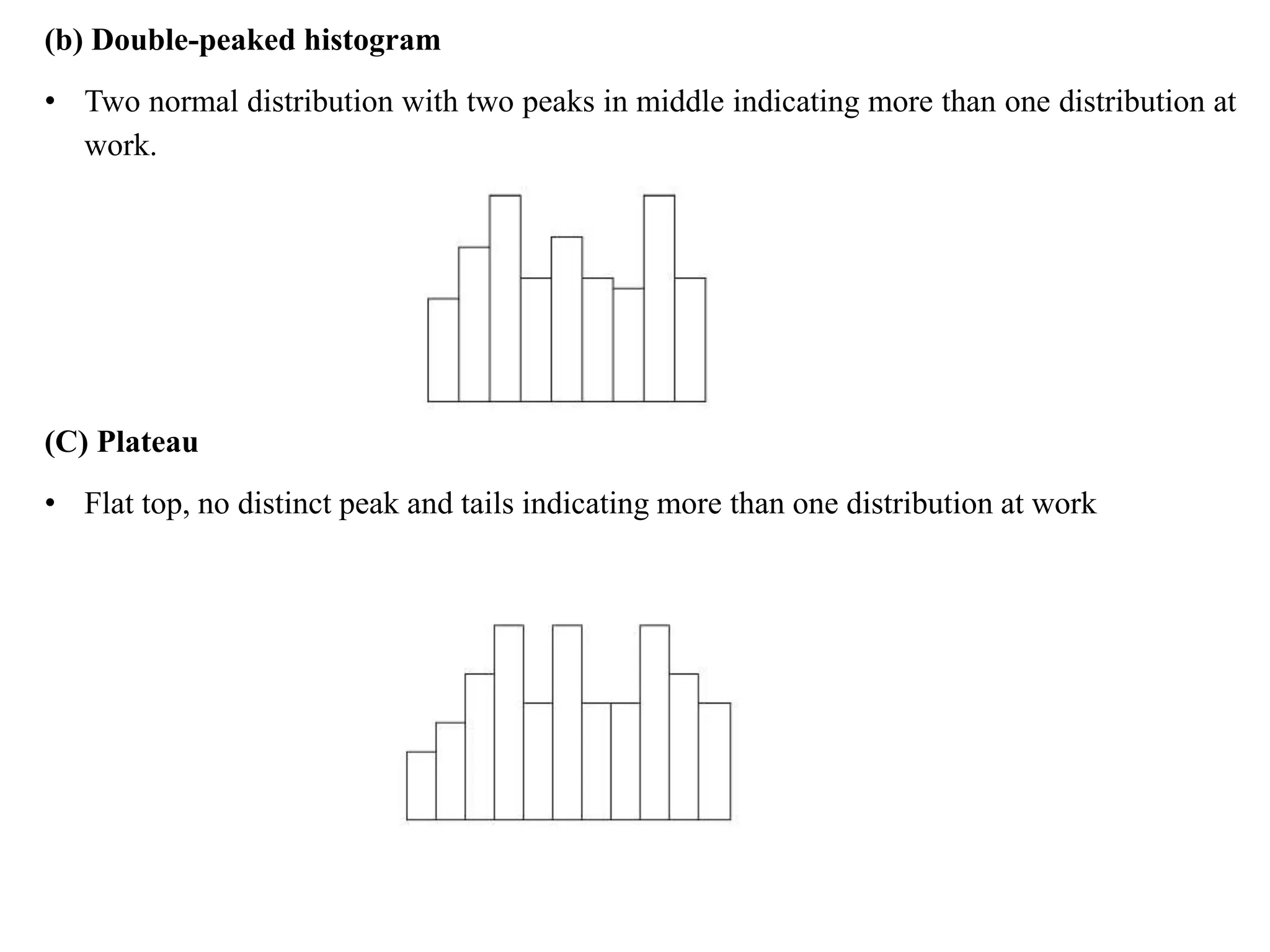
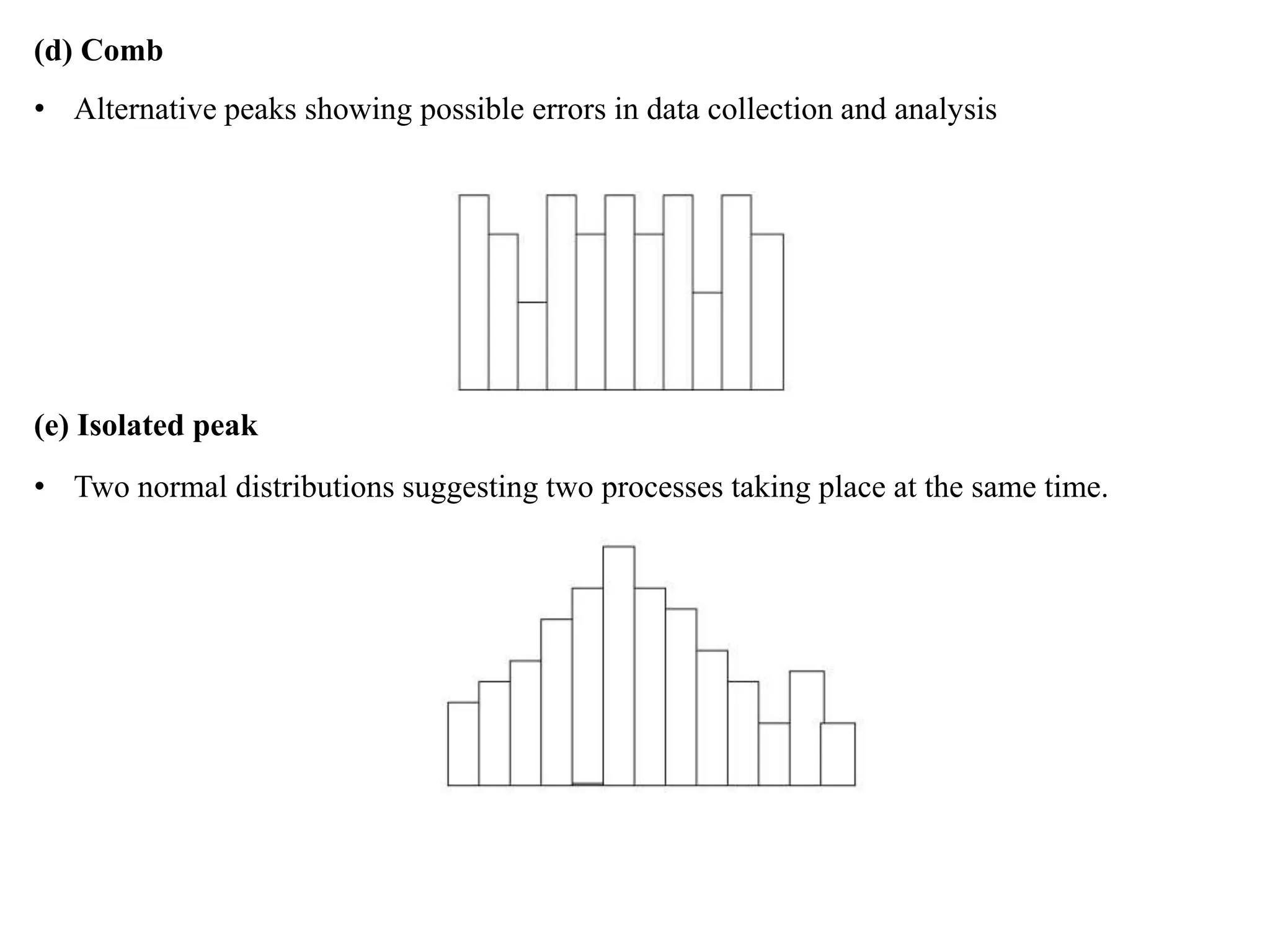
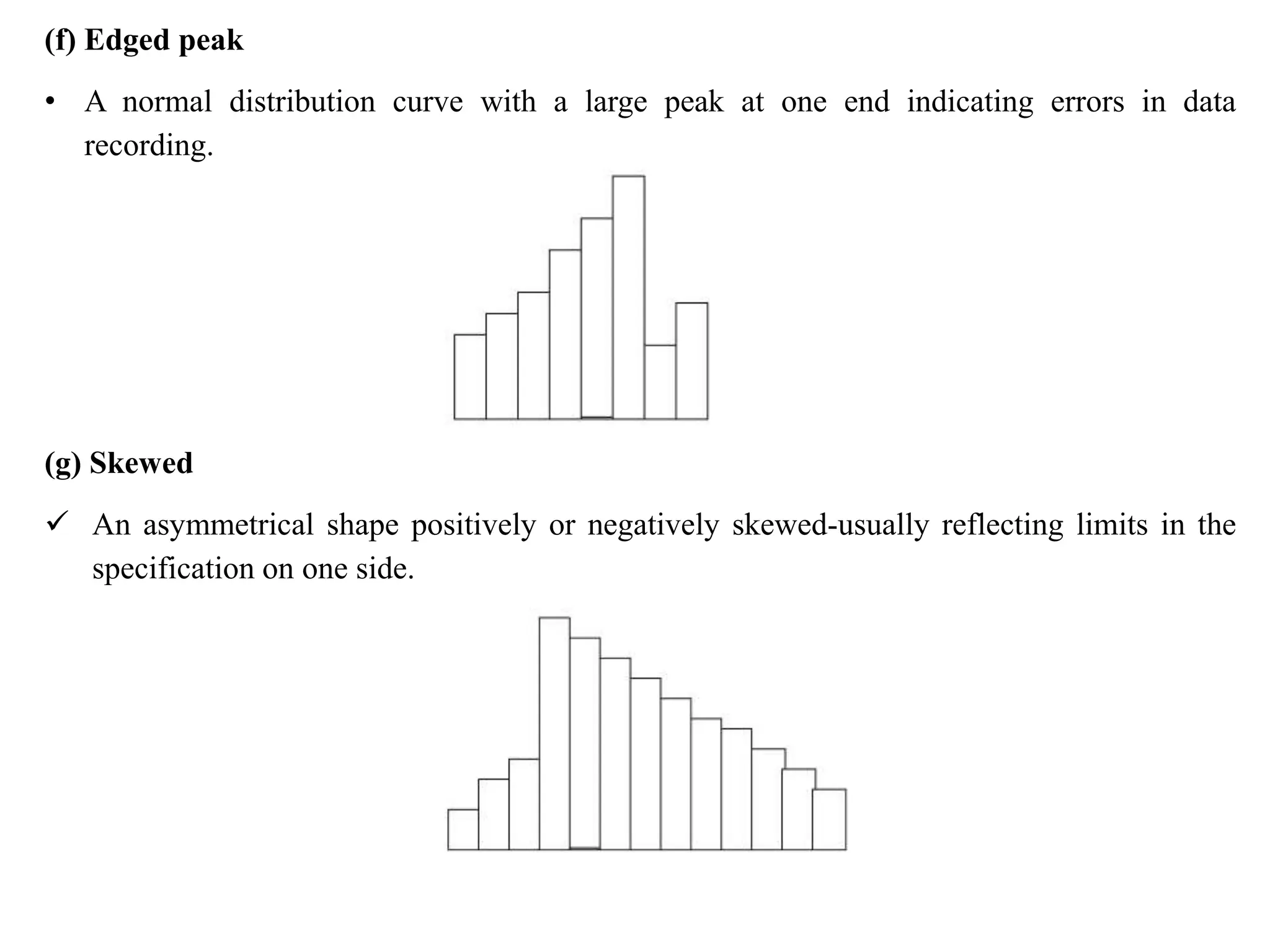
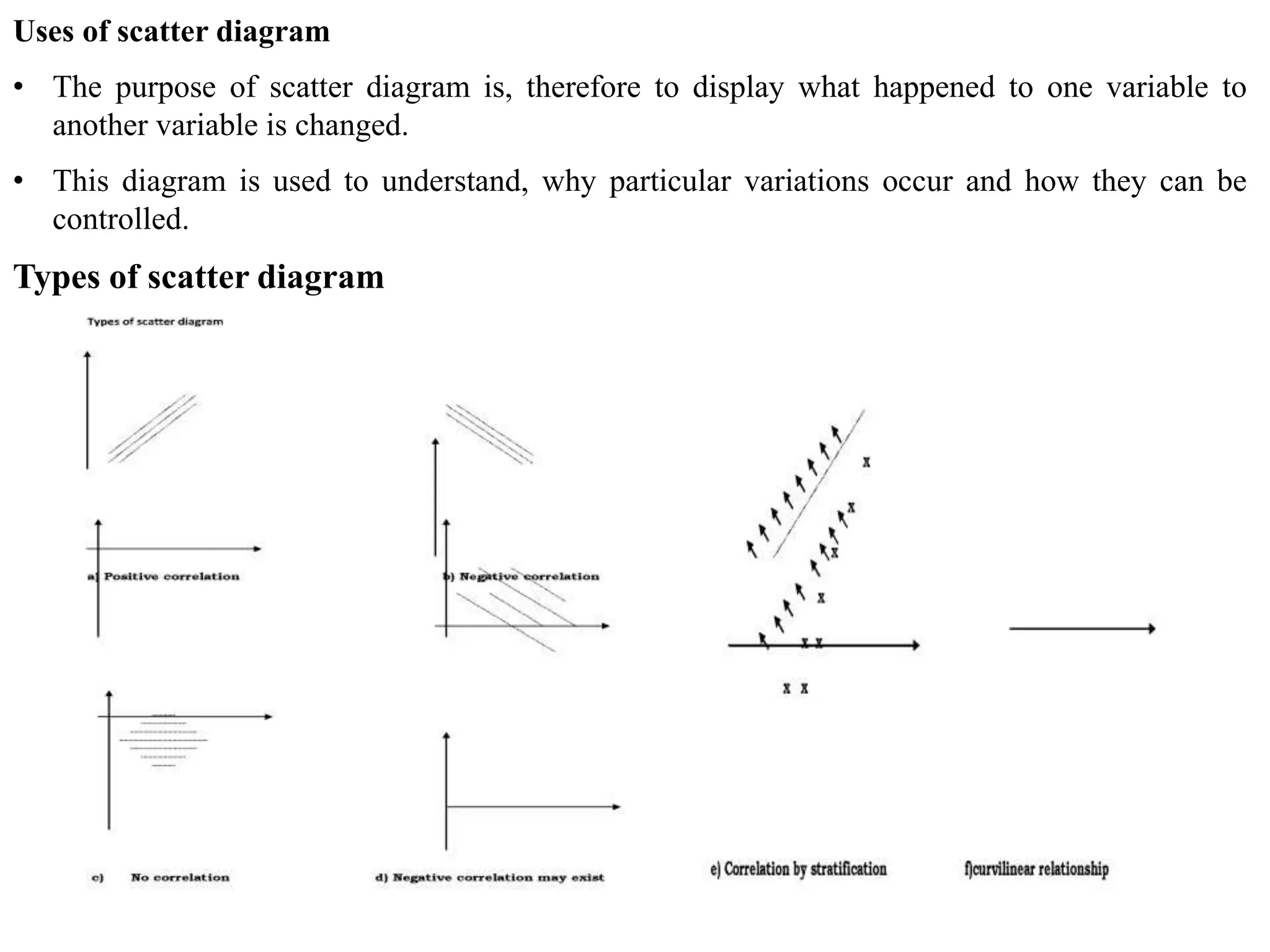
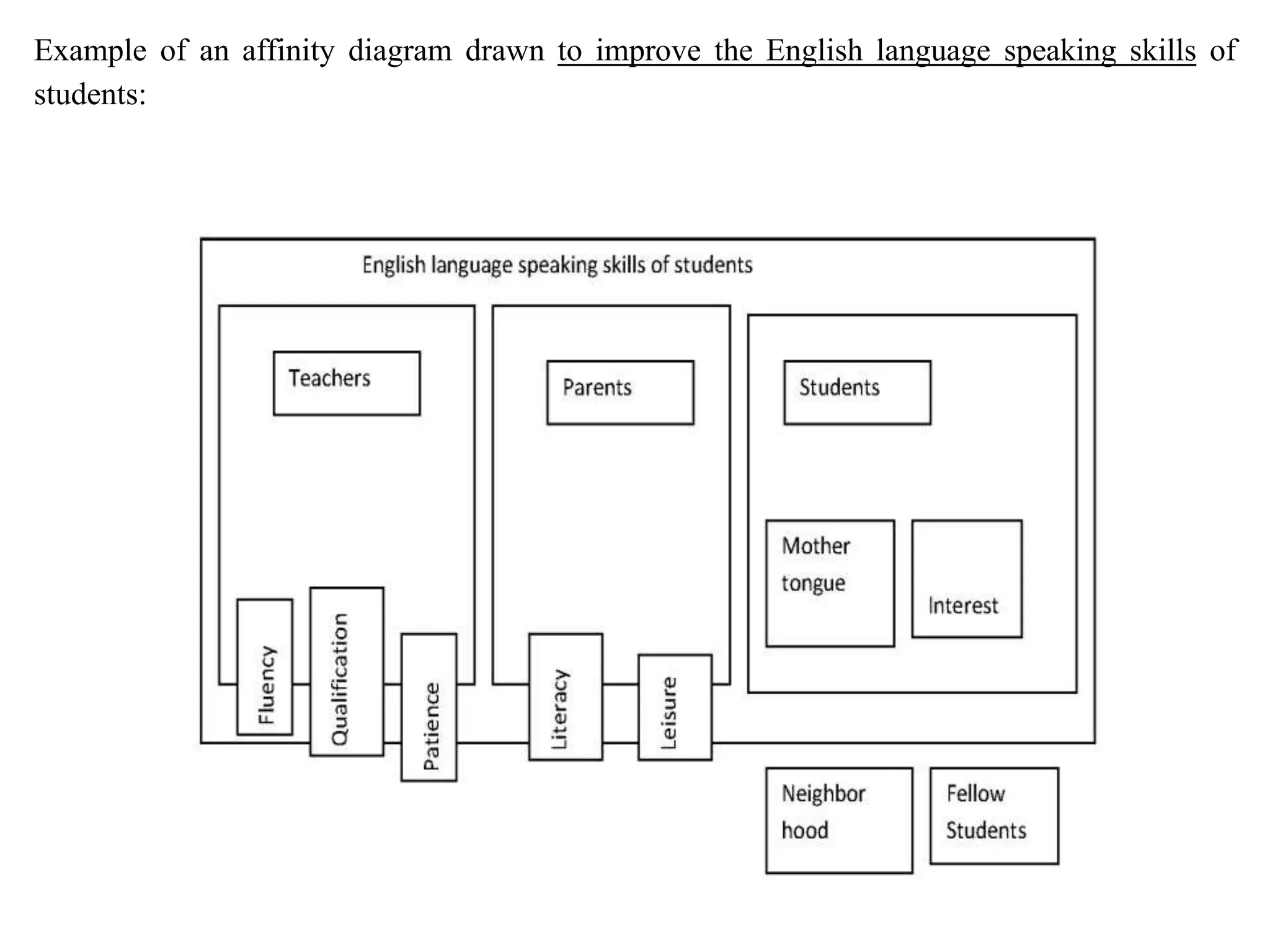
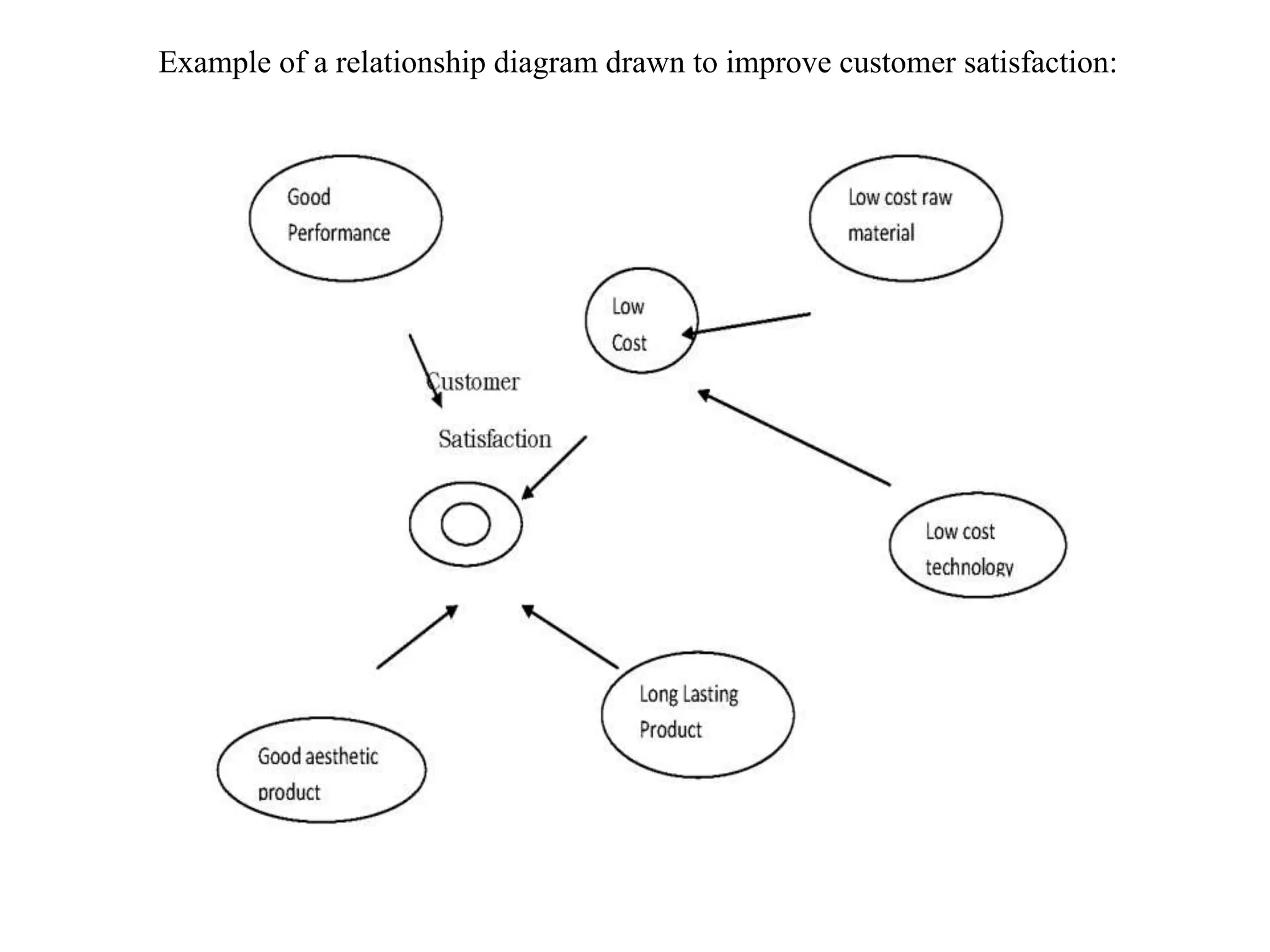
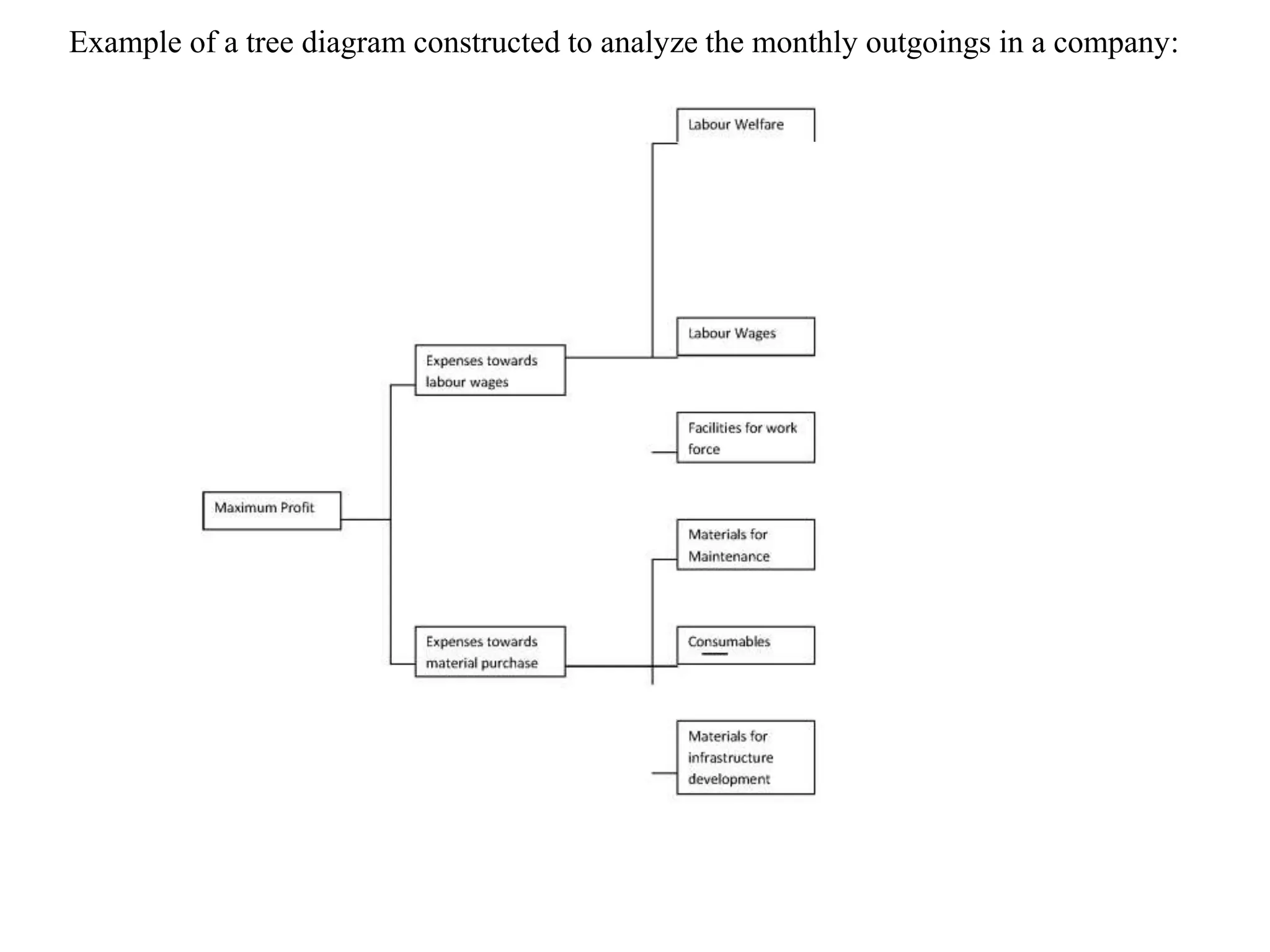
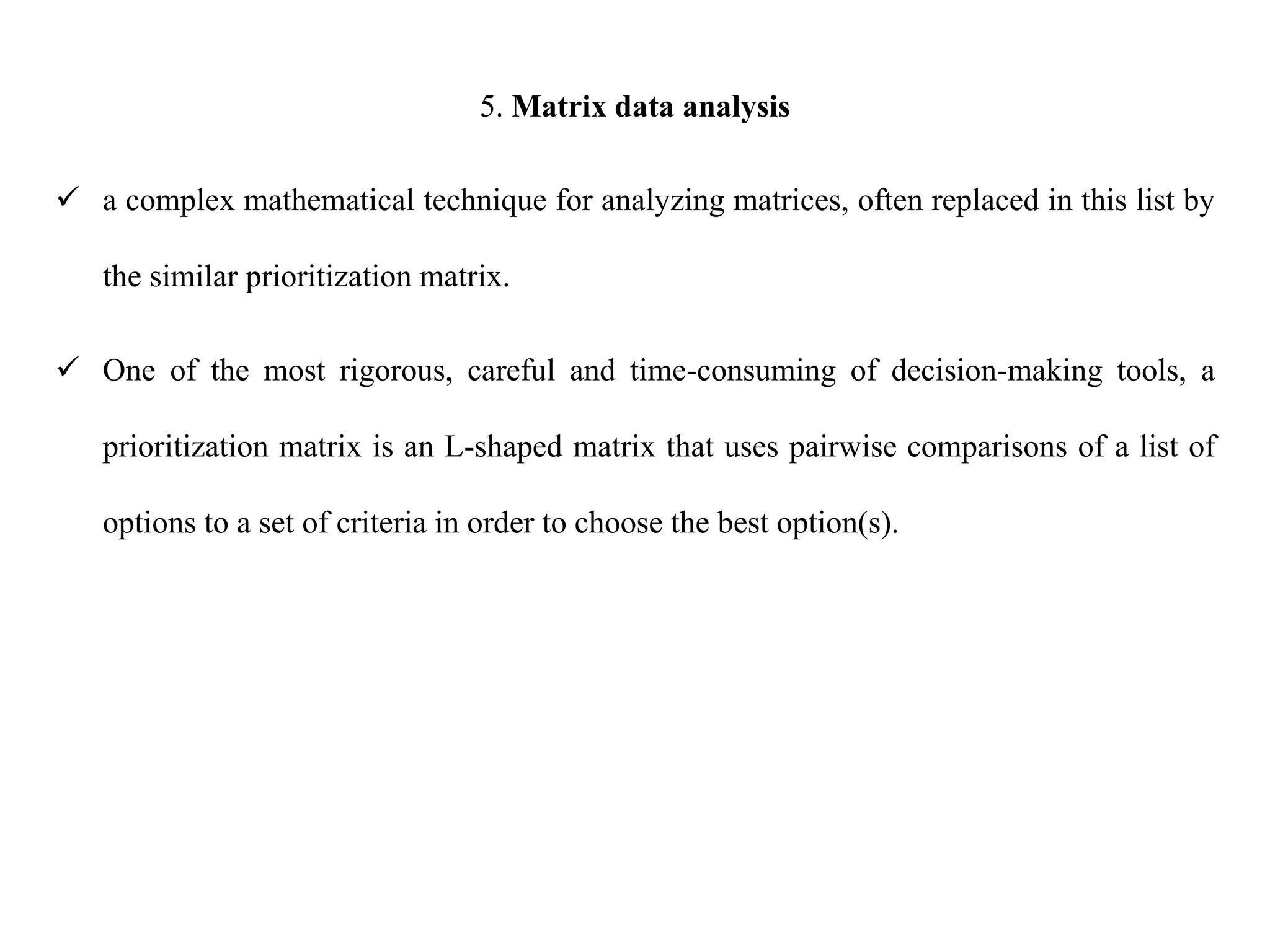
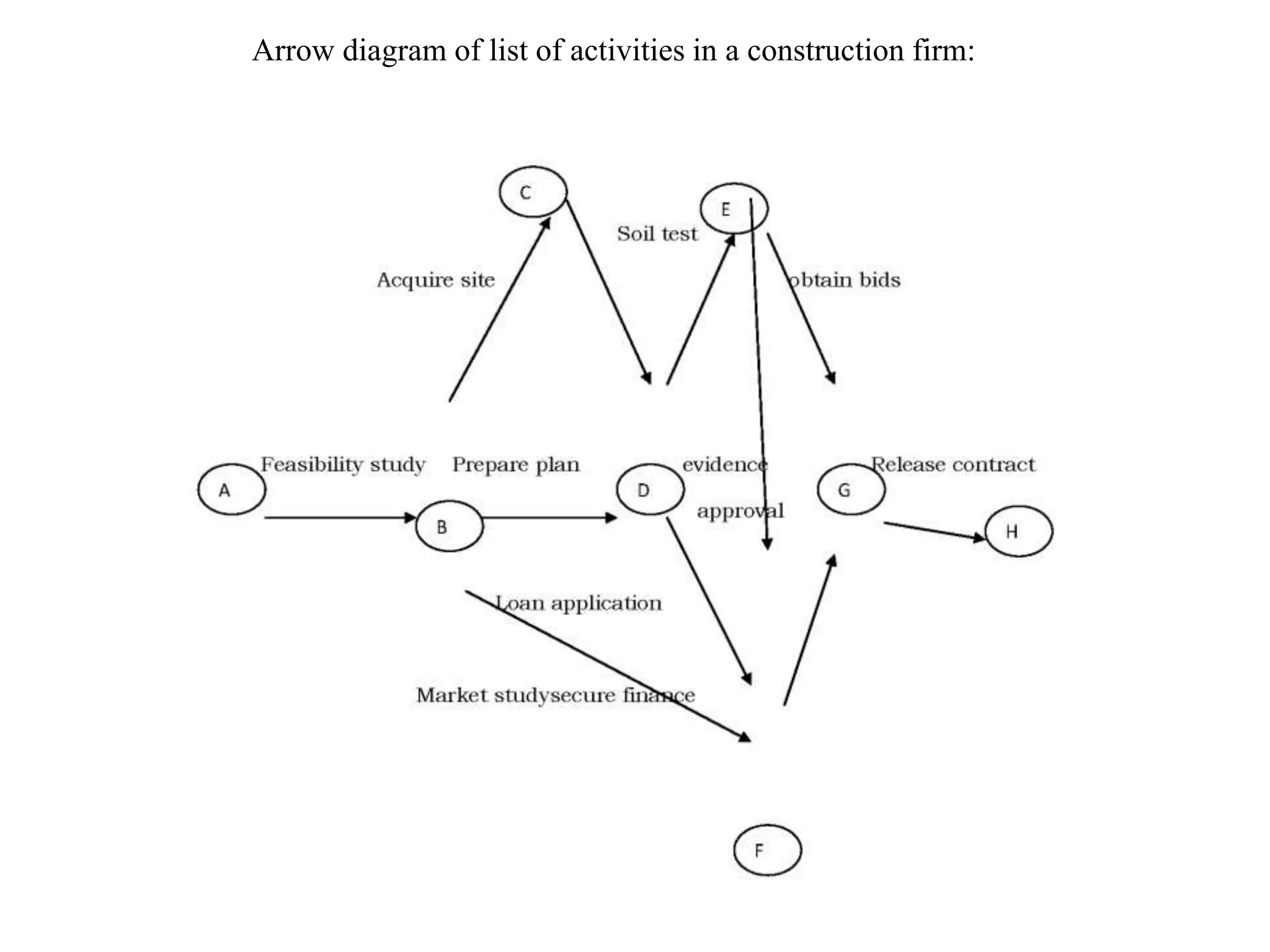
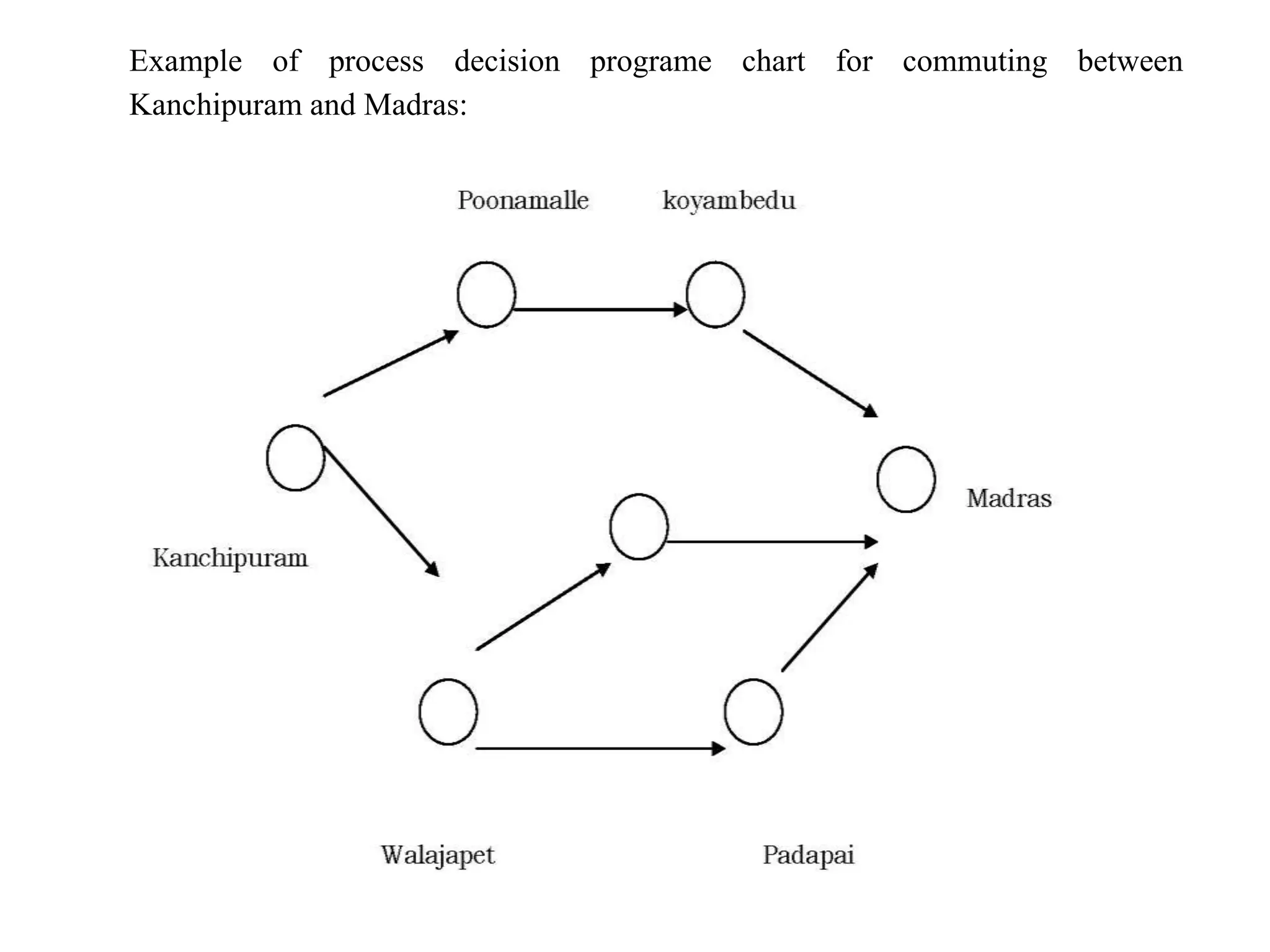
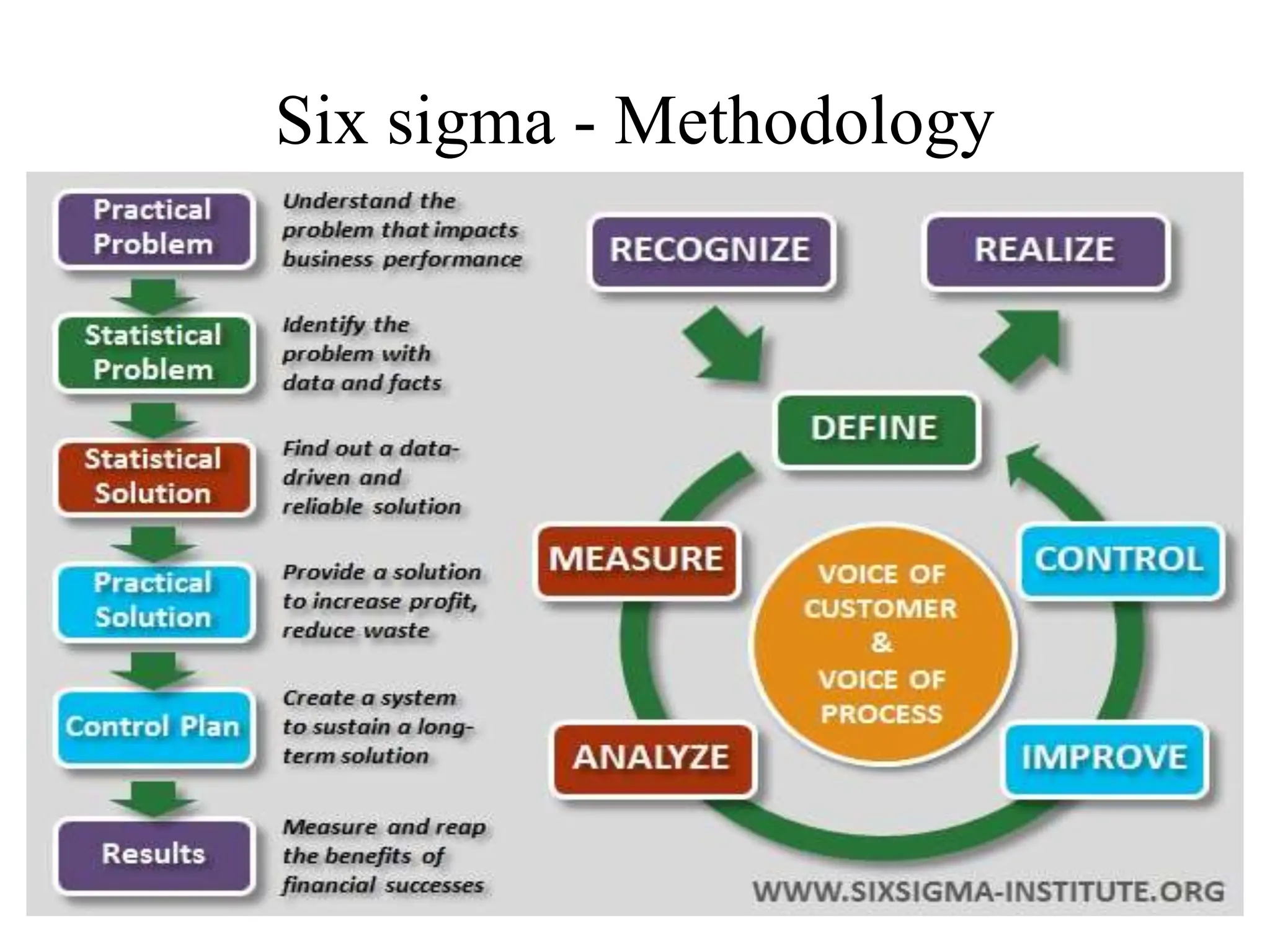
The document discusses various quality management tools and techniques, including the seven traditional quality tools, Six Sigma methodology, and new management tools. It provides details on each tool, including definitions, examples, and uses. The seven traditional quality tools described are flow chart, check sheet, cause and effect diagram, Pareto chart, control chart, histogram, and scatter diagram. Six Sigma follows the DMAIC methodology of define, measure, analyze, improve, and control. The seven new management tools discussed are affinity diagram, interrelations diagram, tree diagram, matrix diagram, arrow diagram, and process decision program chart.