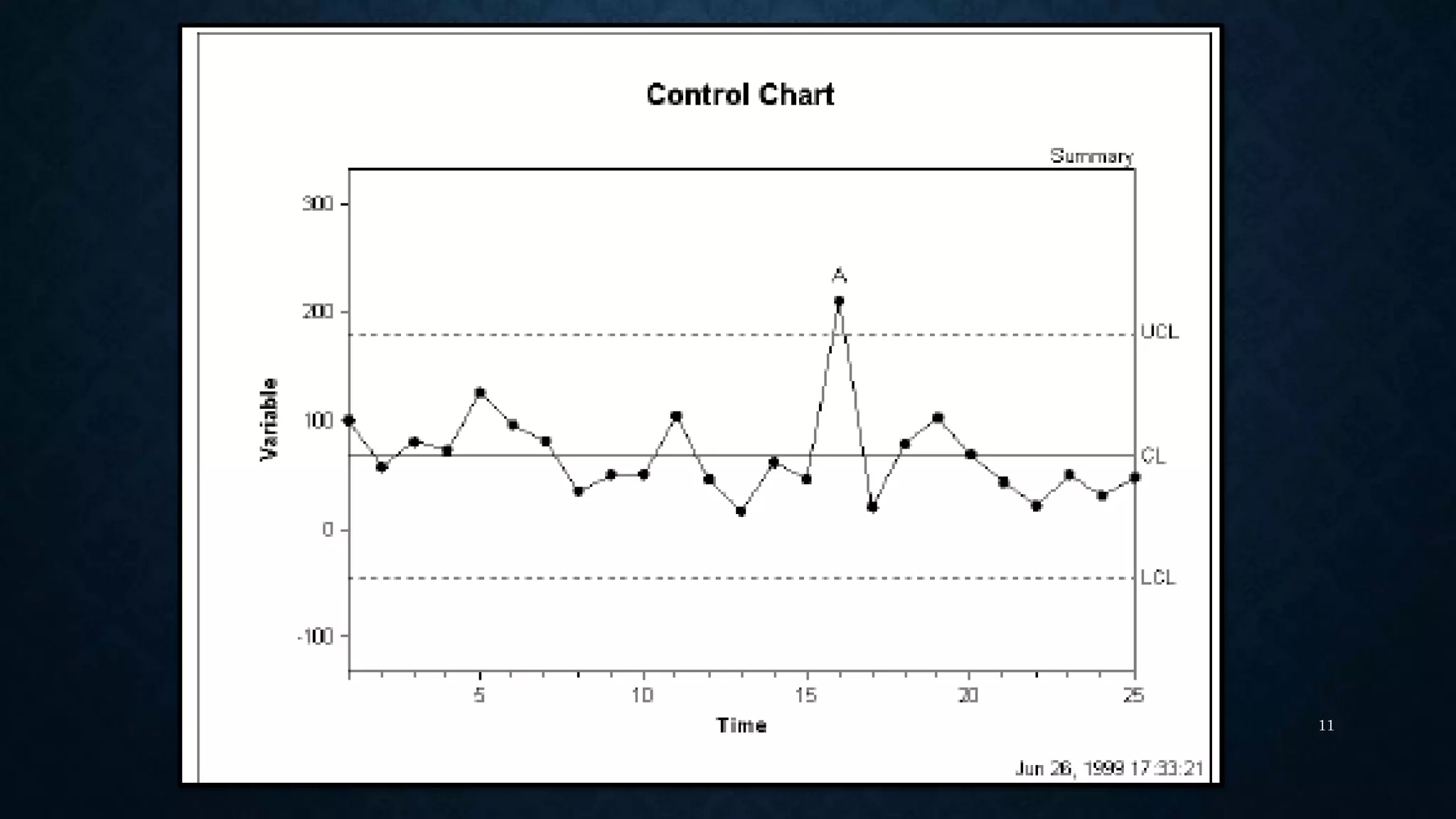
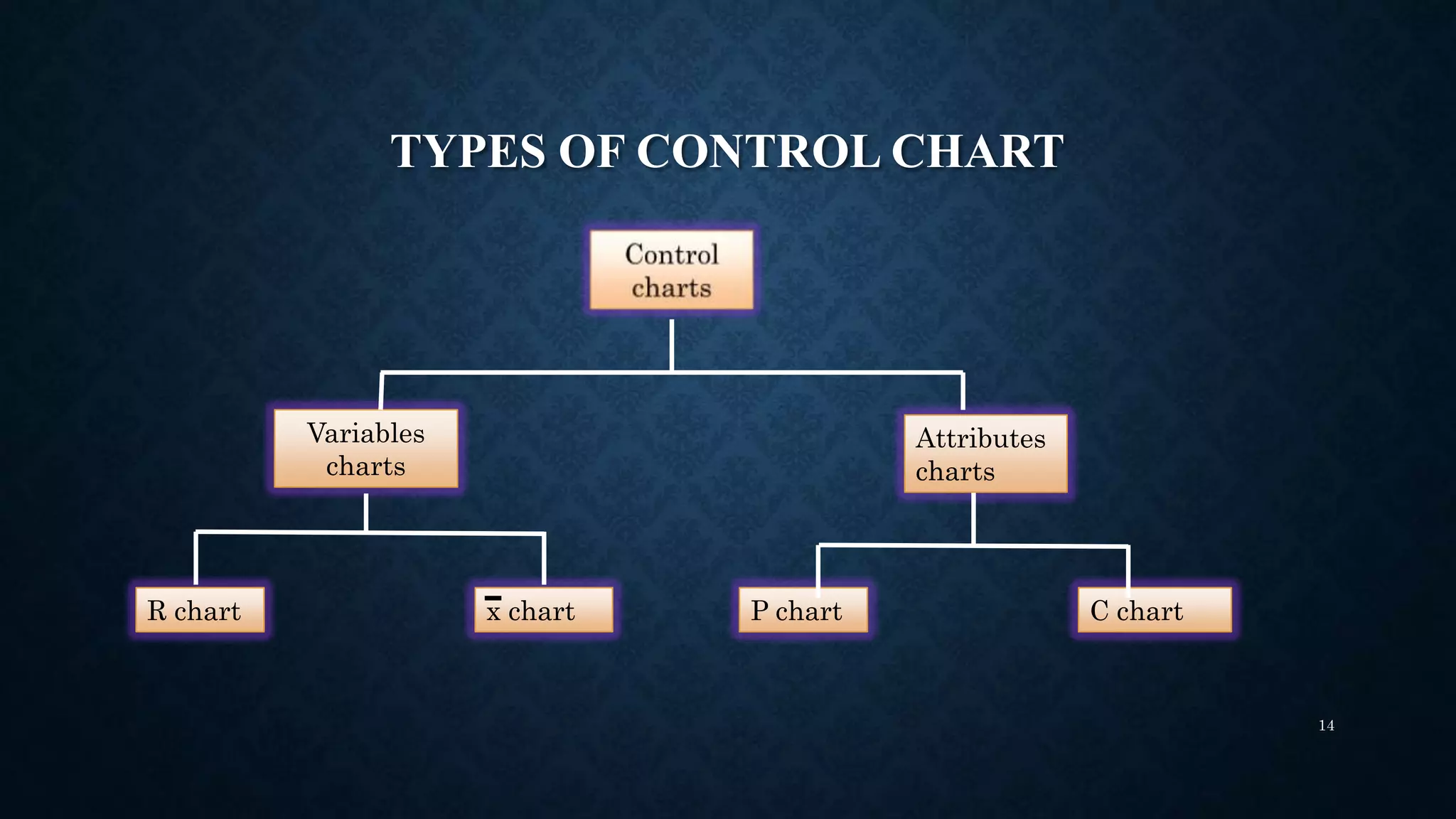
Statistical process control (SPC) techniques apply statistical methods to measure and analyze variation in manufacturing processes. SPC uses control charts to distinguish between common cause variation inherent to the process and special cause variation that can be assigned to a specific reason. Control charts monitor process data over time against statistical control limits. Process capability analysis compares process variation to product specifications to determine if the process is capable of meeting specifications. Key metrics like Cp, Cpk and Cpm indices quantify a process's capability relative to the specifications. For a process to have a valid capability analysis, it must meet assumptions of statistical control, normality, sufficient representative data, and independence of measurements.






















![CAPABILITY INDEX (CPK )
Cp index measures potential capability, assuming that the process avg. is equal to the mid point of the
specification limit and the process is operating in statistical control because the avg. often not at the mid point it
is useful to have capability index that reflects both variation and the location of the process avg. Such index is the
capability index (Cpk) .
Where,
x process mean
standard deviation of the process population
Cpk = [ Upper Specification limit – x ] or
3
[ x - Lower Specification Limit ]
3
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ankitagorhestatisticalprocesscontrol-181207135420/75/statistical-process-control-25-2048.jpg)