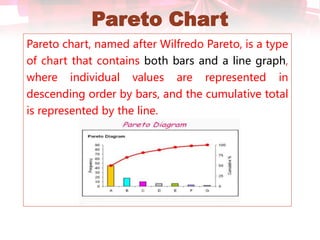
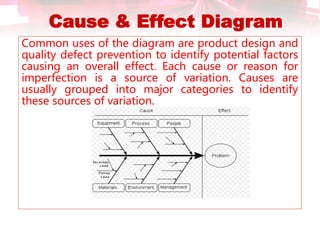
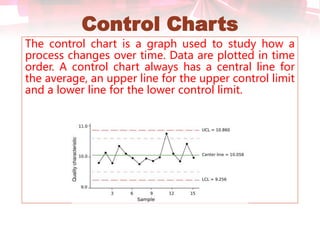
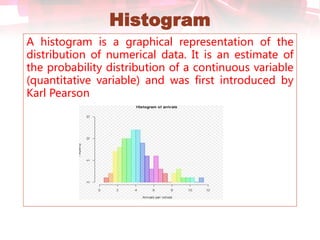
This document discusses quality control tools. It describes seven basic quality control tools: Pareto chart, check sheet, cause and effect diagram, control chart, histogram, scatter diagram, and flow chart. For each tool, it provides a brief definition and example use in quality control. The tools can be used to measure quality, identify sources of variation, and make process improvements.