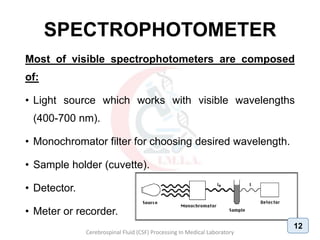
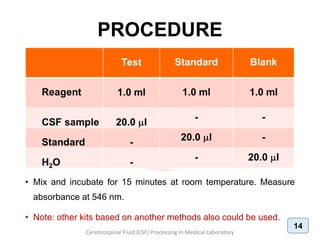
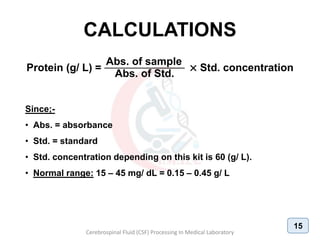
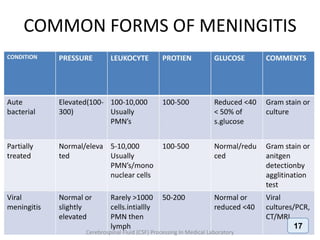
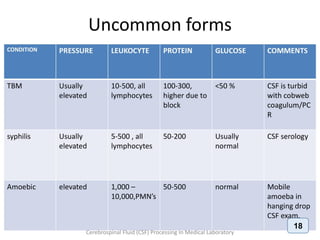
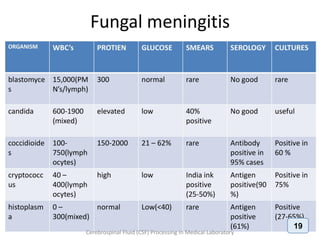
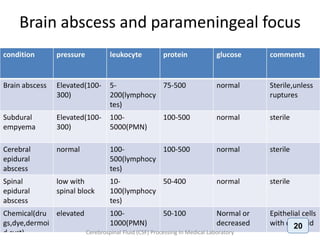
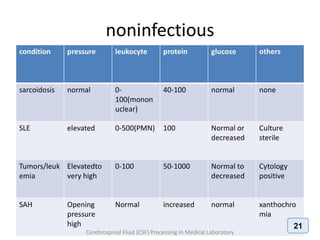
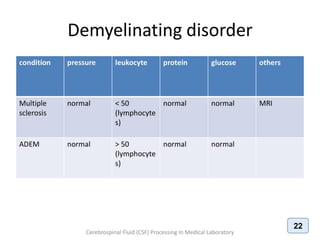
The document discusses biochemical analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in medical laboratories. Routinely tested parameters in CSF include glucose, protein, electrolytes, lactate, and enzymes. Proper handling and centrifugation of CSF samples is important to avoid contamination. Abnormal levels of glucose, protein, lactate and enzymes can indicate conditions like meningitis or tumors. The Pandy's test and Biuret method are described for measuring CSF protein levels, along with normal ranges. Spectrophotometry is used to analyze results from colorimetric assays.