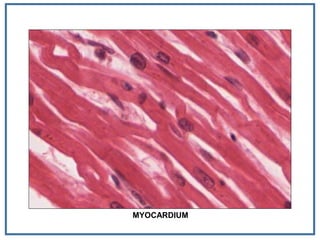
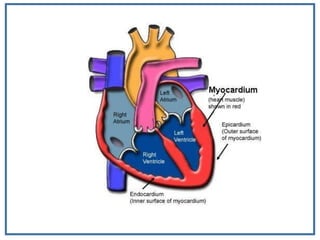
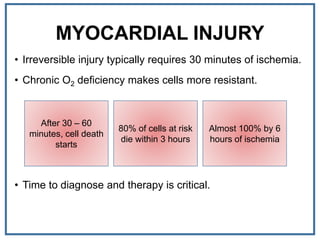
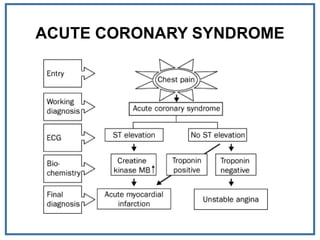
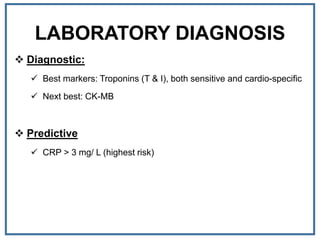
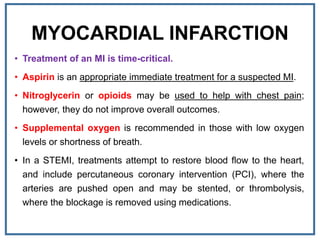
1. Myocardial infarction, also known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow to part of the heart is blocked, damaging heart muscle.
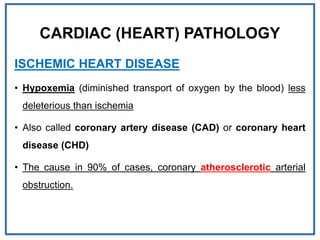
2. It is usually caused by a buildup of fatty plaques in the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart. When a plaque ruptures, a blood clot forms that blocks one of the arteries.
3. Symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort that may travel to the arm, shoulder, or jaw. Early treatment is critical to reduce damage to the heart.