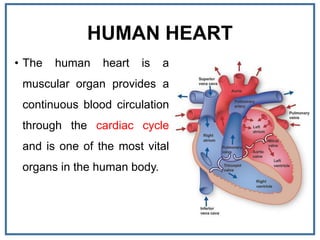
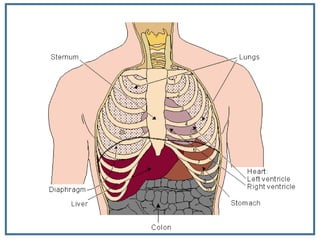
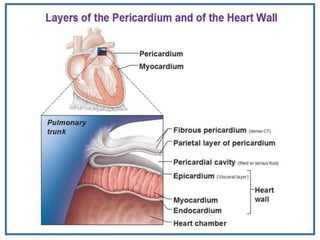
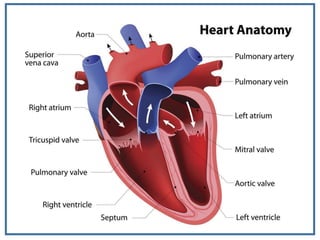
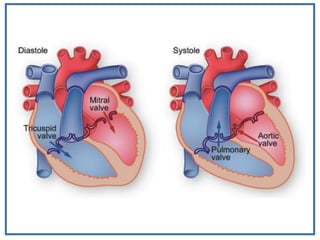
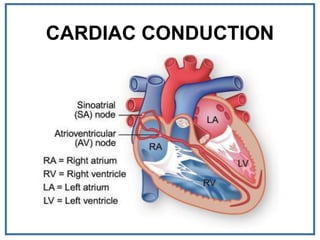
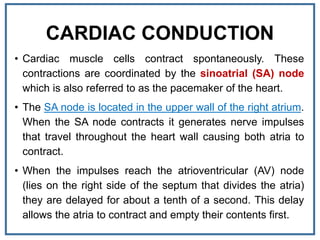
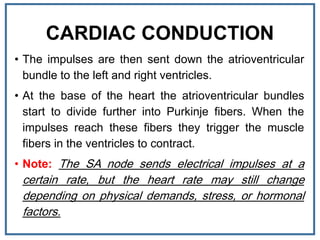
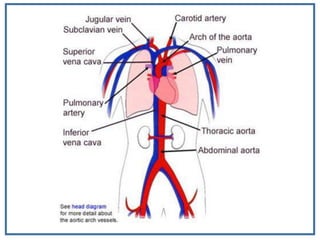
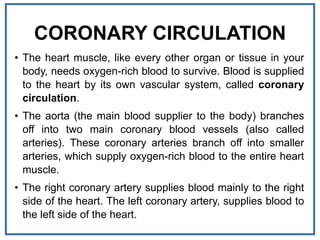
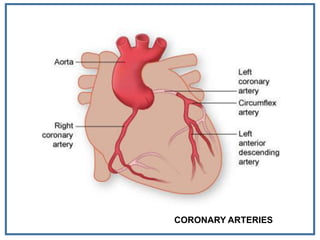
The human heart is a muscular organ that provides continuous blood circulation through the cardiac cycle. It is located in the middle of the chest behind the sternum. The heart is divided into four chambers - two upper atria and two lower ventricles. Blood flows through the heart via heart valves which allow blood to flow in one direction. The heart's rhythm is controlled by the sinoatrial node which generates electrical signals to coordinate contractions. The cardiac cycle consists of diastole where chambers fill with blood and systole where ventricles contract to pump blood out of the heart. The circulatory system transports blood from the heart to tissues and back again via different circulatory routes.